File - Chemistry at Loyola
advertisement

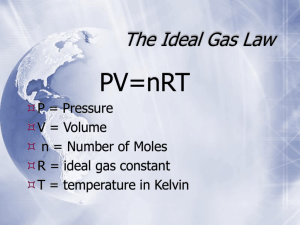
SCH 3U EXAM REVIEW UNIT 1 – Matter, Chemical Trends and Chemical Bonding & UNIT 2 – Chemical Reactions 1. What are the names, symbols, and electrical charges of the three subatomic particles? 2. Where is nearly all of the mass of an atom located? What contributes to this mass? 3. Define the terms atomic number and mass number. 4. If an atom gains an electron to become an ion, what kind of electrical charge does the ion have? 5. What is a “period”? What is a “group/family”? 6. How many electrons, protons, and neutrons in each of the following particles? 3+ 2+ + a) 35 b) 56 c) 64 d) 39 17𝐶𝑙 26𝐹𝑒 29𝐶𝑢 19𝐾 7. a) What is an alkali metal? Ca, Cu, In, Li, S b) What is a halogen? Ce, Hg, Si, O , I c) Which is a transition element? Pb, W, Ca, Cs, P d) Which is a noble gas? Xe, Se, H, Sr, Zr e) Which is an alkaline earth metal? Mg, Fe, K, Cl, Ni 8. Why are the noble gases not reactive? 9. Describe the trend in atomic sizes in the periodic table. Explain this trend. 10. Choose the larger atom in each pair: a) Na or Si b) P or Sb c) Cl- or Ar d) Na or Na+ 11. a) Define ionization energy. b) Describe the trend in ionization energies in the periodic table. Explain this trend. 12. Choose the atom with the higher ionization energy in each pair. a) B or C b) O or S 13. a) Define electronegativity. b) Describe the trend in electronegativities in the periodic table. Explain this trend. c) Which atom has the highest electronegativity? d) If an element has a low electronegativity, is it likely to be a metal or a non-metal? 14. Use the periodic table to choose the element in each set that has the highest electronegativity. a) Si, As, Ge b) P, Mg, Ba, Sb c) B, F, Te, P 15. Use Lewis symbols to diagram the reaction between: a) Ca and Br b) K and S 16. Draw Lewis structures of a) Br2 b) H2O c) NH3 17. What is the octet rule? What is it responsible for? 18. What is the difference between an atom and a molecule? 19. Name the elements that exist in nature as diatomic molecules. 20. Write formulas for ionic compounds formed between a) Na and Br b) K and I c) Ba and O d) Mg and Br e) Ba and F 21. Which of the following formulas are incorrect? a) NaO2 b) RbCl c) K2S e) MgO2 d) Al2Cl3 22. Write the formulas for the following ions: a) Ammonium b) nitrate c) sulphate e) hydroxide f) phosphate g) carbonate d) chlorate 23. Write formulas for the ionic compounds formed from: a) K+ & nitrate ion b) ammonium ion & Cld) Mg2+ & phosphate ion e) Zn2+ & hydroxide ion 24. Name the following compounds: a) CaS b) AlBr3 c) Na3P h) H2SO4 i) Ca(ClO3)2 j) CuO d) NaF k) Hg2Cl2 e) NH4Cl l) PbS 25. Write the formulas for the following compounds a) Ammonium sulphide b) chromium(III) sulphate d) iron(III) oxide e) mercury(II) oxide g) boron trichloride h) calcium nitrate c) Fe3+ & carbonate ion f) NaNO3 m) SnO2 g) SO3 c) tin(IV) chloride f) silicon tetrafluoride i) aluminium oxide 26. Complete the following equations and state the type of reaction. a) __ CO2 → ____ + ____ b) __CuSO4 + __AgNO3 → ____ + ____ c) __C2H2 + __O2 → ____ + ____ d) __Al + __Cl2 → ____ e) __H3PO4 + __NaOH → ____ + ____ f) __Zn + __HCl → ____ + ____ ANSWERS: 1. Subatomic particle Charge Symbol Proton + P+ Neutron 0 N0 Electron - e- 2. In the nucleus. The protons and the neutrons. 3. Atomic number is the number of protons in the atom. Mass number is the mass of the atom (mainly composed of neutrons and protons) 4. negative 5. A row in the periodic table, each element has one more electron than the previous element in that period. A column in the periodic table. 6. a) 17 p+, 18 e-, 18 n0 b) 26 p+, 23 e-, 30 n0 c) 29 p+, 27 e-, 35 n0 d) 19 p+, 18 e-, 20 n0 7. a) Li b) I c) W d) Xe e) Mg 8. They have a full octet 10. a) Na b) Sb c) Cld) Na 12. a) C b) O 14. a) As b) P c) F 15. a) b) 16. a) 17.Octet Rule: Atoms that have full valence shells of 8 electrons (2 for hydrogen) Octet rule is responsible for the stability of an atom. 18. Atom is the smallest unit of matter that can be broken down chemically. Molecules are made of 2 or more atoms. 19. H2 N2 O2 F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 20. a) NaBr b) KI c) BaO d) MgBr2 e) BaF2 21. a), d), e) 22. a) NH41+ b) NO31c) SO42d) ClO31e) OH1f) PO43g) CO3223. a) KNO3 b) NH4Cl c) Fe2(CO3)3 d) Mg3(PO4)2 e) Zn(OH)2 24. a) calcium sulphide b) aluminium bromide c) sodium phosphide d) sodium fluoride e) ammonium chloride f) sodium nitrate g) sulphur trioxide h) sulphuric acid i) calcium chlorate j) copper(II) oxide k) mercury(I) chloride l) lead(II) sulphide m) tin(IV) oxide 25. a) (NH4)2S b) Cr2(SO4)3 c) SnCl4 d) Fe2O3 e) HgO f) SiF4 g) BCl3 h) Ca(NO3)2 i) Al2O3 26. a) CO2 C + O2 (decomposition) b) CuSO4 + 2AgNO3 Cu(NO3)2 + Ag2SO4 (double displacement) c) C2H2 + 3O2 2CO2 + 2H2O (combustion) d) 2Al + 3Cl2 2AlCl3 (synthesis) e) H3PO4 + 3 NaOH 3H2O + Na3PO4 (neutralization / double displacement) f) Zn + 2HCl ZnCl2 + H2 (single displacement) UNIT 3 – QUANTITIES IN CHEMICAL REACTIONS 1. How many atoms are represented per molecule in each of the following formulas? a) HC2H3O2 b) (NH4)2SO4 c) (CH3)3COH 2. A sample of magnesium contains 1.204 x 1024 atoms. a. How many moles does this sample contain? b. What is the mass of this sample, in grams? 3. How many moles of water are in 9.00 g of water? 4. How many moles of sodium nitrate are in 1.70 g of sodium nitrate, NaNO3, a substance used in fertilizers and gunpowder? 5. a) b) c) d) e) f) 35.8 mol of ammonium sulfate = g 0.500 mol of table sugar, C12H22O11 = g 0.665 mol NH4NO3 = atoms of nitrogen 1.00 kg of Tl2SO4 = moles 2.61 g of NaCl = molecules 7.5 L of CO2 at STP = g 6. Calculate the percentage of nitrogen in two important nitrogen fertilizers ammonia, NH3, and urea, CO(NH2)2. 7. The molecular formulas of some substances are written below. Write their empirical formulas. a) C2H2 c) C8H18 b) C6H12O6 d) NH4NO3 8. A compound of mercury with a formula weight of 519 g/mol contains 77.26% Hg, 9.25% C, 1.17% H, and the rest is oxygen. Determine its empirical and molecular formulas. (the order: Hg, C, H, O) 9. Balance the following equations. a. Ca(OH)2 + HCl b. P4O10 + H2O CaCl2 + H2O H3PO4 10. Terephthalic acid, an important raw material for making Dacron, a synthetic fibre, is made from the reaction of para-xylene with oxygen by the following reaction: C8H10 + 3 O2 C8H6O4 + 2 H2O How many grams of terephthalic acid (C8H6O4) could be made from 154 g of para-xylene (C8H10)? 11. The octane (C8H18) present in gasoline burns according to the following equation: a. 2 C8H18 + 25 O2 16 CO2 + 18 H2O a) How many moles of oxygen gas are needed to react fully with 4 mol of octane? b) How many moles of carbon dioxide can form from 1.0 mol of octane? c) How many moles of water are produced from the combustion of 6 mol of octane? d) How many moles of oxygen gas and octane are needed to synthesize 8 mol of carbon dioxide? 12. If 80 g of magnesium react with 100 g of sulphur, how many grams of magnesium sulphide are formed? 13. If 12 moles of hydrogen gas react with 5 moles of oxygen gas, how many moles of water are produced? 14. If 130 g of iron react with 120 g of oxygen gas, how many grams of iron (III) oxide are produced? ANSWERS: 1. a) 8 b) 15 c) 15 2. a) 2 mol b) 48.6 g 3. 0.500 mol 4. 0.02 mol 5. a) 4730 g b) 171 g c) 8.01 x 1023 atoms d) 1.98 mol e) 2.69 x 1022 molecules f) 14.7 g 6. 82.4 % (ammonia) 46.7 % (urea) 7. a) CH b) CH2O c) C4H9 d) NH4NO3 8. HgC2H3O2 9. a) 1,2,1,2 b) 1,6,4 10. 241 g 11. a) 50 mol b) 8 mol c) 54 mol d) 12.5 mol, 1 mol 12. 176 g 13. 10 mol 14. 186 g UNIT 4 – SOLUTIONS AND SOLUBILITY 1. Calculate the molarity for: a) 3 moles of NaCl in 6.0 L of solution. b) 65 g of calcium chloride in 2.0 L of solution. 2. Calculate the final concentration if 2.00 L of 3.00 M NaCl and 4.00 L of 1.50 M NaCl are mixed. 3. What volume of 0.250 M KCl is needed to make 50.0 mL of a 0.100 M solution? 4. a) What volume of a 12.0 M stock solution is needed to prepare 500 mL of a 2.0 M HCl solution? b) What volume of water must be added to this volume of stock solution? 5. Which of these substances are soluble in water? a) lithium sulfate b) magnesium phosphate d) calcium hydroxide e) ammonium sulfide c) lead (II) sulfide 6. Name the precipitate that forms when aqueous solutions of sodium sulfide and copper (II) sulfate are mixed. 7. A solution of sodium sulfide is mixed with a solution of copper (II) chloride. a) Write the total ionic equation. b) Write the net ionic equation. c) Identify the spectator ion(s). 8. Solutions of silver nitrate and sodium chloride react. a) Name the precipitate that forms. b) How many grams of silver chloride will be produced if 20 mL of 0.25 M sodium chloride reacts with excess silver nitrate? 9. Calculate the volume of 0.110 mol/L sodium sulfate that is needed to precipitate the maximum mass of barium sulfate from 60.0 ml of 0.145 mol/L barium chloride. 10. If an excess of sodium carbonate solution is added to 75.0 mL of calcium chloride solution, 7.50 g of precipitate is formed. Calculate the concentration of the calcium chloride solution. 11. If 75 mL of 0.25 M HCl reacts with 2.6 g of zinc metal, how many grams of hydrogen gas are produced? 12. Determine the pH of each solution, given the concentration of H+ ions. a) lemon juice, if the concentration of hydronium ions is 1.0 x 102 mol/L b) baking soda solution, if the concentration of hydronium ions is 6.3 x 10 9 mol/L 13. Calculate the volume of 0.250 mol/L sulfuric acid that is needed to react completely with 10.0 mL of 1.5 mol/L potassium hydroxide. ANSWERS: 1.a) 0.5 M b) 0.29 M 2. 2.00 M 3. 20.0 mL 4. a) 83 mL b) 417 mL 5. (a) and (e) 6. copper (II) sulfide 7. a) 2 Na+ (aq) + S2 (aq) + Cu2+ (aq) + 2 Cl (aq) 2 Na+ (aq) + 2 Cl (aq) + CuS (s) b) S2 (aq) + Cu2+ (aq) CuS (s) c) Na+ and Cl 8. a) silver chloride b) 0.717 g 9. 79.1 mL 10. 0.999 mol/L 11. 0.0189 g 12. a) 2.0 b) 8.2 13. 30 mL UNIT 5 – GASES AND ATMOSPHERIC CHEMISTRY 1. If a gas occupies 5.0 L at 120 kPa, calculate the pressure if it is to occupy 6.5 L. 2. At a temperature of 45C, a gas occupies 180 mL. At what temp (C) will the gas occupy 130 mL? 3. A balloon, filled with a gas at 20C and 97.4 kPa pressure, occupies 500 L. What will be the volume of the balloon if it ascends to the stratosphere where the temperature and pressure are -13C and 3.29 kPa? 4. How many moles of oxygen gas are present in a 2.5 L container at 80C and 40 kPa? 5. Calculate the pressure if 3.0 moles of nitrogen gas is present in a 5.0 L container at 25C. 6. A 6.0 L balloon contains sulfur dioxide gas at 37C and 120 kPa. What is the mass of the gas? 7. If 9.06 x 1024 atoms of sodium, 0.33 KL of chlorine gas at STP, and 500g of oxygen gas react, how many grams of sodium chlorate are produced? 8. What is the density of carbon monoxide gas at a pressure of 100 kPa and 10C? 9. The explosive nitroglycerine decomposes according to the equation: 4 C3H5(NO3)3 (s) 12 CO2 (g) + 10 H2O (g) + 6 N2 (g) + O2 (g) a. What volume of oxygen at STP will be produced from 10.0 g of nitroglycerin? b. What volume of nitrogen at 99.5 kPa and 275C will be produced from 10.0 g of nitroglycerin? ANSWERS: 1. 92.3 kPa 6. 17.9 g 2. - 43.3 C 7. 1109 g 3. 13000 L 8. 1.19 g/L 4. 0.034 mol 9. a) 0.25 L 5. 1500 kPa b) 3.02 L