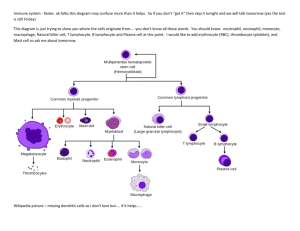
AP Biology Chapter 43 Notes
advertisement
AP Biology Chapter 43 Notes Immune System What you need to know… • Several elements of an _______________________________ response. • The differences between _____and _____ cells relative to their activation and actions. • How ___________________ are recognized by immune system cells. • The differences in _________________ and _________________________ immunity. • Why ______________________ cells are central to immune responses. 43.1 – Innate Immunity, recognition, and response _______________________________ is present before any exposure to pathogens and is effective from the time of birth It involves _____________________ responses to pathogens Innate immunity consists of __________________________ plus internal cellular and chemical defenses 4 Innate Defenses: ____________________________ – first line of defense ___________ and ______________ membranes Ex. Ciliated epithelial cells in the _______________ (on next slide) ____________________________ – combat pathogens that get through the skin Phagocytic white blood cells Antimicrobial proteins ___________________________ – fever and septic shock ______________________________ – help remove diseases Barrier Defenses: Secretions of the __________ and ____________ membranes Environment that is often hostile to ____________ Skin Secretions Give the skin a pH between ________ and ___________, which is acidic enough to prevent colonization of many microbes Also include proteins such as ____________, an enzyme that digests the cell walls of many bacteria Cellular Innate Defenses: Internal cellular defenses depend mainly on _______________ __________________ - types of white blood cells Ingest invading microorganisms and initiate inflammatory response 3 Types: _____________________ – WBCs that ingest and destroy microbes _____________________ – WBCs that migrate into tissues and develop into macrophages (giant phagocytic cells) _____________________ – WBCs defend against parasitic invaders such as worms by releasing hydrolytic enzymes Attach to their prey via __________________________________ ____________________ – proteins that provide defenses against viral infections; cause cells adjacent to infected cells to produce substances to inhibit viral replication Inflammatory Response Triggered by damage to tissue by ___________________________ or entry of _________________________ Leads to release of lots of _________________________ Such as _______________________ – trigger dilation and permeability of nearby capillaries; aids in delivering clotting agents and phagocytic cells to injured area Responses include ___________________ and _______________________ Natural Killer Cells Patrol the body and attack virus-infected body cells and cancer cells Trigger apoptosis (suicide) in the cells they attack 43.2 Acquired Immunity • • • • • • ____________________________________ – specific responses – Is the body’s __________________ major kind of defense – Involves the activity of ____________________ – Also called __________________ immunity – Develops only after exposure to inducing agents such as microbes, toxins, or other foreign substances – Involves very __________________ response to pathogens ______________________ - Foreign molecules that are specifically recognized by lymphocytes; elicit a response from them ______________________ - Soluble proteins secreted by B cells during immune response ______________________ - Recognize and bind to a small, accessible portion of the antigen called an ______________ Types of Lymphocytes: – _______________________ (B cells) – ________________________ (T cells) – Which circulate through the blood – Plasma membranes of both B cells and T cells = ~100,000 antigen receptors that all recognize the same epitope B or T Cell Activation • • • • B-Cell activation - Enhanced by __________________; bind to intact ___________ – Forms 2 clones of cells in a process called ______________________________ – results in 1000s of cells, specific to this antigen – _________________________ – combat this antigen – ________________ – long-lived, bear receptors for same antigen; remembers them – B Cell Receptors – are often called __________________or membrane___________________ T-Cell Activation - Bind antigens that are displayed by ___________________________ – ___________________ (APCs) on their MHCs (majors histocompatibility complex molecules) – Bind to small fragments of anigens that are bound to normal cell-surface proteins called MHS molecules – _______________________________ – are encoded by a family of genes called major histocompatibility complex; 2 types – Infected cells produce ___________________________ • Bind to antigen fragments an then are transported to the cell surface in a process called antigen presentation • Nearby T cells detect the antigen fragment displayed on the cell’s surface MHC Types – _____________________ MHCs – found on almost all cells of the body, except RBCs • Display peptide antigens for ________________________________ – _____________________ MHCs – made by dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells • Display antigens to _______________________________ • Primary and Secondary Immune System – ________________Immune Response - Occurs when the body is first exposed to an antigen and a lymphocyte is activated – ________________ Immune Response - Occurs when the same antigen is encountered at a later time; Faster and of greater magnitude 43.3 Acquired Immunity • ________________________ immune response – involves the activation and clonal selection of B cells, resulting in the production of secreted antibodies • ________________________ immune response – involves the activation and clonal selection of cytotoxic T cells, which identify and destroy infected cells • 2 Main types of cells: o __________________________ Aid both in humoral and cell-mediated responses Produce CD4, a surface protein, enhances their binding to class II MHC molecule-antigen complexes on antigen-presenting cells o __________________________ Bind to class I MHC molecules by CD8 Proteins Destroy infected body cells • Modes of Antibody Action o _______________________ – antibodies bind the pathogen’s surface proteins, which prevents it from entering the infecting cells o _____________________ – results in increased phagocytosis of the antigen o ________________ – caused by activation of the complement system - 5 major classes of antibodies, or ___________________________ • Active Immunity - Develops naturally in response to an infection; Can also develop following _______________________, also called vaccination • • o An immunization - A nonpathogenic form of a microbe or part of a microbe elicits an immune response to an immunological ___________________ for that microbe Passive immunity – provides immediate, short-term protection; Occurs when an individual receives __________________ o From the placenta of the mother to fetus or from mother to infant in breast milk o Or artificially by injecting antibodies into a non-immune person MHC Molecules - Responsible for stimulating ___________________ of tissue grafts and organ transplants; Patients ____________ need to closely match donors _____________ 43.4 Disruptions in Immune Responses Cause Diseases _______________________ – exaggerated (hypersensitive) responses to certain antigens called allergens • IgE antibodies produced after first exposure to allergen attach to receptors on mast cells • The next time the same allergen enters the body, cell releases histamine and other mediators that cause vascular changes • An acute allergic response sometimes leads to _________________________________ – whole body, life-threatening reaction that can occur within seconds of exposure to an allergen ___________________________- When the immune system turns against particular molecules of the body, generating antibodies that attach and damage the bodies own healthy cells • Examples include – Lupus, Rheumatoid arthritis, Multiple sclerosis ___________________________ • An ___________________ or primary immunodeficiency - Results from hereditary or congenital defects that prevent proper functioning of innate, humoral, and/or cell-mediated defenses • An ____________________ or secondary immunodeficiency - Results from exposure to various chemical and biological agents You Should be able to… 1. Distinguish between innate and acquired immunity 2. Name and describe four types of phagocytic cells 3. Describe the inflammation response 4. Distinguish between the following pairs of terms: antigens and antibodies; antigen and epitope; B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes; antibodies and B cell receptors; primary and secondary immune responses; humoral and cell-mediated response; active and passive immunity 5. Explain how B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes recognize specific antigens 6. Explain why the antigen receptors of lymphocytes are tested for self-reactivity 7. Describe clonal selection and distinguish between effector cells and memory cells 8. Describe the cellular basis for immunological memory 9. Explain how a single antigen can provoke a robust humoral response 10. Compare the processes of neutralization and opsonization 11. Describe the role of MHC in the rejection of tissue transplants 12. Describe an allergic reaction, including the roles of IgE, mast cells, and histamine 13. Describe some of the mechanisms that pathogens have evolved to thwart the immune response of their hosts 14. List strategies that can reduce the risk of HIV transmission