4.4 Cell Transport
advertisement

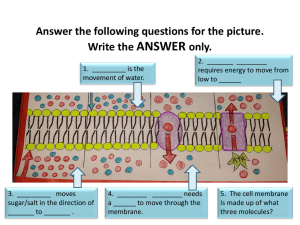
4.4 Cell Transport Cell Transport What do cells need to transport across the membrane? ◦ Nutrients, waste, water, oxygen Types of Transport Passive transport: movement of materials across a membrane without the use of energy (ATP) ◦ Molecules move from high concentration to low concentration ◦ “down the concentration gradient” ◦ Three types: Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated diffusion Types of Transport: Passive transport Passive Transport: Diffusion Diffusion: movement of molecules across a selectively permeable membrane ◦ Molecules move from high concentration to a low concentration; down or “with” the concentration gradient Passive Transport: Diffusion = solute = solute Which solute will pass the barrier? Why? Passive Transport: Diffusion Example: Oxygen diffuses into the blood stream because of high oxygen concentration in the lungs Passive Transport: Osmosis Osmosis: movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane ◦ Water moves from a high concentration of water (low [solute]) to a low concentration of water (high [solute]) ◦ Remember: A lot of water = not much solute A little bit of water = LOTS of solute Passive Transport: Osmosis Passive Transport: Osmosis Passive Transport: Facilitated Diffusion Facilitated diffusion: diffusion of large particles across a membrane with the help of membrane proteins ◦ Molecules move from high concentration to low concentration Passive Transport: Facilitated Diffusion Glucose molecules High Concentration Cell Membrane Low Concentration Prote chan Quick Review: Does passive transport require energy? Give 3 examples of passive transport What direction to molecules move in passive transport? How does diffusion differ from facilitated diffusion? What type of passive transport describes how water moves? Types of Solutions Movement of water depends on the [solute] ◦ Water always moves towards the area of low [water] or high [solute] Types of Solutions Hypertonic solution: ◦ Has a higher [solute] than another solution Low[solute] High [solute] Types of Solutions What will happen to a cell in a hypertonic solution? ◦ Water moves OUT of the cell towards the area of high [solute] ◦ Cell shrinks (plasmolysis) Types of Solutions Hypotonic Solution: ◦ Has a lower [solute] than another solution High [solute] Low [solute] Types of Solutions What will happen to a cell in a hypotonic solution? ◦ Water will move in to the cell towards an area of high [solute] ◦ Animal cell: lysis (burst) ◦ Plant cell: turgid (fat plant cells) ◦ Ideal environment for plants Types of Solutions: Isotonic solutions: ◦ Two solutions have the same concentration of solute Types of solution What will happen to cells placed in isotonic solutions? ◦ Water moves into & out of the cell equally ◦ Cells stay the same ◦ Ideal environment for animals Cell Transport Active Transport Active transport: proteins are used to move molecules (minerals & nutrients) across the membrane by using ATP energy ◦ Molecules move from low concentration to high concentration Types of Active Transport Endocytosis: process when a cell surrounds and takes in large materials or large amounts of materials from the environment Active Transport: Endocytosis The amoeba heads toward the unsuspecting paramecium. It begins to spread out its body to catch its prey. Too late for the paramecium, it's been caught! Active Transport: Endocytosis The amoeba spreads out even more to surround its lunch. The paramecium will soon be completely inside the amoeba! The amoeba will absorb its lunch now that it is inside its cell membrane. Types of Active Transport: Types of endocytosis: ◦ Pinocytosis: movement of liquids into the cell ◦ Phagocytosis: movement of solids into the cell Type of Active Transport Exocytosis: the exit or secretion or materials from the cell ◦ Ex: cell getting rid of waste 2 1 3 Active Transport Endocytosis and Exocytosis often work together http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::535::535::/sites/dl/free/0072437316/120068/ bio02.swf::Endocytosis%20and%20Exocytosis