Brief History of Macro
advertisement
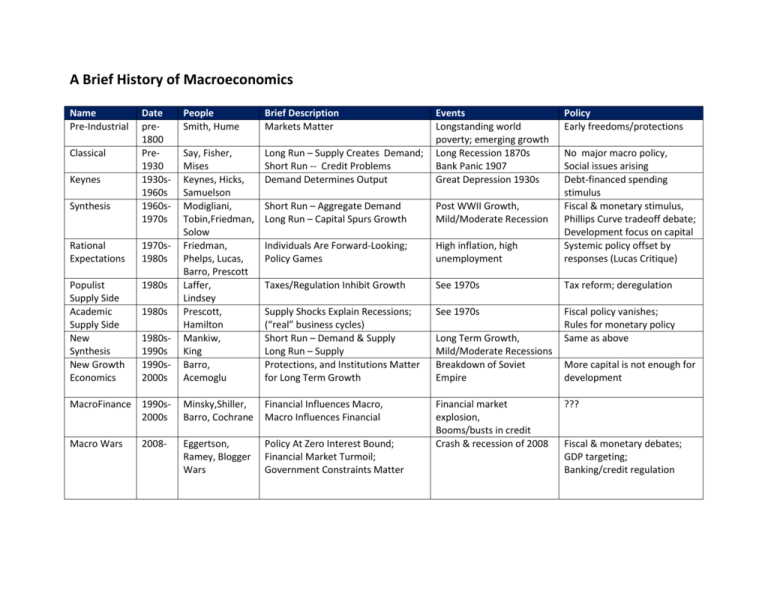
A Brief History of Macroeconomics Name Pre-Industrial People Smith, Hume Brief Description Markets Matter Long Run – Supply Creates Demand; Short Run -- Credit Problems Demand Determines Output Short Run – Aggregate Demand Long Run – Capital Spurs Growth Post WWII Growth, Mild/Moderate Recession Individuals Are Forward-Looking; Policy Games High inflation, high unemployment No major macro policy, Social issues arising Debt-financed spending stimulus Fiscal & monetary stimulus, Phillips Curve tradeoff debate; Development focus on capital Systemic policy offset by responses (Lucas Critique) Taxes/Regulation Inhibit Growth See 1970s Tax reform; deregulation Supply Shocks Explain Recessions; (“real” business cycles) Short Run – Demand & Supply Long Run – Supply Protections, and Institutions Matter for Long Term Growth See 1970s 1980s1990s 1990s2000s Say, Fisher, Mises Keynes, Hicks, Samuelson Modigliani, Tobin,Friedman, Solow Friedman, Phelps, Lucas, Barro, Prescott Laffer, Lindsey Prescott, Hamilton Mankiw, King Barro, Acemoglu Events Longstanding world poverty; emerging growth Long Recession 1870s Bank Panic 1907 Great Depression 1930s Fiscal policy vanishes; Rules for monetary policy Same as above MacroFinance 1990s2000s Minsky,Shiller, Barro, Cochrane Financial Influences Macro, Macro Influences Financial Macro Wars Eggertson, Ramey, Blogger Wars Policy At Zero Interest Bound; Financial Market Turmoil; Government Constraints Matter Financial market explosion, Booms/busts in credit Crash & recession of 2008 Classical Keynes Synthesis Date pre1800 Pre1930 1930s1960s 1960s1970s Rational Expectations 1970s1980s Populist Supply Side Academic Supply Side New Synthesis New Growth Economics 1980s 1980s 2008- Long Term Growth, Mild/Moderate Recessions Breakdown of Soviet Empire Policy Early freedoms/protections More capital is not enough for development ??? Fiscal & monetary debates; GDP targeting; Banking/credit regulation











