Student Notes Sect. 1 and 2 - Greater Latrobe School District
advertisement

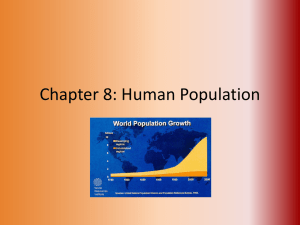
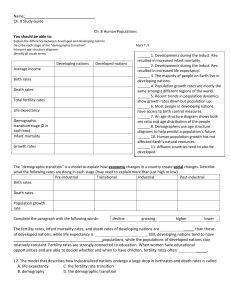
Name: Ch. 8 Human Population Chapter 8 – Section 1 & 2 Notes SLIDE #2 – History of Population Growth • Tech advances, mostly in _______ and _____________________, changed the ways people lived and triggered increases in population size. • Prior to the _________________________________ _______________________________, humans relied on hunting/gathering/and farming to survive. SLIDE #3 – Growth over Time • The human population grew faster in the ___________________century than ever before. • WHY? Because of improvements in health and _______________________, increased availability of ____________, advances in ______________________________ and science. • It is projected that the human population will reach _________ billion people by the year _________________(Oops! 2011! Wait…we are there already!) SLIDE #4 – Industrial Revolution The Industrial Revolution = life improvements = population explosion. 1. _____________________________ 1. Louis Pasteur – Germ Theory of disease. 2. Improved living conditions – no more dumping human waste 3. Decreased disease 2. ______________________________________________ 1. Antibiotics and vaccines 2. Knowledge of diseases, infections, etc. 3. _______________________________________________________ 1. Shift to large scale agriculture. 2. Pesticides and fertilizers developed to improve yield. SLIDE #5 – Recent Trends in Population • Recent growth rate , but population . • __________________________________ – the number of babies out of 1,000 that die during their first year of life. • _____________________________________________ – the average number of years an individual is expected to live. • When babies have a greater chance for survival and adults live longer, a population is likely to grow! SLIDE #6 – Growth Rate • Population growth rates vary by _____________________________. Some nations have negative population growth rates, meaning ____________________________________________________________________________, • Humans use technology to extend Earth’s _________________________________________________ for our species. • ________________________________ refers to how a population changes in size during a specific period of time. SLIDE #7 – Why Study Population Growth? • Scientists have been carefully monitoring the human population for many reasons. 1. Do we have the resources on this planet to provide for all people? 2. What impact do the people have on our environment and natural world?\ 3. What impact do we have on each other? SLIDE #8 – Describing the Human Population Demographers look at a variety of things when studying populations: Population size, population density, population distribution, fertility rates, survivorship, birth rates, death rates, etc. • Population____________________ – Clearly, the size of the human population is changing every second. • Population __________________________ – describes how many people live per square mile or square kilometer. – Using your current knowledge, explain where you think the human population is dense and where population is less dense? • Population _____________________________ – In ecological terms, the human population is ______________________. What does this mean? SLIDE #9 – When Studying Population Growth, Demographers Consider • ___________________________________________ : A model that explains a population’s change from high birthrates and death rates to low birthrates and death rates – Pre-industrial stage: Birthrates and death rates are high. – Transitional stage: Birthrates are high but death rates are declining. – Industrial stage: Birthrates start to decline; death rates stay low. – Post-industrial stage: Both birthrates and death rates fall to low and stable levels. SLIDE #10 – When Studying Population Growth, Demographers Consider • ______________________________________: factors such as wealth and education can affect a nation’s population growth and its resource use. • __________________________________________ – refers to nations with moderate to low income. Worldwide, more people live in developing nations. – Tend to have higher fertility rates, infant mortality, and death rates. – Despite many negative factors, population growth is ___________________________ in developing nations. – There are programs that encourage “smart family planning” to help curb population growth in these countries. SLIDE #11 – Predicting Population Growth Some scientists predict that there will be 9 billion people on Earth by 2050, while others maintain that the population will be closer to 10.5 billion. SLIDE #12 – To Predict Growth, Demographers Look At… • Age Structure • It describes the relative numbers of organisms of each age within a population. • • It shows the proportion of those that are currently at reproductive age and those that could reproduce in the future. Helps demographers to predict how a population could change over time SLIDE #13 – To Predict Growth, Demographers Look At… Fertility Rate – Total ____________________________________: the average number of children a female member of a population has during her lifetime. – What factors could influence fertility rate? – Recently, total fertility rates have started to drop in several nations. – _____________________________________ fertility rate: the total fertility rate for a nation that would keep its population size stable. This rate will defer due to death rates. SLIDE #14 – To Predict Growth, Demographers Look At… • Sex Ratios – Describes the number of males compared to the number of females in a population. – Normally, for every 100 females born, there are 106 males born. SLIDE #15 – Why be concerned about population size? • We are using ______________________________________ resources faster than they can be replaced. Such as trees, water, and food crops. • We are using _______________________________________________ resources at a faster rate each year. Such as oil, coal, minerals, natural gas. • We are __________________________________________ the land, water, and air at a faster rate than ever. There are more people producing more pollutants. SLIDE #16 – What an Impact! Obviously it is difficult to control population growth. It is in our nature as humans to reproduce and grow. • What we can control is what we all do while we are on the planet. • Because this is an environmental science course, we are going to look at the environmental impacts created by the human population. You will find that as we explore those, we will discover many social and economic impacts as well. Chapter 7 Section 3 Notes – People and Their Environment SLIDE #1 – An Interesting Question… 1. How does the human population in the Greater Latrobe School District impact our local environment? Brainstorm with your table and see how many things you can list. SLIDE #2 – Environmental Impacts • The environmental impact of humans depends on the way they live. • _______________________________societies tend to have _________________________________ ecological footprints than affluent societies, but still strain the environment: – Overwhelmed _____________________________ can’t supply clean water or adequate sewage treatment. – Poverty often leads to land overuse. – _______________________________________, flooding, disease, and habitat loss can become common, as land is cleared for farming. – As these societies transition, they use more and more resources, thus catching up with the rest of society. SLIDE #3 – The Wealth Gap • Currently, the richest _______ of the world’s people use _________ of its resources. • As developing nations such as China continue to develop, new environmental problems will emerge, as the need for and use of resources increases. • Resource availability affects quality of life. • Did You Know? Globally, 1.4 billion people live on less than $1.25 per day, and another 2.6 billion live on less than $2 per day. Globally, 1.4 billion people live on less than $1.25 per day, and another 2.6 billion live on less than $2 per day. SLIDE #4 – Impacts of Technology – Negative impacts: • Has enabled and _________________________resource exploitation • Has resulted in ____________________, biodiversity loss, and climate changes – Positive impacts: • Enables longer, healthier, more comfortable lives • Technologies such as _____________________ can help reduce environmental impact. • __________________________energy technology can produce cheap, clean energy. SLIDE #5- Ecological Footprint • The average ecological footprint of a person in each nation can vary greatly. Often it is listed in acres or _____________________________ indicating the amount of land one person needs to survive on Earth. • What is a Hectare? __________________How big is an Acre?________________ • Please complete the Ecological Footprints activity on pg. 253 – answer the questions on the back of this paper. • What is your ecological footprint? Grab a “foot print” paper from the front of the room. Follow the directions to determine… HOW MANY EARTHS WOULD WE NEED IF EVERYONE LIVED LIKE YOU?