CHAPTER 43: IMMUNE SYSTEM
advertisement

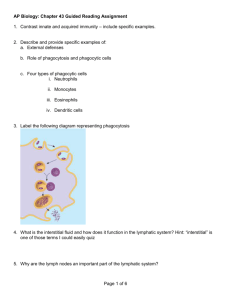
AP Biology Campbell 8th Edition Chapter 43 Study Guide 1. Match the description/definition/function with the correct term. A. Chemotaxis B. Complement C. Cytokines D. Diapedesis E. Fever F. Immunological 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. surveillance G. Inflammation 9. H. Interferons I. Lysozymes 10. J. Macrophages K. Microphages 11. L. Phagocytes M. Pyrogens 12. 13. Name: ___________________ ______ Enzymes present in some secretions that have antibiotic properties ______ Cells that engulf and destroy pathogens and foreign materials ______ Neutrophils & eosinophils ______ Large, actively phagocytic cells derived from monocytes ______ Movement of white blood cells through the walls of capillaries by squeezing between adjacent epithelial cells ______ Movement of cells toward or away from a chemical stimulus ______ Constant monitoring of normal tissues by NK cells ______ Small proteins released by activated lymphocytes, macrophages, & cells infected with viruses; cause cells to produce proteins that interfere with viral reproduction ______ Chemical messengers released by tissue cells to coordinate local activities; hormones of the immune system; released to alter activities of cells and tissues throughout body ______ Plasma proteins that interact in a chain reaction following exposure to activated antibodies or to surfaces of certain pathogens; promote cell lysis, phagocytosis and other defense mechanisms ______ Localized tissue response to injury; characterized by swelling, redness, warmth, pain, and some loss of function ______ Maintenance of body temperature above 99 degrees Fahrenheit ______ Circulating proteins that can reset the thermostat in the hypothalamus and cause a rise in body temperature 2. Why does a bacterial infection cause a fever? _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 3. What are the purposes of inflammation? _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ SPECIFIC IMMUNITY QUESTIONS: 1. T cells are responsible for ___________________________ immunity. 2. B cells are responsible for ___________________________ immunity. 3. What is the difference between active and passive immunity? Give examples _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 4. Why (or How) do B and T cells ignore normal (self) antigens and attack foreign (nonself) antigens? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 4. Explain the relationship between an MHC and an APC? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 5. How do cytotoxic T cells destroy pathogens, foreign cells and abnormal cells? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 6. Helper T cells produce cytokines when they bind to targeted inactive B cells. What are the functions of these cytokines? __________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 7. Listed below are characteristics of the primary and secondary responses to a specific antigen. Determine if the statement is true of the primary response (1) or the secondary response (2.) a. ______ Initial response to antigen b. ______ Does not appear immediately c. ______ Gradual, sustained rise in concentration of circulating antibodies d. ______ Antibody activity peaks several weeks after exposure to antigen e. ______ Appropriate B cell must be activated and, once activated, must divide and differentiate into plasma cells f. ______ Activates memory B cells g. ______ Very rapid increase in antibody activity and concentration h. ______ Memory B cells divide and differentiate into plasma cells i. ______ Produces a much faster and stronger response j. ______ Can be substituted with immunization 8. Identify the parts of this diagram. ______ viral particle ______ APC ______ T-cell ______ MHC ______ T-cell receptor Describe one type of immune system hyperactivity and indicate where it acts in the immune systems discussed above and how. 2.D.4 On an attached page, create a Graphic Organizer to Compare the Innate/ Nonspecific Immune System to the Adaptive/Specific Immune System. Within the Specific Immune System, compare humoral and cellular Immune responses Within humoral responses, compare active and passive humoral immunity.