TS Eliot – The Winter Evening Settles Down
advertisement

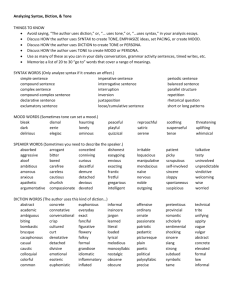
ELA 11 January 22 and 23, 2014 ACT Prep Questions 7-10 Bell Ringer In your notebooks write down today’s date. Answer the following question Which of the following sentences does not contain an allusion? A. Jennifer is as lovely as a rose. B. After she was told that the chocolate bar was like forbidden fruit, she wanted it even more. C. The hill next to school looked like Mount Everest to the small child. D. The food poisoning last week set off Hiroshima in my stomach. I. Imagery A. Creating a picture in the reader’s mind.. 1. Frequently use adjectives and adverbs. 2. Show, don’t tell. B. Appeals to any of the five senses 1. sight, sound, touch, taste, smell 2. Also uses metaphor, simile, and personification. Examples of imagery The following images might be used to describe a stroll on a summer night: Sight - a full moon in a black sky Sound - the chirp of crickets Taste - the tang of cold glass of lemonade Touch - a warm breeze Smell - freshly mowed grass Practice- Find the images T.S. Eliot – The Winter Evening Of withered leaves about Settles Down your feet The winter evening settles down And newspapers from vacant lots; With smell of steaks in passageways. The showers beat Six o’clock. On broken blinds and chimney-pots, The burnt-out ends of smoky And at the corner of the days. street And now a gusty shower wraps A lonely cab-horse steams and stamps. The grimy scraps And then the lighting of the lamps. Create the images In your notebook create the following chart and describe your perfect Saturday morning. Sense Sight Taste Touch Smell Hear image II. Diction A. The author’s choice of words. 1. Diction depends on topic, purpose, and occasion. a. The topic often determines the specificity and sophistication of diction. 2. The writer’s purpose—whether to entertain, inform, or persuade—partly determines diction. 3. Diction also depends on the occasion. As with clothes, level of formality influences word choices. Diction B. When studying diction, I must understand… 1. connotation (the meaning suggested by the word) 2. denotation (the word’s literal meaning). Practice Explain the differences in connotation among the members of each of the following groups of words: 1. Hurl, throw, chuck 2. Giggle, laugh, snicker, cackle 3. Mansion, dwelling, residence, house, home, habitat III. Tone vs. Mood A. Tone: - the writer's attitude toward the audience/Subject he or she is writing about 1. a writer's tone can be… a. serious b. sarcastic c. objective d. satirical e. solemn f. wicked, etc. B. Mood - is the feeling a piece of literature evokes in the reader. Mood is the overall feeling of the piece, or passage. Tone vs mood Tone Example 1A Tone Example 1B Tone Example 2A Tone Example 2B Tone Example 3A Tone Example 3B The Yellow Wallpaper Charlotte Perkins Gilman 1860-1935 Gilman was born in Hartford Connecticut in 1860. Aspiring to be an artist, she briefly attended the Rhode Island School of Design and married artist Charles Stetson. After the birth of her daughter she went into a deep and long-drawn depression. The medical treatment available not only failed to help her, it angered her. She was told to limit herself to a quiet domestic life and “never to touch pen, brush, or pencil again.” From her anger sprang “The Yellow Wallpaper” She ended her own life in 1935.