Anatomy: structure of body parts Physiology: function of body parts
advertisement

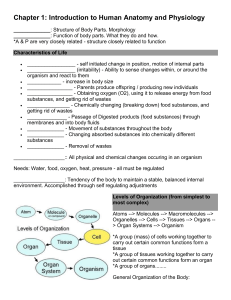
Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Essential Question: What happened to Kati Mori at the London Marathon? Anatomy: structure of body parts Physiology: function of body parts; what they do and how. How are they related? Characteristics (Processes) of Life 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Movement - self initiated change in position, motion of internal parts Responsiveness - ability to sense changes and react Growth - increase in body size Reproduction - DNA passed from parents to offspring Respiration - obtaining oxygen (O2) Digestion - chemically changing (breaking down) food Absorption -passage of digested products (food) through membranes and into body fluids Circulation - movement of substances throughout the body Assimilation -changing absorbed substances into chemically different substances Excretion - removal of wastes Video: How a Bean becomes a Fart 1. Why do Beans make you fart? 2. Which of the life processes from the list above were mentioned in the video? Review the list of life processes and consider Kati Mori’s symptoms. that you think might be related. Choose three of the processes METABOLISM: All physical and chemical changes occuring in an organism All of these processes require: ENERGY - Where does the energy for our bodily processes come from? Needs: Water, food, oxygen, heat, pressure HOMEOSTASIS: Tendency of the body to maintain a stable, balanced internal environment. Feedback Loops - how the body makes adjustments when the environment changes Negative Feedback Loop Positive Feedback Loop What is hypnatremia? How does Kati's story relate to HOMEOSTASIS? Which of the 10 life processes were compromised in Kati's situation? Levels of Organization (from simplest to most complex) Atoms → Molecules → Macromolecules →Organelles → Cells →Tissues → Organs → Organ Systems → Organism General Organization of the Body: Axial Portion - head, neck, trunk | Appendicular Portion - arms & legs 1. Several body cavities and layers of membranes within cavities 2. Variety of organs and organ systems within cavities (VISCERA = internal organs. also: "visceral organs") What does "eviscerate" mean? Body Cavities (see p.9) Dorsal Cavity | Ventral Cavity 1. Thoracic Cavity - right and left separated by mediastinum. 2. Abdominopelvic Cavity (abdominal + pelvic cavity) DIAPHRAGM - separates thoracic and abdominal cavity SEROUS MEMBRANE - two layers, covers organs outer layer = PARIETAL layer and forms a "lining" inner layer = VISCERAL layer, covers the surface of organs 1. Pleura (or pleural membrane) - surrounds the lungs 2. Pericardium (or pericardial membrane) - surrounds the heart 3. Peritoneum (or peritoneal membrane) - surrounds organs within the abdominopelvic cavity *Between the layers of each membrane is a lubricating fluid which is called SEROUS FLUID How does this system maintain homeostasis? ORGAN SYSTEMS 1. Integumentary Body covering. Skin, hair, nails, sweat glands. - protect underlying tissues, regulate body temperature 2. Skeletal Bones, ligaments, cartilage - Support, movement, protection; production of blood cells 3. Muscular Muscles of the body - Movement, posture, production of body heat 4. Nervous Brain, spinal cord, nerves - Communication, mental activities 5. Endocrine Glands = pituitary, thyroid, pancreas, ovaries, testes - Secretion of hormones, chemical communication 6. Digestive Mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, - Breakdown of food (digestion), absorbtion 7. Circulatory Heart, blood vessels, blood. - Transports materials throughout the body. 8. Lymphatic ( Immune System) - fights infections 8. Urinary Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra - filters wastes from the blood, maintains water balance 9. Reproductive Reproductive organs, primarily the ovaries (females) and testes (males) Anatomical Terminology Anatomical Position Superior / Inferior Medial / Lateral Anterior/ Posterior Proximal / Distal Superficial / Deep Sagittal | Transverse | Frontal (coronal) *Learn to Identify and Describe the Body Regions (Body Regions Handout) *Learn the names of specialized medical fields. (Medical and Applied Science)