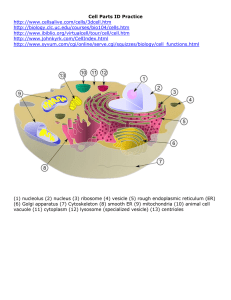
Differences between plant and animal cells....
advertisement

By Jodi Longden Animal Cell Plant Cell Cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth and Rough): Ribosomes Mitochondria Golgi Apparatus Microtubules/ Microfilaments Flagella Maybe present in some Maybe present in some Nucleus Plants cells have a cell wall over the cell membrane, whereas, animals cells lack cell wall. In plant cells, there is a single large vacuole present in the middle, whereas, in animals cell, there are more than one vacuoles. Plant cells possess plastids, but, animal cells don't. Animal cells have centrioles, whereas, plant cells don't. Plant cells are more square shaped, animal cells are more round. Plant cells have chlorophyll for Photosynthesis (make their own food), and animal cells don't. There are three main differences between plant and animal cells. Cell Walls One main difference between plant and animal cells is that plant cells have cell walls and animal cells don’ t. Cell walls direct the growth and shape of plant cells and determine the formation cells which will presume in the creation of the plant. Cell walls hold carbohydrates and protect cells from disease. Plant cells have specific shapes because of cell walls. Animal cells, on the other hand, do not have exact shapes. While animal cells have cell membranes for protection, these membranes are shapeless and will have any shape a cell assumes. Animal cells do not need a definitive shape because animals have firm skeletons. Chloroplast Plant cells contain an enzyme known as chloroplast. Animal cells don’ t have chloroplast; though contain vesicles known as Lysosomes. Chloroplast enzymes produce glucose from the carbon dioxide and water consumed by a plant. This glucose in turn feeds the plant. Lysosomes are digestive vesicles that hold enzymes produced by the cell. When a cell absorbs food material, Lysosomes break that food down so that it can be easily digested by the cell and animal's body. Vacuole Both plant and animal cells contain vacuoles. A vacuole is an empty space within a cell that is used to store molecules or transport and store nutrients and waste products. Animal cells have a quantity of small vacuoles, which are used in the digestion process alongside lysosomes. Plant cells have one large vacuole. This vacuole assists the plants to maintain firmness. Large vacuoles are used for storing water, which is steadily changed into carbon dioxide then glucose by chloroplast. Vacuoles with limited water lose form, causing plants to wilt. Useful Links