File cell structure and function

Cell Structure and
Function
The Discovery of the Cell
• Robert Hooke – first to see and identify cork
“cells” using a microscope.
www.nerdscience.com
7-1
Schleiden
The Cell Theory
Cell Theory:
1. All living things are made of one or more cells.
2. Cells are the smallest unit of life.
3. New cells are produced from pre-existing cells.
Schwann
Virchow
7-1 www.nerdscience.com
Basic Cell Substances
• The main ingredient of any cell is water.
• The structure of a water molecule makes it ideal for dissolving many other substances
Macromolecules
• Macromolecules form when many small molecules join
• The 4 types of macromolecules are:
1. Nucleic acids-
• form when long chains of nucleotides join.
• Important because they contain genetic information
• Ex: DNA and RNA
Macromolecules
4. Proteins-
• Necessary for nearly everything cells do
• Made up of long chains of molecules called amino acids.
• Some help break down nutrient in food
3. Lipids-
• large molecule that does not dissolve in water
• Store energy
• Plays an important role as protective barriers in cells (membranes)
Macromolecules
4. Carbohydrates-
• Made up of one or more sugar molecules
• Store energy
• Provide structural support
• Used for communication between cells
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Cells can be grouped into 2 types:
1. Prokaryotes – cells that do not contain nuclei. o Ex: (Bacteria)
2. Eukaryotes – cells that contain nuclei and have membranesurrounded components called organelles which have specialized functions o Ex: plants, animals, fungi, protist
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
• Organelles – structures in a cell that act like “little organs.”
• Cytoplasm – the jelly-like fluid where the organelles
“float.” o It contains salts and other molecules
The Nucleus
• Nucleus – large membrane-enclosed structure that contains the cell’s genetic information and directs cell activities o Nuclear Envelope – membrane that surrounds the nucleus.
Nuclear Envelope
Mitochondria
• Mitochondria – converts chemical energy stored in food into energy(ATP).
o “Powerhouse of the Cell!” o Converts glucose and oxygen into ATP, Carbon Dioxide
(CO2) and Water (Cellular Respiration)
• ATP- the fuel for cellular processes such as growth, cell division, and material transport www.nerdscience.com
Mitochondria
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
• Ribosomes – Make Proteins!
o Found in a cells cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (E.R)
Ribosome
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
• Endoplasmic reticulum – transports proteins to the
Golgi apparatus and breaks down toxic material. o Rough ER – has ribosomes o Smooth ER – no ribosomes
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Rough ER
Smooth ER
Golgi Apparatus
Golgi Apparatus (Golgi bodies)- prepares proteins and packages them into ball-like structures called vesicles
Golgi
Apparatus
Lysosomes
Lysosomes – small organelles filled with enzymes that help recycle cellular components
Vacuoles
• Vacuoles – store food, water, and waste material o Animal cells have small vacuoles o Plant cells have large Central Vacuoles
Vacuoles
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts – organelles that capture energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy. (Photosynthesis) o Found only in plants.
Chloroplast
Cytoskeleton
Cytoskeleton – made of a network of threadlike proteins that are jointed to form a framework inside a cell.
• helps cell to maintain shape, move, and move organelles.
Cell Boundaries
Cell membrane – thin, flexible membrane that surrounds the cell and protects the inside of a cell from the environment outside.
• Controls what enters and leaves the cell.
• Made of phospholipids (2 layers) and proteins.
Two layers!
Cell Boundaries
Cell wall – rigid layer around the membrane that provides structure and support.
• found only in bacteria, fungi and plants.
Cell Appendages
Cell appendages are often used for movement.
• Flagella- long, tail- like appendage that whip back and forth and move a cell.
• Cilia- short hair like structures that can move a cell or move molecules away from a cell.
Moving Cellular Material
• The exchange of materials between as cell and its environment takes place at the cell
membrane.
• A cell membrane is semipermeable- it allows only certain substance to enter or leave a cell
Passive Transport
1. Passive transport – the movement of substances through a cell membrane without using the cell’s energy
a. Diffusion – movement of particles from an area of high to low concentration.
• Diffusion continues until the concentration of a substance is the same on both sides of a membrane.
b. Osmosis – the diffusion of water through a membrane.
Concentrations are equal, so no net movement of water!
www.nerdscience.com
Osmosis Practice
90% H2O
Cell
10% NaCl
90% H2O
10% NaCl
7-3
Concentration of water is greater in the cell than out, so water will move out!
www.nerdscience.com
www.nerdscience.com
Osmosis Practice
90% H2O
Cell
10% NaCl
80% H2O
20% NaCl
Concentration of water is greater outside the cell than in, so water will move
In!
www.nerdscience.com
Osmosis Practice
80% H2O
Cell
20% NaCl
90% H2O
10% NaCl
7-3
Active Transport
2. Active Transport- The movement of materials across a cell membrane with the use of energy
• Moves substances from areas of low concentration to areas oh high concentration
a. Exocytosis – a cell’s vesicles releases their contents outside of the cell.
b. Endocytosis – the cell surrounds a large particle and brings it into the cell
Cell Size and Transport
• For a cell to survive, its surface area must be large compared to its volume.
• As a cell grows, its volume increases faster than its surface area
Cells & Energy
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
All living things need energy to survive
Cellular Respiration – converts the energy in food molecules into a usable form of energy called ATP
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Step 1 : Glycolysis - occurs in the cytoplasm of all cells
• Glucose is broken down into smaller molecules
Step 2 : Occurs in the mitochondria of Eukaryotic cells and requires oxygen
• Small molecules made during glycolysis are broken down
• Large amounts of usable energy called ATP are produced
• Water and Carbon Dioxide is given off
www.nerdscience.com
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
7-3
FERMENTATION
• Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells use fermentation to obtain energy from foods when oxygen levels are low.
• It occurs in the cell’s cytoplasm
Lactic- acid fermentationOccurs in muscles
C
6
H
12
0
6
ATP + Lactic Acid
(Glucose) (energy)
Some types of bacteria and yeasts make ATP during alcohol fermentation .
C
6
H
12
0
6
ATP + Alcohol + CO
2
(Glucose) (energy)
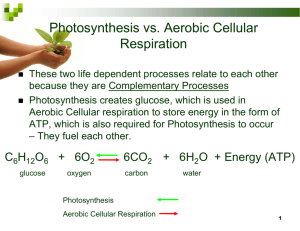
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
• Plants and some unicellular organisms obtain energy from light (radiant energy)
• Photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions that converts light energy into chemical energy (Glucose)
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
• In plants light energy is absorbed by pigments called chlorophyll
• Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts
• Uses CO
2 that is released during cellular respiration to make food energy and release oxygen.