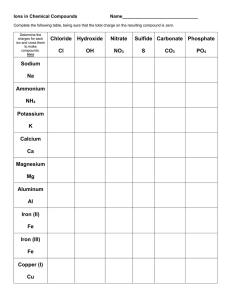
Type II Compounds
advertisement
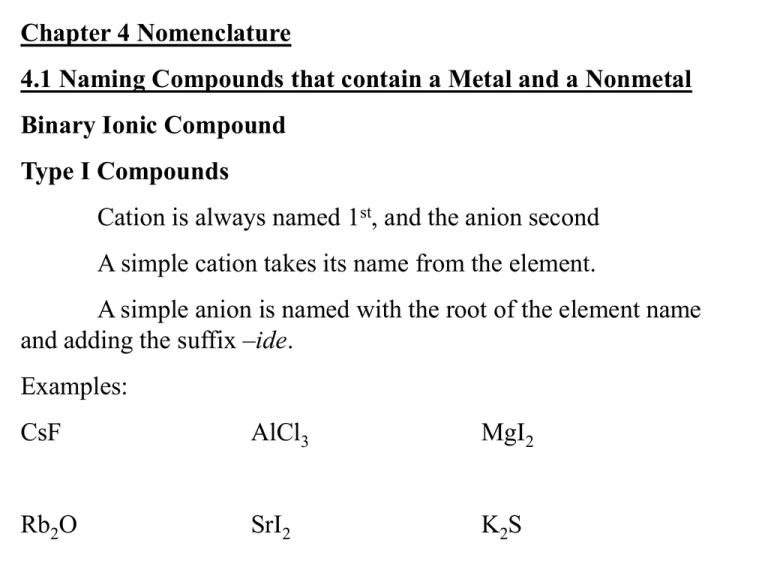
Chapter 4 Nomenclature 4.1 Naming Compounds that contain a Metal and a Nonmetal Binary Ionic Compound Type I Compounds Cation is always named 1st, and the anion second A simple cation takes its name from the element. A simple anion is named with the root of the element name and adding the suffix –ide. Examples: CsF AlCl3 MgI2 Rb2O SrI2 K2S Table 4.1 Type II Compounds Older nomenclature: the cation with the higher charge ends in –ic the cation with the lower charge ends in –ous. Examples: CuCl CuCl2 Stock system- naming system using Roman numerals in parentheses for the charges; no other suffixes are needed (This is the most commonly used system) Examples: CuCl HgO MnO2 PbCl4 Fe2O3 Table 4.2 4.2 Naming Binary Compounds that contain only Nonmetals (Type III) Prefixes: Mono- hexa- Di- hepta- Tri- octa- Tetra- nona- Penta- deca- (Sometimes it is appropriate to eliminate an extra vowel sound: decaoxide to decoxide) Do not use prefix for mono- on 1st element if it is only one. Continue to use suffix –ide on second element name Examples: CCl4 NO2 IF5 BF3 NO N2O5 Figure 4.1: A flow chart for naming binary compounds. 4.4 Naming Compounds that contain Polyatomic Ions YOU MUST MEMORIZE THESE!! Oxyanions: hypochlorite chlorite chlorate perchlorate Examples: Na2SO4 KH2PO4 Fe(NO3)3 Mn(OH)2 Na2SO3 Ca(OH)2 Na3PO4 KMnO4 (NH4)2Cr2O7 Co(ClO4)2 KClO3 Ca(NO2)2 Table 4.4 Figure 4.2: Overall strategy for naming chemical compounds. 4.5 Naming Acids Binary Acid (no oxygen). Use prefix hydro-, and suffix –ic Examples: HCl HBr HI H2S H2Se HF Tertiary acids (oxygen present) If anion ends in –ite, acid ends in –ous. If anion ends in –ate, acid ends in –ic. Examples:HNO3 HNO2 HC2H3O2 H2SO4 H2SO3 H3PO4 H3PO3 HClO HClO2 HClO3 HClO4 4.6 Writing Formulas from Names Criss-cross method (always check that a neutral compound is made) (You cannot reduce subscripts that would change a polyatomic ion) (BUT you should reduce subscripts in other cases) Magnesium oxide Examples: tin(II)oxide potassium hydroxide Cobalt (III) nitrate calcium chloride tin(IV)oxide sodium carbonate lead (IV) oxide Dinitrogen pentoxide ammonium perchlorate Ammonium sulfate vanadium (V) fluoride Disulfur dichloride rubidium peroxide Aluminum oxide