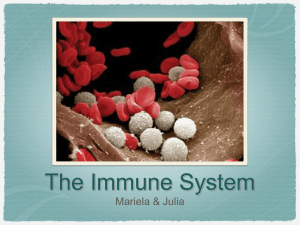
The Immune System
advertisement

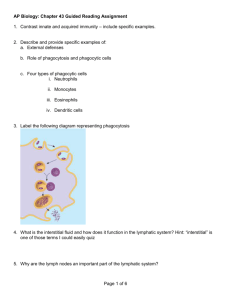
The Immune System Ch43 Tori-Section 1, Julia- Section 2, RyleeSection 3 & 4 43.1 In innate immunity, recognition and response rely on traits common to groups of pathogens Innate immunity- a defense that is active immediately upon infection and is the same whether or not the pathogen has been encountered previously. Adaptive immunity- a defense found only in vertebrates, they produce a vast arsenal of receptors, each of which recognizes a feature typically found only on a particular part of a particular molecule in a particular pathogen. Innate Immunity of Invertebrates ● In vertebrates, intact skin and mucous membranes form barriers to pathogens ● Mucus produced by membrane cells, the low pH of the skin and stomach, and degradation by lysozymes also deter pathogens. ● Microbes that penetrate barrier defenses are ingested by phagocytic cells, including macrophages and dendritic cells. Innate Immunity of Vertebrates •The immune system of mammals is the best understood of the vertebrates •Innate defenses include barrier defenses, phagocytosis, antimicrobial peptides •Additional defenses are unique to vertebrates: natural killer cells, interferons, and the inflammatory response phagocytosis When any pathogen breaches an insects barrier defenses encounter a number of internal immune defense. Immune cells called hemocytes travel throughout the body in the hemolymph. ● Some of those hemocytes carry out a defense called phagocytosis ● There are different types of phagocytic cells –Neutrophils engulf and destroy pathogens –Macrophages are found throughout the body –Dendritic cells stimulate development of adaptive immunity ● phagocytosis Barrier Defenses •Barrier defenses include the skin and mucous membranes of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts •Many body fluids including saliva, mucus, and tears are hostile to many microbes •The low pH of skin and the digestive system prevents growth of many bacteria Cellular Innate Defenses ● Pathogens entering the mammalian body are subject to phagocytosis ● Phagocytic cells recognize groups of pathogens by TLRs, Toll-like receptors. TLR Signaling 43.2 In adaptive immunity, receptors provide pathogen-specific recognition Lymphocytes ● Lymphocytes are responsible for the specificity of adaptive immune responses ● There are about 2 × 10^12 lymphocytes in the human body, making the immune system comparable in cell mass to the liver or brain ● Have cell-surface antigen receptors for foreign molecules ● The response during its first encounter with an antigen ensures that a more rapid and effective response occurs on subsequent encounters with the same antigen Adaptive Immunity ● Adaptive immunity relies on lymphocytes that arise from stem cells in the bone marrow and complete their maturation in the bone marrow (B cells) or in the thymus (T cells) ● Lymphocytes usually respond to foreign antigens only if the innate immune system is first activated ● All receptor proteins on a single B or T cell are the same, but there are millions of B and T cells in the body that differ in the foreign molecules that their receptors recognize Antigen Recognition ● Each B cell antigen receptor is a Y-shaped molecule consisting of four polypeptide chains-two identical heavy and light chains ● For a T cell, the antigen receptor consists of two different polypeptide chains, an alpha chain and a beta chain, linked by a disulfide bridge Antigen Recognition Cont. ● Recognition of foreign molecules involves the binding of variable regions of receptors to an epitope-a small region of an antigen ● Antigen presentation- the display of the antigen fragment in an exposed groove of the MHC protein Antigen Recognition Animation https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GP5d7C yU8WA Section 43.3: Adaptive Immunity Defends Against Infection of Body Fluids and Body Cells Helper T Cells: A Response to Nearly All Antigens ● Helper T cells trigger hormonal and cellmediated immune responses. ● Hormonal responses occur in blood and lymph, antibodies help neutralize toxins and pathogens. ● In cell-mediated immune responses, T cells are specialized to destroy infected host cells. Activation In order to activate a helper T cell: ● A foreign molecule must be present and it must bind to an antigen receptor of the T cell. ● The antigen must be shown on the surface of an antigenpresenting cell. Antigen-presenting cell can be a macrophage, B cell, or a dendritic cell. ● The protein CD4 binds to the class II MHC molecule, this keeps the helper T cell bound to the antigen-presenting cell. ● The T cells are then able to secrete cytokines that stimulate other lymphocytes Cytotoxic T Cells In the cell-mediated immune response, cytotoxic T cells are effector cells. The cytotoxic secretes a protein that disrupts the membrane integrity and triggers apoptosis B Cells and Antibodies The hormonal response when triggered, secretes B Cells and Antibodies B cells then secrete plasma cells, the effector cell of this process. Different Ways Antibodies Work Extras ● Active Immunization- develops naturally in response to an infection. (vaccination) ● Passive Immunization- short immediate protection ● Blood transfusions, organ transplants, etc. can be rejected because of different MHC molecules Section 43.4 Disruptions in immune system function can elict or exacerbate disease Immune Diseases/Problems ● Allergies are exaggerated responses to antigens known as allergens. ● In autoimmune diseases, the immune system will lose tolerance on its body turn on its molecules. ● Immunodeficiency is hereditary and prevents proper functioning of different cell defenses. (AIDS) HIV and AIDS ● HIV affects helper T cells, the lose of these cells affects hormonal and cell-mediated responses leading to AIDS. ● HIV is able to escape the attention of the immune system because of antigenic variation and can be latent in the host DNA. Sources ● http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26921/ ● https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GP5d7CyU8WA ● https://www.google.com/search?q=the+structure+of+a+ b+cell+antigen+receptor ● http://www.slideshare.net/jayswan/chapter-43-textbookpresentation?related=2