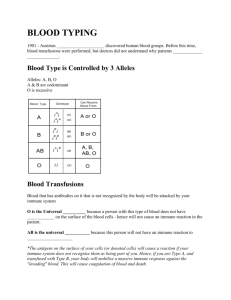
File
advertisement

How is the human body like a battlefield? How does your body know when a substance is an invader? Your body can recognize what is yours, & what is not yours! It does this by recognizing proteins on the surface of your cells. The Immune System Why do we have an immune system? 1. Recognize “self” vs. “non-self” 2. Destroy “non-self” Foreign Invaders (non-self) • Antigen: any surface marker capable of triggering an immune response Antigens can be found on bacterial cells, viruses, or any non-self cell. They could even be allergens or cancerous cells! Antigens are displayed on the surface of cell membranes & viral protein coats. Your body knows when an antigen is not yours! Fighting Foreign Invaders • Antibodies: proteins in the body that recognize & attach to pathogens (things that cause disease – bacteria, viruses, etc.) – Pathogens display antigens! Antibodies attach to antigens! Once the body has been exposed to a pathogen, it remembers! This will reduce your chances of another infection. A. Antibody B. Antigen Antigen! Any pathogen (virus, bacteria, etc.) displays antigens! A patient gets a heart transplant. The new heart displays: A. Antibodies B. Antigens Antigen! Even if the heart is made of human cells, the patient’s body still recognizes it as an invader. The patient’s body could reject the new heart. Which antigen will this antibody bind to? A. B. C. D. Antigen A Antigen B Antigen C None of the above Antigen B! They match like a lock & key or puzzle pieces! A B C Anatomy of the Immune System • Localized in several parts of the body: – Immune cells develop in the bone marrow & thymus. – Immune responses occur in the secondary organs. Anatomy of the Immune System • Spleen: filters & removes old & damaged red blood cells • Bone Marrow: tissue inside bones that produces blood cells Anatomy of the Immune System • Thymus: T-cells mature here • Lymph Nodes: small organs that filter out dead cells, antigens, etc. to present to white blood cells Anatomy of the Immune System • Lymphatic Vessels: collect fluid (lymph) leaked from blood into the tissues & return it to circulation • Tonsils: 3 pairs of masses of lymphoid tissue that help protect against bacteria around the throat Where are blood cells made in the body? A. B. C. D. Spleen Lymph Nodes Bone Marrow Appendix Bone Marrow! There are many different types of cells involved in the immune system! Defense Mechanisms • Non-Specific: the body’s attempt to destroy all types of foreign invaders – General, not targeted to a specific pathogen – Born with it • Specific: immune response specific for a certain pathogen – Could be learned (your body remembers!) Antibody-Antigen binding represents which type of defense? A. B. C. D. Non-Specific Specific Neither Both Specific! Antibodies only bind to 1 type of antigen. Once it binds, your body will always remember that antigen! Which type of defense are baby’s born with? A. B. C. D. Non-Specific Specific Neither Both Non-Specific! Specific immune responses are learned! Some scientists believe that the reason baby’s have an instinct to eat dirt is to build up their immune system. Specific vs. Non-specific Defense • Non-specific defenses will target any invader (general)! – You are born with non-specific defenses. • Specific defenses are learned! When a pathogen invades your body, your immune system creates antibodies that target that specific pathogen. – If the pathogen tries to invade again in the future, your body will be ready, because it remembers! The 3 Lines of Defense Against Infection • Before a pathogen triggers your immune system & makes you sick, your body has other lines of defense against infection! 1st Line of Defense – The Outer Layer of the Body Non-Specific • Goal: prevent organisms from gaining access to the body – Physical Barriers: skin & hair – Chemical Barriers: sweat, tears, saliva, mucus (these contain enzymes that break down cell walls of bacteria) What if a pathogen breaks past the 1st line of defense? 2nd Line of Defense – Cells/Proteins in our Blood Stream Non-Specific • Goal: recognize, neutralize, & destroy invaders – Inflammation & Fever – Increased blood flow to the area brings white blood cells to fight infection 3rd Line of Defense – The Immune Response Specific • 2 types of cells are involved: 1. B Cells 2. T Cells 3rd Line of Defense – The Immune Response Specific • B Cells: provide immunity against antigens & pathogens in the body by making antibodies – – This is how vaccines work! This is called humoral immunity. 1. 2. 3. 4. B-Cell binds to an invading antigen. T-Cell sends a signal the B-Cell. B-Cell is activated to become a plasma cell. Plasma cell releases antibodies specific to the antigen. 3rd Line of Defense – The Immune Response • T Cells: provide defense against abnormal cells & pathogens inside of living cells – Cell-mediated immunity Steps of the Immune Response 1. Virus infects the body. 2. Macrophage eats the virus & displays viral antigens. Macrophages are white blood cells that engulf pathogens. This is a macrophage engulfing bacterial cells! Steps of the Immune Response 3. Macrophage activates helper T-Cells. 4. Helper T-Cells activate B-Cells & killer T-Cells. Macrophages engulf pathogens & display the antigen proteins! This signals the T-Cells. Steps of the Immune Response 5. B-Cells will become memory cells & plasma cells; they remember the antigen for the future! 6. Plasma cells make antibodies, which bind to the viral antigens. Steps of the Immune Response 7. Antibodies attach to the virus & infected body cells, which signals their destruction. 8. Killer T-Cells DESTROY! This is a killer T-Cell attacking cancer cells! You get a cut on your finger and it gets red and swollen around the area. A. First Line of Defense B. Second Line of Defense C. Third Line of Defense Second Line of Defense! If a person has B-Cells against a certain pathogen, the person is: A. Likely to develop the disease. B. Less likely to develop the disease a second time. C. Able to spread the disease to others with physical contact. D. Probably still sick with the disease. This person is less likely to develop the disease a second time! B-Cells are memory cells, meaning they remember pathogens & prevent them from causing disease in the future! How do vaccines work? • Vaccines are composed of dead or weakened pathogens (bacteria or viruses). • When injected, the vaccine triggers an immune response! If you get the flu vaccine, your body will begin to make antibodies to fight the flu virus so that you won’t get sick in the future! The polio vaccine contains weakened polio viruses. A vaccinated individual becomes protected against polio, because the weakened viruses: A. B. C. D. Prevent further viral invasion. Induce an inflammatory response. Promote the production of antibodies. Are too weak to cause illness. The weakened viruses promote the production of antibodies to prevent further disease!