Chemistry of life

Introduction to Biology 2
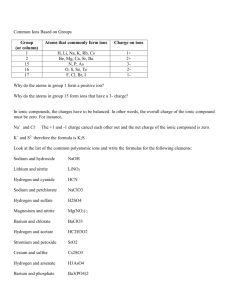
Think, pair, & share to complete the “What
Makes up an Atom” notes
Complete the “What Makes up an Atom” homework; Read & take notes on Chapter 2 from the book
Is it more dangerous to swim in the ocean or in a lake during a lightning storm?
Substances that release ions in water
The electrically charged (either + or -) ions can conduct an electric current
+ ions are cations
- ions are anions
For example, NaCl in H
2
Na + and Cl -
O dissociates into
Water is a polar molecule
Polar = electrons are not shared equally, thus the distribution of charges is uneven
Water has a unique shape due to its polarity and can form hydrogen bonds with other water molecules
The slightly charged ends of the water molecule cause the ions to separate and interact with water instead
Now that’s salty!
Na+ (sodium) is the major cation found outside of cells & is necessary for the transmission of nerve impulses and muscle movement
Hypernatremia – too much sodium in the bloodstream
Can simply drink more water!
Usually due to dehydration
Hyponatremia – too little sodium in the bloodstream
Normal blood Na+ levels = 135-145 mmol/L
Potassium (K+) is the major cation found inside cells & functions in transmission of nerve impulses and muscular function
Hyperkalemia - too much K+
Kidneys may not be working properly to secrete
K+
Hypokalemia – too little K+
Kidney disease, poor diet, loss of electrolytes via excessive exercise/sweating
Normal K+ levels = 3.5 - 5.0 mmol/L
http://brainu.org/fil es/movies/action_pot ential_cartoon.swf
http://highered.mhe
ducation.com/sites/0
072495855/student_v iew0/chapter14/anim ation__the_nerve_im pulse.html
Let’s summarize this process!
Strongest Acids:
HCl, HNO
3
, H
2
SO
4
,
HBr, HI
Strongest Bases:
LiOH, NaOH, KOH,
Ca(OH)
2
What do you notice?
…that release hydrogen ions (H+) in water
HCl releases H+ and Cl- ions
H+ donors
…that release ions that bond with hydrogen ions called hydroxide ions (OH )
NaOH is a base that dissociates to Na+ and
OH- in water
H+ acceptors
pH measure the H+ concentration
The concentration of H+ and OH- in body fluids affect chemical reactions and bodily functions!
(too acidic or too basic = very dangerous)
pH of 7 means there is an equal number of
H+ and OH- ions (Neutral)
pH < 7 means there is a greater number of
H+ (Acidic)
pH > 7 means there is more OH- (Basic)
Buffers keep the body’s pH in a safe range
Blood pH is normally at 7.4
Buffers combine with H+ ions when they are in excess (too acidic) OR they can donate H+ ions when there are too few (too basic)
If blood pH drops below 7.35, the person has acidosis
If blood pH rises above 7.45, the condition is alkalosis.
Bicarbonate ion HCO
3
- is a weak base, accepting excess H+ ions
Carbonic acid H
2 donate extra H+
CO
3 is a weak acid that will
Organic = chemicals that include both carbon and hydrogen atoms (C and H)
Macromolecules: lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids
Inorganic = the chemicals that do not include both carbon and hydrogen
Water, carbon dioxide, salts, oxygen, etc.
Large molecules made up of smaller building blocks or subunits
Define monomer
Define polymer
Make a model of a polymer, showing 3 monomers