ppt - Faculty

Election Law:
Regulation & Policy
Democracy: the Most Critical Infrastructure
Elections: the Information, Security & Risk Profiles
Democracy Law: Legal Structure of Political Processes
Constitution, Federalism, Statutes, Decisions, Regulations & Voter
Behavioral Empirical Approaches by
John W. Bagby, Prof. of IST
Set the Tone
“Vote Early and Often”
Traditional Chicago Democrat allegation of voter fraud by the dead, stuffing ballot boxes, intimidated voters
(S)Elected Officials Own the Decision-making
Prerogative
Sir Winston Churchill’s famous quote:
"Democracy is the worst form of government, except for all those other forms that have been tried from time to time." (speech, UK House of Commons,
11.11.47)
Captures widely felt frustration with both de jure and de facto political realities
Voters get what they deserve
Democracy
Contrast with Autocratic Forms of Gov’t
EX: dictatorship, feudal monarchy, oligarchy
Direct Democracy
Eligible citizens may all be enfranchised
Presumes low apathy, free marketplace of ideas, broad commitment to political efficacy
Representative Democracy
Eligible citizens elect representatives
Presumes voter apathy or inability to govern adequately AND statesmen will become informed
Genesis: Aristotle’s Politics & Plato’s Republic
Democracy Impacts Spheres
Governmental
Int’l, National, State/Provincial, Local
Corproate Governance
SH democracy, proxies,
Shared Governance in Academia
Administration largely Selected by Board
Professional Managerial Class w/ Ltd Ideological Conflicts
Faculty share in certain matters
Curricular or within Zones of Expertise
Democracy in the World
Relationships among Law, Politics
& Technology
Democracy is Implemented through Elections &
Representative Government
Law Defines Political & Election Processes
Legislators, Regulators, Courts Interpret Election Law
Election Methods require Deployments of Tools
Technological Links between Information Sciences and Security & Risk Analysis to Election Law &
Practices
Skillsets & Useful Technologies for Election Design,
Maintenance, Operations, Risk Analysis & Security
Some Provisional Definitions
Republic (res publica):
Political process participation by at least some citizens,
Much diminished influence of monarchies, dictators
Democracy: decision-making by the governed
Direct: more decisions by voters
Representative: more decisions by s/elected representatives
Elections:
Decision-making through voting by defined electorate or membership
Campaign Electioneering:
Organized effort to influence political decision making
Federated Democratic Republic:
U.S. System of federal, state & local governments, using mostly representative democracy & some direct democracy
Questions for Analysis: Election Law,
Regulation & Policy
What are the links between (1) election law & practices and (2) information technology (IT), security and risk remediation?
Extend beyond the most obvious EX:
Federal & state laws require electronic voting;
Internet as a growing tool for political fundraising;
Demographic granularity in GIS enhances electioneering & Gerrymandering.
What contributions can be made by political scientists and IT security specialists to resolve election security & risk vulnerabilities as elections migrate from traditional techniques to eDemocracy methods & practices?
Questions for Analysis: Election Law,
Regulation & Policy
What skill sets from IT, security & risk analysis could become useful in the design, maintenance, operations & the analysis or security with respect to the election matters either directly regulated under law or indirectly regulated using standards?
Extend beyond the most obvious EX:
Hackers or programmers “stuff ballot boxes,”
eVoting standards frustrate/eliminate traditional balloting security;
Traditional voting confidentiality gradually replaced by privacy vulnerability.
The U.S. Constitutional “Ontology”
Art. I, § 2 - House of Representatives
2 yr terms; min. age-35 yr old; 7 yr. US citizen; state resident; apportioned according to census; @ least
1/state; governor fills vacancies; House selects
Speaker; Pres. Impeachment starts in House
Art. I, § 4 - Elections of Senators & Representatives
States control election law for their House
Representatives & Senators unless Congress preempts; minimum required Sessions of Congress: 1/yr
Art. II, § 1 - Elect, Install, Remove the Pres & VP
Pres. is Exec Pwr, 4 yr term, min. age-45 yr old; must be natural born citizen; extensive Electoral College procedures; Pres. pay limits; Presidential succession;
THE oath of office
U.S. Constitutional Foundations: the Amendments
1 st A. (1792) – Speech, Press, Religion, Assembly
12th A. (1804) - Pres. & VP Elections
14 th A. (1868) – All persons are citizens, Privileges &
Immunities, Due Process (states), Equal Protection, overruled the Dred Scott decision
15th A. (1870) - Right to Vote Not Denied on
Account of Race, Color, Previous Servitude
17th A. (1913) - Election of Senators
19th A. (1920) - Women's Suffrage
23rd A. (1961) - D.C. Suffrage Presidential Elect
24th A. (1964) - Eliminates Poll Taxes
26th A. (1971) - Right to Vote at Age 18
Federal Election Laws
1907 Tillman Act bans corp. contributions
Federal Corrupt Practices Act of 1925
Taft-Hartley Act of 1947
1971 Federal Election Campaign Act (FECA),
Amended in ‘74, ‘76, ’79
Established Fed. Election Comm’n (FEC)
Limits contributions, disclosure required, for candidates, parties & Political Action Comms (PAC)
Spending limits
Bipartisan Campaign Reform Act of 2002 (BCRA) a/k/a
“McCain-Feingold”
Election Law: Functional Ontology
Structural
Election Administration
Forms of Balloting
Voting Rights
Electoral College
Districting, Redistricting &
Reapportionment
Gerrymandering
Political Parties
Campaign Electioneering
Ballot Propositions:
Initiatives & Referenda
Electioneering
Remedial
Remedying Defective &
Contested Election Results
Voter Suppression
Motor Voter
Campaign Finance &
Disclosure
Turnout Enhancements
Voter Fraud
Campaign Financing Control
Anti-Retaliation
Anti-Apathy
Recount
Election Administration
Federal Election Commission
Administers: ‘75 FECA, HAVA,
Local Admin: mostly Co. Election Bd./Commis.
Huge Differentials under State & Local Law
EX: NYC Mayor Michael Bloomberg’s 3 rd term
33 States elect partisan state election directors
Arguably: have irreconcilable conflicts of interest
EX: FL’s Katherine Harris 2000 election certifications
Primaries vs. General Elections
Establishing Candidacy
Form of Ballots
Paper
in person
Absentee, Proxy, Early, Excuse-Required, Mail
Ballot Confusion, e.g., Butterfly, Punch
Punch Card
Lever Mechanical Machines
Control Mechanisms
Bi-partisan polling place judges, paper trail
Auditable DRE code?!?
Direct Recording Electronic (DRE)
eVoting Arguably Obviates Apathy
The “stakes” drive voter turnout
Low stakes – low turnout
Will of the minority
Hi states – higher turnout
Will of the majority eVoting may raise turnout
Corp.Gov.-Proxies needed to meet Quorum
Like the “cloud” promises to reduce transaction costs
BUT eVoting Disadvantages
Traditional Checks & Balances of in person
Polling Places do not Adapt well to eVoting
Issues: Costs, Ubiquitous Voting, Computer
Accuracy, Hacking Potentials, Apathy/Stakes
EXs
Early 90s: SH Proxy voting migrate online
Fla’s ’00 hanging-chads illustrate limits of traditional paper ballot voting
Politicians control recount & voting mechanisms
FLs Sec’y of State Katherine Harris
Bush v. Gore U.S. Sup.Ct. 12.9.00 (5-4)
Diebold Voting Machines
Walden O’Dell CEO in 2003
"committed to helping Ohio deliver its electoral votes to the president next year." Krugman, Paul, Hack The Vote . NYT 6.21.03
Resigned 2005 in midst of SEC investigation of Diebold for securities fraud & insider trading
Direct Recording Electronic (DRE)
Electronic implementation of traditional mechanical lever systems
Voters enter choices into electronic storage using touch-screen, push-buttons, etc. perhaps alpha keyboard for write-ins
Votes stored in removable/networked memory
Vulnerable? How? To What?
See: “Hacking Democracy”
Ohio Everest Proj.-PSU’s Prof.Patrick McDaniel http://siis.cse.psu.edu/everest.html
Help America Vote Act (HAVA)
Funding: state plans, election admin
E.g., proliferate DREs
Election Assistance Commission
Accessibility, Grant Admin, Research, Voting systems, Reports, Registration, Voter IDs,
EAC Stds Bd: Voluntary Voting System
Guidelines (VVSG)
NIST’s Tech. Guidelines Develop. Comm. (TGDC)
BUT, recidivism towards maintaining
“Paper trail” for recount & audit
Under PA Const voters:
Banfield v. Cortez (Pa.Commw.Ct.2007) may challenge use of DRE “that provide no way for Electors to know whether their votes will be
independent audit entitled to reliable & secure voting systems
Findings:
examination criteria” which “do not approximate those that are customary in the information technology industry for systems that require a high level of security.”
Order Stayed pending PA S.Ct. appeal
Warren Zevon’s Prophetic words http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lP5Xv7QqXiM pro bono armies: http://moritzlaw.osu.edu/electionlaw/
██ States with both in-person and postal no-excuse early voting.
██ States with only in-person no-excuse early voting.
██ States with only postal no-excuse voting.
██ States without no-excuse early voting.
Voting Rights
U.S. Const. & 15 th , 19 th , 23 rd , 24 th , 26 th A’s
14 th A. disenfranchised “rebels” if previously under oath of U.S. office
Natural born & naturalized citizens
But not felons (approx: 5 mil.)
Registration Required; Voter IDs ?!?
Voting: a main focus for antidiscrimination law since the Founders
The Electoral College
Virginia Plan-Connecticut Compromise (1787)
Based on Federalist Pap.#39 (James Madison) hybrid state-based representative & popular election
Nobility wisdom: skepticism of populace competence
Electors may exercise indep. J/
½ states punish “Faithless Electors”
Electoral College disproportionate power to small states
If unable to elect, thrown into the House as a
“Contingent Election”
The Electoral College
Like Senate’s “all states equal power”
Contingent Elections (House) favor small states
1801 (Jefferson)
Each state’s House delegation casts 1 vote
12 th A.: “In choosing the President, the votes shall be taken by states, the representation from each state having one vote;”
1825 (John Q. Adams, only post-12 th A. House election)
Thus, boundaries matter!
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Territorial_evolution_of_the_United_States
Bloody KS 1855-1860
neither Ft. Sumter nor harpers’ Ferry!
1825 Contingent (House) Election
Electoral College under 2000 Census
Electoral College after 2010 Census
Remedying Defective & Contested
Election Results
Defective voting apparatus: levers, punch
Help America Vote Act 2002 (HAVA)
Recounts:
Bush v. Gore
, 531 U.S. 98 ‘00
FL's S.Ct. ordered recount deadline extension
U.S. S.Ct. held violated 14 th A. unauth. by FL law
FL Secy of State Katherine Harris:
How is Turnout a Policy Issue?
Some nations have compulsory voting
Voter Suppression
Wide Variety of Methods & Tactics taregeting:
Voters, Registration, Polling Place Access, Balloting
Jim Crow Laws, post-reconstruction, segregation, poll taxes, literacy, disenfranchisement
Plessy v. Ferguson, 163 U.S. 537 (1896) (separate but equal)
20 th Century unconstitutionality
LBJ: Civil Rights Act ’64 & Voting Rights Act of ‘65 outlawed
Slash tires of poll-ride vans
Photo ID Requirements OK’d
Crawford v. Marion Co. Elect. Bd (’08)
Voter Suppression
Interference, Intimidation & Dirty Tricks
PhoneGate: Allen Raymond convicted of telephone harassment: jammed phones (DDoS attack) @ NH
Dems' get-out-the-vote efforts; John Sunnunu won
Senate by 19K-vote margin over Dem. Gov. Shaheen,
Lying to FBI, accessory before/after, conspiracy, aid & abet
Calls (many automated) making various threats:
Pkg tkts, polling place moved, improperly registered, arrest
Challenge Registration Rolls
EX: fictitious, padding, purging, caging
ACORN claims 1.3 mil. 95% error free new regis
Few suspicious: Mickey Mouse, Jimmy Johns; ACORN flagged
Districting, Redistricting &
Reapportionment
Census is the basis for Representation
Approx 650,000/U.S. House Member (2000)
Must revise after every census
Geography: Justifiable Basis for Clustering
Demographic affinity, physical proximity, reducing transaction costs, historical development
States, boundaries, counties, precincts, wards
Gerrymandering
Racial Gerrymandering: generally unlawful
Baker v. Carr , 369 U.S. 186 (1962) (reapportionment not forbidden political question)
Reynolds v. Sims , 377 U.S. 533 (1964) (state legislature districts must be roughly equal in population, thus: 1 person/1 vote)
Partisan Gerrymandering: generally not unlawful
Vieth v . Jubelirer , 541 U.S. 267 ( 2004 )
(gerrymandering claims non-justiciable, political questions if manageable standards unavailable)
Economic & demographic GIS optimization
What ARE Political Questions?
Non-Justiciable by courts if no standards exist
Political Question Doctrine Baker v. Carr
1.
constitution committed subject to a coordinate branch
2.
3.
4.
5.
Inadequate standards exist for courts to apply deciding requires clearly non-judicial initial policy determination
Independent court determination disrespects another branch potential for embarrassment
Political Parties
1 st A. Association Rights
Sordid Patronage & Graft history, gilded age
Of Mugwumps & Stalwarts
1883 Pendleton Act established Civil Service
Contrast Two-Party System from Multi-Party
Systems in other Nations
Until 50s/60s, parties dominated elections
Limits on coordinated expenses
But, unlimited independent expenses
Campaign Finance: Contributions,
Disclosure & Expenditures
Federal Election Commission Oversight
Donor Disclosures & Donation Limitations
Political Committees
“527” Organizations & PACs
Issue Ads
Soft Money
The Public Funding Alternative
Buckley v. Valeo, 424 U.S. 1 (1976)
Facts: Senators challenged ’74 FECA amends
Holding:
$ contributions/expenditure are forms of
“speech”
Rationale:
Absolutely free political market-place not required by 1st A, nor is desirable; corruption likely w/o reasonable regulation; but
“exacting scrutiny” of campaign finance regulation required:
1.
Govt’s interests compelling to regulate
2.
3.
Regulation burdens and outweighs 1 st A liberty
Is regulation narrowly tailored?
Contribution Sources: ’08 Pres Election
Campaign Electioneering
Political Advertising
Accuracy in Campaign Claims
Why is Fraud apparently inapplicable?
4 th Estate: Role of Media as “Truth Squads”
Intellectual Property (IP) Chills Political Discourse
DMCA Take Down notices hide political speech
McCain Campaign use of Heart’s Barracuda to characterize Sarah Palin as forceful maverick
IP also undermines balloting integrity & security
eVoting Machine Mfgs argue s/w must remain unauditable despite alarming vulnerabilities
Few s/w are patentable, all s/w is copyrightable work
But, s/w licenses prohibit de-compile to protect trade secrets
Ballot Measures/Propositions:
Initiatives & Referenda
Direct Democracy
Safety valve check/balance to unresposive legislature
No or Minimal representative intervention
Indirect initiative: on ballot only after legislature’s inaction
Initiative-citizen petition drives ballot measure
Force public vote: statute, constitutional A., charter
A., ordinance, etc.
CA Propositions since 1910: very extensive experience
Referendums in U.S. referred to electorate
Usually to recall officials or overturn legislation
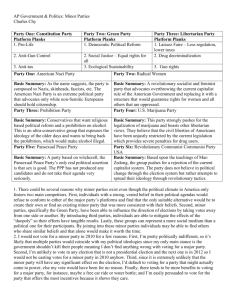
IST eBalloting Initiative
FC Members approved an e-voting integrity demonstration :
The Faculty Council discussed e-voting integrity at the last meeting,
Wednesday, Oct. 30, 2013, and has decided to use the Faculty
Constitution voting from last spring as a demonstration for a proposed solution for enhancing e-voting verifiability. Staff are the only persons with access to the actual e-mail votes (unless an audit is ordered); your anonymity is protected through this demonstration.
A random list of one-word U.S. city names was used to select an alias for each voting member of the faculty (as of spring, 2013). A record of your vote by alias can be found on the Faculty intranet page
At this site you will find a list of all faculty eligible to vote in the
Constitution election and a list of votes by alias with totals of yes, no and of those who did not vote. Please go to the site and verify your vote by your alias.
Your feedback is welcomed regarding this demonstration.
JWB… Your alias is: ___