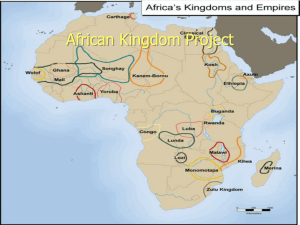
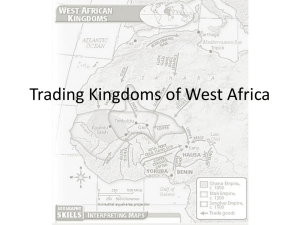
Classical Africa
advertisement

Warm Up • With the last incident in Connecticut in your opinion what should school districts do to ensure the safety of the students and staff? • Remember you must be within reason. Classical Africa Northeast Africa • Early Nubia: Egypt as a model, gold and slaves • Napata (Kush): 8th- 6th century fought with Egyptians • Meroë: Nubians adopted Hellenism, gold and ivory, irrigation technology, 5 independent female rulers, shifting trade patterns lead to decline Blue Nile, Northern Ethiopia Kushite Pyramids Christian Nubia (NEA) • Missionaries converted nobility (543-1504) • Divided into feudal kingdoms • Christian society with monasteries, cathedrals, and castles ruled by African bishops and knights Ethiopian Highlands (NEA) • South of Nubia: outside Nile valley • 2nd oldest African civilization • Arab colonists intermarried and absorbed by locals: State of Axum • Axum kings: Merchant princes of Red Sea trade • Major regional power until coming of Islam Ethiopian Highlands West Africa • Horse: military system rested on armored, mounted knights • Camel: major event in African history, TRANS-SAHARAN TRADE with North Africa • Divine Kingship: used to establish ideology for the centralized politics and economy • Gold: success rested on camels, new fields, and strong kingdoms Ghana (WA) • Oldest historical West African kingdom • Greatest period 10-13th centuries • Gold: biggest, wealthiest, most powerful state in west Africa • Traditional religions: Divine Kingship Ghana and Islam • Muslim merchants in 9th century • Ghana kings learned to capitalize on writing and administration skills • Merged into a single society • Sacked by Muslim Berbers from the Sahara • Lost preeminence in Africa Mali (WA) • United WA after fall of Ghana • Sundiata: Alexander of Africa • Mansa Musa: MVP of Mali society – Ruled at height of power – Pilgrimage – Wide spread inflation Mansa Musa Songhai (WA) • • • • • • Final and greatest kingdom 1464-1592 Overthrew Mali Great centers of Islamic learning and culture Timbuktu Overthrown by Moroccans in 1591 Benin and Ifo (Art and Statues) Southern and Central Sub-Saharan Africa • Numerous ethnic groups collectively known as Bantu, a linguistic term • Not native, migrated from western Africa (Niger river) as early as 400 BCE • Iron tools: increased population, powerful military states • Social organization: male solidarity, expands power and land Eastern Zimbabwe cave paintings, carbon dated at nearly 1000 years ago Mwenemutapa (Great Zimbabwe) • Flourished in 13-17th centuries • Power: Bantu military traditions, gold, good agricultural production, and control of trade routes • Most famous part is walled complex at Great Zimbabwe: supreme example of indigenous African architecture. Included stone places, walls, towers, and shrines Great Zimbabwe Ruins