5-themes-definitions
advertisement
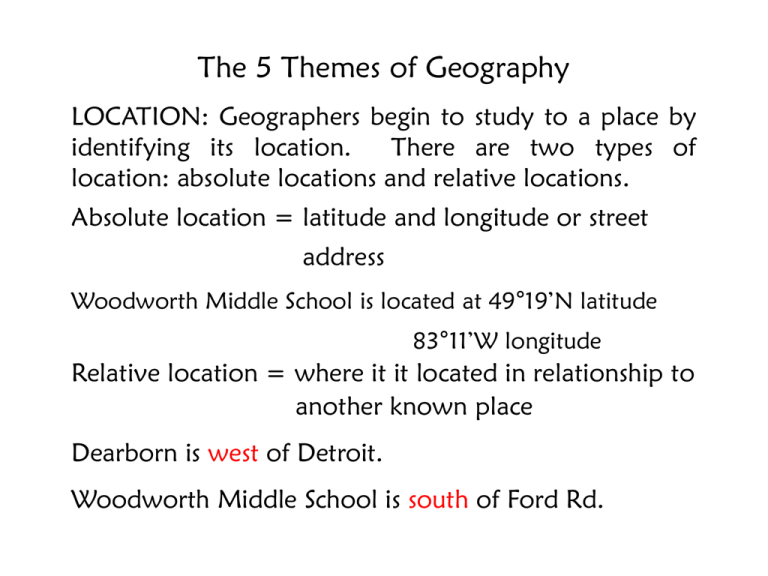
The 5 Themes of Geography LOCATION: Geographers begin to study to a place by identifying its location. There are two types of location: absolute locations and relative locations. Absolute location = latitude and longitude or street address Woodworth Middle School is located at 49°19’N latitude 83°11’W longitude Relative location = where it it located in relationship to another known place Dearborn is west of Detroit. Woodworth Middle School is south of Ford Rd. Location EXAMPLE 1: Geographers can talk about the location of a place by telling which continent it is on. This is an example of a relative location because it is telling where it is located compared to the other continents. The 5 Themes of Geography PLACE: Place refers to the physical and human characteristics of an area. When geographers are studying place, they want to know what an area is like. This includes: what is the land like (land and water features), what the climate and vegetation is like, what buildings or man-made structures are there, the amount of people that live there, what is the culture like, and even what language is spoken there. PLACE EXAMPLE 1: When geographers study the United States, they might talk about the Appalachian Mountains, the Great Plains, and the Rocky Mountains as major land features found there. This is an example of place because these specific land features are only found in the United States. The 5 Themes of Geography REGION: Geographers group areas of the world that have common characteristics into regions. A region can be identified by a common climate, a shared physical feature, a common language, a common national government, or in many other ways. REGION EXAMPLE 1: The area around Michigan is known at the Great Lakes Region. It is an example of a region because the states and Canada that border the lakes all share in using the water and resources that the lakes provide. The 5 Themes of Geography MOVEMENT: Geographers study the way people, goods, and ideas travel or spread from one place to another. Geographers look for relationships and try to find out why these movements happened and how they affect or affected the people living there. MOVEMENT EXAMPLE 1: Pineapples are brought to Michigan from Hawaii. This is an example of movement of goods because pineapples are a fruit that is not able to be grown naturally in Michigan. The 5 Themes of Geography HUMAN-ENVIROMENT INTERACTION (H.E.I): Geographers study Human-Environment Interaction to see how people have changed and adapted to live in their natural surroundings, how they have used their land and natural resources, and how they have changed or affected the place they live. HUMAN-ENVIROMENT INTERACTION (H.E.I): EXAMPLE 1: The Panama Canal was dug through the isthmus of Panama to connect the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean. It is an example of H.E.I. because people changed the land to help make travel easier between the western and eastern coasts of North and South America.