Chapter 1
advertisement

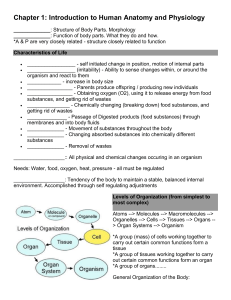
Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Anatomy The branch of science that deals with the structure of body parts Their forms and arrangements Physiology Deals with the functions of body parts What they do and how Human Organism A well-organized unit of body parts Characteristics of Life: (10) *Movement Self-initiated change in position *Responsiveness The ability to sense changes and react *Growth An increase in body size *Reproduction *Respiration Obtaining oxygen and using it in the release of energy from food *Digestion Food chemically changed into forms that can be absorbed by the body *Absorption The passage of substances through membranes *Circulation Movement of body fluids *Assimilation Changing absorbed substances into forms that are chemically different from those that entered the body fluids *Excretion Removal of wastes that are produced by body parts Metabolism Physical and chemical changes in the body Maintenance of Life Organisms need: *Water (the most abundant substance in the body), food, oxygen, heat, pressure Homeostasis The ability to maintain a stable internal environment Ex. shivering, goose bumps, sweat, etc. Levels of Organization: Small to large Atoms, molecules, macromolecules, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, system, organism Body Divisions Axial Portion Head, neck and trunk Appendicular Portion Arms and legs Body Cavities Cavity A natural hollow place within the body Page 8 Figure 1.6 Page 9 Figure 1.7 2 Major Cavities Within the Axial Portion: Dorsal & Ventral Cavities Dorsal Cavity Can be divided into 2 cavities: Cranial-houses brain Spinal-spinal cord Ventral Cavity Divided into 2 cavities: Thoracic-chest Abdominopelvic-abdomen, pelvis Small Head Cavities Oral- teeth, tongue Nasal-right, left nose Orbital-eyes Middle Ear-bones Membrane A thin, soft, pliable layer of tissue Parietal Pleura Membrane that lines the thoracic compartments Visceral Pleura Membrane that lines the lungs Mediastinum Separates the thoracic cavity into 2 compartments The compartments contain right & left lungs Pericardial Membrane Surrounds the heart Peritoneal Membrane The lining membranes of the abdominopelvic cavity Organ Systems Humans consist of several organ systems Made up of organs that work together to provide a specialized function Integumentary System Includes skin, hair, nails, sweat glands, sebaceous glands These parts protect underlying tissues and help regulate body temperature. They also house sensory receptors Skeletal System Consists of bones as well as ligaments and cartilage Serve as attachments for muscles Provide protection/support Tissues within bones produce blood cells Muscular System Muscles are the organs of this system By contracting and pulling their ends together, they provide the forces that cause body movements *posture, body heat Nervous System Includes the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sense organs Nerve cells use chemical signals (nerve impulses) to communicate with each other Endocrine System Includes all glands that secrete chemical messages called Hormones (they travel in fluid) Includes the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal, & thymus glands, pancreas, ovaries, testes The endocrine and nervous systems integrate and coordinate to allow the body to act as a unit Digestive System Receives food from outside Converts to useful & simpler molecules to be absorbed & passed on Includes the Mouth, tongue, teeth, salivary glands, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, small and large intestines Respiratory System Provide intake and output of air for the exchanges of gases between blood and air Includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi/lungs Circulatory System It’s a muscular pump that forces blood through vessels Blood transports gases, nutrients, hormones, and wastes Includes the heart, arteries, veins, capillaries, blood Lymphatic System Carries fluid Includes lymphatic vessels, lymph fluid, lymph nodes, thymus gland, spleen Lymphatic organs also aid the body in defending the body against infections by removing microorganisms from tissue fluids (WBCs) Lymphocytes Cells of the lymphatic system Urinary System Maintains water, electrolyte and acid-base balances (kidneys) Includes the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra Reproductive System Process of producing offspring (progeny) Male: produces/maintains sex cells (sperm) Includes the scrotum, testes, epididymides, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate glands, penis, urethra Female: Provide support and development of embryo and functions in birth process Produce/maintain sex cells (eggs) Includes the ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, vagina, clitoris, vulva Handout on Relative Position!