Respiratory System Anatomy: PHL 212 Presentation
advertisement

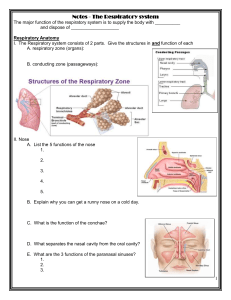
Anatomy Practical [PHL 212] Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Trap irritants / infectious particles Moistens and warms incoming air Breathing process Oversees gas exchanges Exchange O2 Air to blood & Blood to cells Exchange CO2 Cells to blood & Blood to air Exchange of gasses takes place within the lungs in the alveoli Enable speech production Organs of the Respiratory system Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi Lungs – alveoli Upper Respiratory Tract Anatomy of the Nasal Cavity Nose is primary passageway for air entering respiratory system Nasal septum : divides cavity into right & left halves The cavity is lined with respiratory mucosa Moistens air Traps incoming foreign particles Lateral walls have projections called conchae Increases surface area The nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity by the palate Anterior hard palate (bone) Posterior soft palate (muscle) Paranasal Sinuses Cavities within bones surrounding the nasal cavity Frontal bone Sphenoid bone Ethmoid bone Maxillary bone Function of the sinuses Lighten the skull Produce mucus that drains into the nasal cavity Pharynx (Throat) Pharynx is shared by digestive & respiratory systems Muscular passage from nasal cavity to larynx Three regions of the pharynx Nasopharynx – superior region behind nasal cavity Oropharynx – middle region behind mouth Laryngopharynx – inferior region attached to larynx The oropharynx and laryngopharynx are common passageways for air and food Tonsils of the pharynx Pharyngeal tonsil (adenoids) in the nasopharynx Palatine tonsils in the oropharynx anterior to ear Lingual tonsils at the base of the tongue Larynx (Voice Box) Inspired air leaves pharynx by passing through a narrow opening – glottis Larynx surrounds & protects glottis Routes air and food into proper channels Plays a role in speech CARTILAGES OF LARYNX Thyroid cartilage Epiglottis Cricoid Cartlage Cuneiform cartilages Corniculate cartilages Arytenoid cartilages PAIRED Trachea (Windpipe) Trachea is a tough, flexible tube with diameter of 2.5cm & length of 11cm Connects larynx with bronchi Branches to form right & left primary bronchi Lined with ciliated mucosa Beat continuously in the opposite direction of incoming air Expel mucus loaded with dust and other debris away from lungs Bronchi Primary bronchi formed by division of the trachea Enters the lung at the hilus (medial depression) Right bronchus is wider, shorter, and straighter than left Bronchi subdivide into smaller and smaller branches Lungs Occupy most of the thoracic cavity Apex is near the clavicle (superior portion) Base rests on the diaphragm (inferior portion) Each lung is divided into lobes by fissures Coverings of the Lungs Pulmonary (visceral) pleura covers the lung surface Parietal pleura lines the walls of the thoracic cavity Pleural fluid fills the area between layers of pleura to allow gliding Lungs Respiratory Tree Divisions Primary bronchus Secondary bronchus Tertiary bronchus Bronchiole Terminal bronchiole Bronchioles & Alveoli Smallest branches of the bronchi Terminal bronchioles end in alveoli Structure of alveoli Alveolar duct Alveolar sac Alveolus