Population Growth and Economic Development: Causes
advertisement

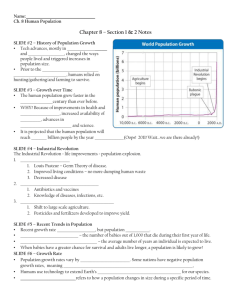
Population Growth and Economic Development: Causes, Consequences, and Controversies Lecture 7 The Basic Issue: Is Population Growth Good or Bad? 1. Argument: – Population is a serious problem in developing countries? 2. Theories: – Demographic transition – Malthusian model – Microeconomic theory of fertility 3. Facts: – Some empirical evidences 4. Policies: – What can developing countries do? 1.1 Population Growth Is A Problem! • Population and the Global Crisis – Poverty, low levels of living, malnutrition, ill health, environmental degradation, etc. • Population-poverty cycles – Population growth, saving, per capital income growth • 7 Negatives – Lower Y per head – Poor people bear burden of population growth – Large population limits educational opportunities – Health of women is harmed – Family food is limited – Environmental degradation occurs – Illegal international migration and over urbanization 1.2 Population Growth Isn’t A Problem! • Other Issues – Underdevelopment – Resource Depletion and Environmental Destruction – Population Distribution – Subordination of Women • False Issue – Neocolonial dependence theory • Desirable – Consumer Demand – Economies of Scale – Labor Supply (sufficient-low cost) – Non-economic reasons 2.1 The Demographic Transition • Stage I: high birthrates and death rates • Stage II: continued high birthrates, declining death rates • Stage III: falling birthrates and death rates, eventually stabilizing 2.2 The Malthusian Model Criticisms of Malthus’ model 2.3 The Household Model • The microeconomic household theory of fertility Demand for Children Equation Cd f (Y , Pc, Px, tx ), x 1,..., n Where Cd is the demand for surviving children Y is the level of household income Pc is the “net” price of children Px is price of all other goods tx is the tastes for goods relative to children Demand for Children Equation Cd f (Y , Pc, Px, tx ), x 1,..., n Under neoclassical conditions, we would expect: Cd 0 Y Cd 0 Pc Cd 0 Px Cd 0 tx 3.1 Population Growth: Numbers 3.2 Population Growth: Structures 3.3 Population Growth: Relations – Population growth & income – Population density & income – Population growth & structure (Number & Structure) – Producer & consumer Income and Population Growth Population Nature Growth Rate % 4 Series1 Linear (Series1) Log. (Series1) 3 2 y = -0.6778Ln(x) + 7.1688 R2 = 0.4948 1 0 0 5,000 10,000 15,000 20,000 25,000 30,000 35,000 40,000 45,000 -1 y = -8E-05x + 2.088 R2 = 0.3562 -2 GNI PPP per capita (1999 US$) Source: Populat ion Ref erence Bureau, 2001World Populat ion Dat a Sheet , (N=158) 4. Some Policy Approaches • What developing countries can do: – Long run: increase the price of child • opportunity cost of mother’s time • Cost of educating child – Short run: control fertility • • • • • • Persuade people Family-planning programs Economic incentives and disincentives Redistribute population Coerce people Raise women’s social and economic status Cd 0 Pc