Five Themes of Geography
advertisement

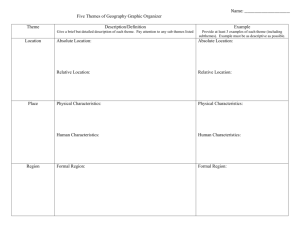
Five Themes of Geography What is Geography? Greek Word describing the earth It studies the distribution and interaction of physical and human features on earth Geographers use maps to study the use of space on earth Tools like a legend (map key that lists and explains symbols and colors), a compass rose (star-like symbol showing direction – north (N), south (S), west (W), and east (E)) or scale (shows the ratio between a unit of length on the map and a unit of distance) Location Two Types Absolute – exact place something is found Uses imaginary lines (hemisphere, equator, prime meridian) Relative – place in relation of something based on other objects around it Place Physical features and cultural landscape of a location Physical differences include climate, landforms, and vegetation Products of human interaction with the environment such as building houses and roads Region An area of the earth’s surface that is defined by shared characteristics Formal Region – limited number of related characteristics (continental area – USA, Africa) Functional Region – organized by interactions and connections between places (city and suburbs – San Jose and Fremont) Perceptual Region – people perceive the characteristics of a region in the same way Human – Environment Interaction People use what the environment offers, as well as change the environment to meet their needs Movement Three Types Linear – How far across the earth an idea, person or product travels Time – How long it takes for an idea, person, or product to travel Psychological – The way people view distances