GEOGRAPHY 2: HUMAN GEOGRAPHY Exam 1 Study Questions
advertisement

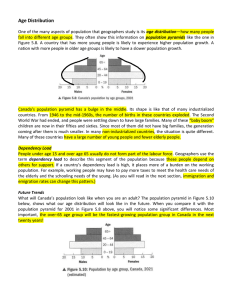
GEOGRAPHY 2: HUMAN GEOGRAPHY Exam 1 Study Questions Exam is TUESDAY, SEPTEMBER 29TH. Bring a Blue Book. Exam covers chapters 1, 9 and 3 (only through population). Chapter 1: Analyze how geographers’ thinking about the relationship between nature and culture has changed over time. Begin your discussion with the dualism of 18th Century Europe and conclude with contemporary approaches to studying cultural ecology. Describe how geographers organize space through regional analysis. The geographer Don Mitchell has said “There’s no such thing as culture.” Evaluate his statement and discuss how geographers use culture in their study of humans on the earth. Contrast the geographic concepts of place and space. Using specific examples, explain how geographers use the concept of scale in their analysis. Chapter 9: Explain the problems with development as a normative process. How have some countries responded to the conventional ideas of development? How does conventional development differ from sustainable development? Describe the three categories of development measures. How are these categories connected? How are these categories combined to evaluate the overall development of a country? Analyze the explanations for, or causes of, underdevelopment. Evaluate how income inequality and gender inequality are connected to the study of development. Describe, compare and contrast the four primary theories of development. What are possible alternatives to these models and theories? Discuss the benefits and problems of large-scale development projects, such as dams. Chapter 3: Describe where in the world humans are concentrated, how fast human population is growing and the historical context for this growth and how the density of human population is evaluated. What measures are used to calculate the fertility of a population? Which of these measures is more meaningful and why? Explain the reasons that fertility rates may be high in some parts of the world, but low (or negative) in other parts of the world. Evaluate the impacts of a high dependency ratio for a country and what measures could be taken to address these problems (evaluate this for the two different types of high dependency ratios possible). Diagram the Demographic Transition Model and explain the types of demographic change and reasons for these changes for each stage of the model. Critique the model by analyzing its limitations in understanding current human population growth and change on the earth. Compare and contrast the theories and predictions of human population growth including Malthus and the Neo-Malthusians, Cornucopians (Optimists) and Social critics, such as those that emphasize food insecurity. Using specific case studies, analyze and evaluate the impacts—social as well as demographic--that government policy can have on population growth.