Unit 12: Respiratory System
advertisement

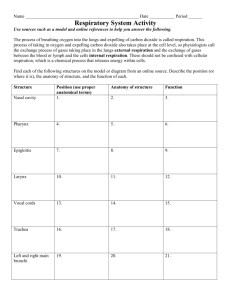
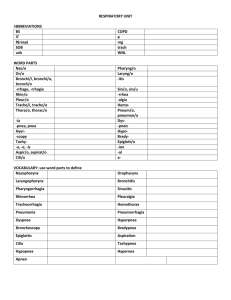
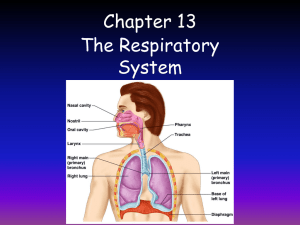
The Respiratory System Functions • Pulmonary Ventilation – • External Respiration – • exchange of gases between ______________ & _______________. Use of Oxygen – • exchange of gases between _____________ & _______________ Internal Respiration – • ______________________ air in & out. cellular _______________________ Production of Carbon Dioxide – a _______________________ of cellular respiration. General Anatomy • Upper Respiratory system: – • Nasal passage to ________________ Lower Respiratory system: – Larynx to ________________ – ________________ cold area Respiratory Disorders • • UPPER RESPIRATORY: – _____________________ - ____________________ - __________________ – _____________________ - ____________________ - __________________ LOWER RESPIRATORY: – ________________ - _______________ - __________________ – ________________ - _______________ - __________________ - __________________ Nose & Sinus Cavity • External ________________ - opens to ____________________________. • Nasal _______________ - contains ______________________. • ___________________ - nasal canal. • Nasal __________________ - divides left & right ________________ passage. • Nasal ___________________ (turbinate bone) ______________ & moistens air. • Internal ______________ - entrance to ______________________ & larynx. Pharynx • • • ___________________________: – Internal nares to soft____________________. – _________________________ tubes – _________________________ tonsils (adenoids) ___________________________: – Soft palate to ___________________ bone. – ____________________ tonsils – ____________________ tonsils ___________________________: – Hyoid bone to entrance of _______________________ & ____________________ Anterior Larynx • Location- ________ to ________ • ____ cartilages of the larynx • 3 major cartilages – ___________________ - hyoid cartilage – __________________ cartilage- anchors adams apple. – __________________ cartilage- below thyroid cartilage Open Glottis • Entrance into __________________. – ___________________ folds (false vocal cords)- soft tissue that surrounds ____________ cords. – ______________ cords (true) vibrate when air passes to produce __________________. Epiglottis in Action - Step 1: _______________________________________________________________________________ - Step 2: _______________________________________________________________________________ - Step 3: _______________________________________________________________________________ Trachea • 11cm long, 2.5 cm wide. • _____________________ layer: – “_____”-shaped. – 15 to 20 tracheal ______________. – ___________________ cartilage. – Open part of “C” covered by _______________________ muscle. Bronchial Tree • ________________ - Right is shorter & thicker, left is longer & thinner. • ________________ – _______________________. – Not ringed in ______________________. – End in ___________________. Lungs • Right lung = ____ lobes • Left lung = ____ lobes – • Smaller because _________ of your heart is on the _____________ side. MEMBRANES: for ____________________ – ________________ Pleura- connects to thoracic cavity. – ________________ Pleura- connects to lungs. – ________________ Cavity- space between parietal & visceral pleura, filled with ___________. Alveoli • Clusters of _______________________ air sacs. • Capillaries are one cell thick, _______________ diffuse easily. • Area of gas _______________ with _______________. • Surrounded in ______________________ beds. Mechanisms & Transport of Gases • Partial Pressure of each gas (02 & C02 mmHg) determines where it will diffuse. • Let’s draw: External Respiration • Gas exchange between alveoli & _______________ • ________ goes from alveoli to blood due to _____________________ gradient & gas ________________. • ___________ + ___________ __________________ • _______ goes from blood to _______________ due to concentration gradient & gas pressures. • _______________ ___________ + _____________ Internal Respiration • Gas exchange between blood and ____________. • Regulated by gas pressures & concentration __________________. • ________ diffuses from blood to cells. • ______________ _____________ + ______________ • ___________ diffuses from ____________ to blood. – _____________ + _____________ ______________ or – _____________ + _____________ ______________ Diaphragm • Muscular sheet that divides the ___________________ & ______________________ cavities. • Contracts & ___________________ to move air in & out. The Inhaling Process 1. Need to __________________ the internal volume of the _______________ cavity - Diaphragm ______________ (lowers), ribcage ______________ 2. Causes lower ________________ pressure (compared to external pressure) - __________ Law = P & V are _____________________ proportional 3. Air rushes __________. The Exhaling Process - the opposite of the inhale 1. Need to ____________________ the internal volume of the thoracic cavity - Diaphragm ________________ (raises), ribcage ___________________ 2. Causes _______________ internal pressure (compared to external pressure) - Boyles Law = P & V are inversely proportional 3. Air rushes _____________.