Good Morning!
advertisement

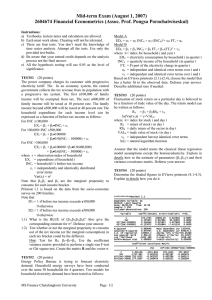
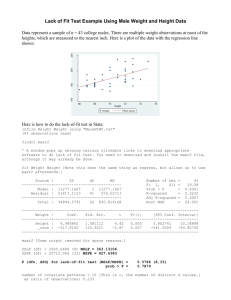
Good Afternoon – 10/18/05 Review from last time Behavioral finance and technical analysis A yahoo example Begin Chapters 14 – 18 – Fed stuff Chapter 7 – rational expectations Rational Expectations Trying to predict how long it takes to get to work (textbook, CH. 7) Are you always right? What are the properties of the forecast errors? Properties of error term Mean of zero Unpredictable with current information set Uncorrelated with itself So what are rational expectations? You do the best with the information set that is available to you. A soon as new (relevant) information arrives, you change you expectations (how quickly?) Football example again! How can you make money in the stock market? On overhead, be sure to discuss all the variables needed to be successful in terms of making the best forecast possible! Discuss why that was a waste of time! A formal look at the forecasting model and properties of error term (on overhead)! A test of the efficient market hypothesis Properties of error term Mean of zero Unpredictable with current information set Uncorrelated with itself A little about regression analysis What do economists do? Theory vs applied work Recall Consumption Function (go to overhead) Dependent Variable: CONEXP Method: Least Squares Date: 10/13/05 Time: 12:15 Sample (adjusted): 1987M02 2005M08 Included observations: 223 after adjustments Variable Coefficient Std. Error t-Statistic Prob. C PINC(-1) REAL_FF(-1) 1837.302 1.015550 -0.078855 457.6706 0.004001 0.016039 4.014465 253.8458 -4.916470 0.0001 0.0000 0.0000 R-squared Adjusted R-squared S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood Durbin-Watson stat 0.998747 0.998735 58.01901 740565.2 -1220.465 1.061403 Mean dependent var S.D. dependent var Akaike info criterion Schwarz criterion F-statistic Prob(F-statistic) 5481.939 1631.541 10.97278 11.01862 87666.56 0.000000 Data – Coke – closing price – daily data; 1/2/70 – 1/25/99 – source, yahoo 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 1/02/70 9/02/77 5/03/85 CLOSE - Coke 1/01/93 So what does our forecasting model of coke look like? Dependent Variable: CLOSE Method: Least Squares Date: 10/24/04 Time: 11:20 Sample(adjusted): 1/05/1970 1/25/1999 Included observations: 7581 after adjusting endpoints Variable Coefficient Std. Error t-Statistic Prob. C CLOSE(-1) 0.113314 0.998174 0.047963 0.000689 2.362514 1449.142 0.0182 0.0000 0.996404 0.996403 1.673779 21232.84 -14660.82 2.008938 Mean dependent var S.D. dependent var Akaike info criterion Schwarz criterion F-statistic Prob(F-statistic) R-squared Adjusted R-squared S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood Durbin-Watson stat 63.79229 27.90979 3.868308 3.870138 2100012. 0.000000 200 150 100 50 20 0 0 -20 -40 -60 -80 -100 1/05/70 9/05/77 Residual 5/06/85 Actual 1/04/93 Fitted 5000 Series: Close (t) - Close (t-1) Sample 1/05/1970 1/25/1999 Observations 7581 4000 3000 2000 Mean Median Maximum Minimum Std. Dev. Skewness Kurtosis -0.003166 0.000000 6.000000 -82.75000 1.674444 -23.14830 962.4173 Jarque-Bera Probability 2.91E+08 0.000000 1000 0 -75.0 -62.5 -50.0 -37.5 -25.0 -12.5 0.0 And finally, a look at trying to predict the error term with past information Dependent Variable: DCLOSE Method: Least Squares Date: 10/25/04 Time: 11:11 Sample(adjusted): 1/19/1970 1/25/1999 Included observations: 7571 after adjusting endpoints Variable Coefficient Std. Error t-Statistic Prob. C DCLOSE(-1) DCLOSE(-2) DCLOSE(-3) DCLOSE(-4) DCLOSE(-5) DCLOSE(-6) DCLOSE(-7) DCLOSE(-8) DCLOSE(-9) DCLOSE(-10) -0.003859 -0.005667 -0.008836 -0.014633 -0.002607 -0.026925 0.004066 -0.019810 -0.004913 -0.003631 -0.021146 0.019250 0.011499 0.011499 0.011499 0.011498 0.011497 0.011498 0.011498 0.011499 0.011498 0.011498 -0.200447 -0.492847 -0.768422 -1.272572 -0.226782 -2.341823 0.353615 -1.723006 -0.427293 -0.315763 -1.839080 0.8411 0.6221 0.4423 0.2032 0.8206 0.0192 0.7236 0.0849 0.6692 0.7522 0.0659 R-squared Adjusted R-squared S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood Durbin-Watson stat 0.001850 0.000529 1.674927 21208.67 -14642.17 2.000118 Mean dependent var S.D. dependent var Akaike info criterion Schwarz criterion F-statistic Prob(F-statistic) -0.003533 1.675370 3.870868 3.880940 1.401002 0.172788 Dependent Variable: COKEERRORS Method: Least Squares Date: 03/14/05 Time: 14:08 Sample (adjusted): 1/09/1970 1/25/1999 Included observations: 7577 after adjustments Variable Coefficient Std. Error t-Statistic Prob. C CLOSE(-1) CLOSE(-2) CLOSE(-3) CLOSE(-4) CLOSE(-5) -0.002946 -0.004620 -0.002241 -0.006108 0.011725 0.001287 0.048054 0.011493 0.016200 0.016200 0.016200 0.011492 -0.061314 -0.401970 -0.138322 -0.377004 0.723806 0.112013 0.9511 0.6877 0.8900 0.7062 0.4692 0.9108 R-squared Adjusted R-squared S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood Durbin-Watson stat 0.000237 -0.000423 1.674370 21225.40 -14653.76 2.000054 Mean dependent var S.D. dependent var Akaike info criterion Schwarz criterion F-statistic Prob(F-statistic) -3.49E-05 1.674016 3.869542 3.875032 0.359482 0.876388 Picking up some loose ends Terms from Finance Portion of course – we discussed all but the terms in black font 1. Options – calls, puts, strike price, writing options. 2. Derivatives – what does this term mean? 3. Stock price determination – formula 4. The efficient market theory. 5. Autoregressive properties. 6. Technical analysis. 7. Shorting stocks and short covering. 8. NEWS. 9. Jawboning. 10. Price to earnings ratio. 11. Earnings per share. 12. Futures. 13. Closing position. 14. Hedging. 15. Inside information. 16. Random walk. 17. Bulls vs. Bears. 18. Exercise. 19. In the money. Discuss Behavioral Finance Definition : Behavioral Finance (BF) is the application of psychology to finance. It is based on the study of behavioral biases and their effects on financial markets, such as anomalies & inefficiencies on prices and returns. BF tries to detect and understand those biases / anomalies, and if possible to use them in investment strategies. Here is another link http://www.wordiq.com/definition/Behavioral_fin ance Behavioral Finance Discuss day trading and Google, Amazon.com, etc See article that is now posted Since efficient market theory suggests that it is impossible to beat the market – let’s move on to technical analysis Example – Bollinger Bands Go to new posting on Bollinger bands Then go to Yahoo finance - Begin Fed stuff – open market operations