PPTX
advertisement

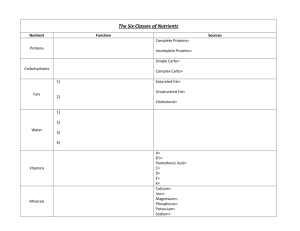
Nick Krienes A runner’s diet Carbohydrates Primarily source comes from plants Small amount comes from animals (Lactose and Glycogen) 3 units of Carbs Monosaccharides Disaccharides Polysaccharides Monosaccharides (GGF) Basic unit of Carbs 3 forms (Glucose, Galactose ,Fructose) Glucose-Carbs converted to this to be used Galactose-When combined with glucose they form Lactose Fructose -Slowest absorbed in bloodstream Disaccharides (SLM) 2 Monosaccharides combined is a Disaccharide Sucrose-Glucose and Fructose combined (Syrup) Lactose -Glucose and Galactose (Milk) Maltose-Glucose and Glucose (Barley) Polysaccharides (SF) Multiple monosaccharides combined Starch -Most important carb to ingest -Potatoes, wheat, corn, rice Fiber -Beneficial in lowering LDL (Bad) cholesterol -Apples, Bananas, Raspberries, cook Whole Wheat Pasta Glycogen Storage form of glucose and carbs Glucose stored in the muscle and liver Body’s main source of fuel/energy Oatmeal is a perfect food to store glycogen Importance of Carbs Average healthy athlete diet is 3000 kcal/day 50-55% of calories should be carbs 4kcal/1g ~80% will be stored in the muscles ~15% will be stored in the liver ~5% circulate in the plasma as glucose Carbs for Exercise Carbs available in muscle immediately Utilized during high intensity activity Used faster than fats and proteins Used primarily so proteins are not How many Carbs? 2-3g/kg BM for Low Intensity Training 3-4/kg BM for Moderate Training 4-6/kg BM for Endurance Training 6-8/kg BM for Competitive Training 8-10/kg BM for Professional Training BM=Body Mass Common Misunderstandings All carbs are the same -Fruits are better than baked goods Carbs cause weight gain -Carbs increase insulin which increase appetite Carbs create indigestion -Gluten is the main component in wheat Misunderstandings Cont. Carbs make you tired -They increase serotonin Carbs always raise cholesterol -Soluble fibers (rich carbs) reduce LDL levels Carbs do no effect memory -Low carb diets can effect visuospatial Fats 3 Groups of Fats Simple- Triglycerides Compound- Phospholipids Derived- Triglycerides and Phospholipids combined (Cholesterol) Types of Fat Triglyceride- Biggest form of storage Saturated Fat- Firmer at room temp (Bad) Unsaturated Fat- Liquid at room temp (Good) Trans Fat- Increase LDL and decrease HDL Fats for Exercise Fuels body at Low Intensity Training 9kcal/1g Prevents protein from being used for energy Cushions internal organs Assists in warming the body Importance for Fats 30% of daily calorie intake ~900-1000 calories <10% of that should be saturated Ex: Fast food, hot dogs, cookies Good choice with <30% calories from fat Common Misunderstandings Saturated and Trans fats are the same -Trans fats are modified unsaturated fats Eating fats makes you fat -High fat low carb diets aid weight loss Margarine versus natural butter -Most margarine have processed vegetable oil Misunderstandings Cont. Fats have no correlation with heart disease -Fats increase risk for cardiovascular disease If it’s “low fat” it’s healthy -Amount of fat must be below 30% Veggie dishes are always healthier -Some veggie dishes contain lots of fat Comparing the Two Carbs Fats Gives energy for moderate-high intensity activities Gives energy for low intensity activities Stored in adipose cells Energy immediately available in muscles More time needed for breakdown Least amount of time to catabolize 9kcal/1g 4kcal/1g Marathon Running https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3ItnxJLAOeY Explanation -Stage 1=Excitement -”Glucosed up” meaning full of carbs -Stage 6= The Wall -Depleted storage of carbs and glucose References -Davis, S. (2014, January 9). Livestrong.com. Retrieved from The best foods to build Glycogen website: http://www.livestrong.com/article/ 101449-foods-build-glycogen/ - Iowa State University Human Sciences. (n.d.). Retrieved 2015, from Role of Carbohydrates website :http://www.extension.iastate.edu/humansciences/content/carbohydrate