Cell Transport - WordPress.com
advertisement

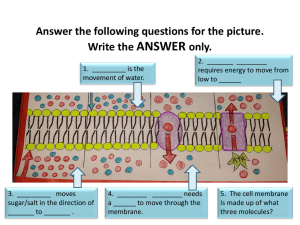
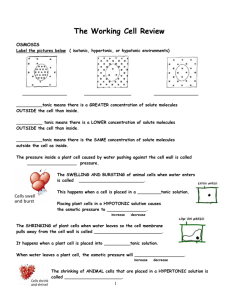
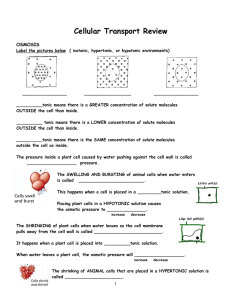
Cell Transport The cell membrane lets thing in and out of the cell Carbohydrates Cholesterol Protein Channel Cytoskeleton Phospholipids The cell membrane is selectively permeable • This means: it selects what can come into the cell • “Semipermeable” outside cell H 2O NH3 inside cell sugar lipid aa salt Remember... • Phosphate group head –hydrophilic (likes water) • Fatty acid tails –hydrophobic (hates water) • Arranged as a bilayer (bi = 2) Cell membrane is the boundary between inside & outside… separates cell from its environment Can it be an impenetrable boundary? IN OUT food carbohydrates sugars, proteins amino acids lipids salts, O2, H2O • OUT waste ammonia salts CO2 H2O products IN cell needs materials in & products or waste out How do things get through the cell membrane? • Passive Transport • Diffusion • Osmosis • Facilitated Diffusion • Active Transport Diffusion • Movement of solutes from high to low concentration • No energy is needed SOLUTE MEMBRANE WATCH • The ink will diffuse in the water Facilitated Diffusion • Facilitated Diffusion: Molecules need a protein channel to pass through the cell membrane, no ATP needed Protein Channel Facilitated Diffusion facilitated = with help • • • Protein channel allows specific molecules to pass Like the bouncer of a club! No energy is needed high low “The Bouncer” Osmosis • Osmosis: the diffusion of water through a cell membrane Concentration of water Direction of osmosis is determined by comparing total solute concentrations Hypertonic - more solute, less water Hypotonic - less solute, more water Isotonic - equal solute, equal water Cell survival depends on balancing water uptake & loss Active Transport • • • Active Transport: Molecules need a protein pump to get into cell Uses Energy = low ATP ATP Goes from low to high= UP the concentration gradient high “The Doorman” Endocytosis phagocytosis • • Endocytosis: taking things into the cell in vesicles Examples: Phagocytosis and Pinocytosis pinocytosis How do larger molecules get in and out of the cell? endocytosis phagocytosis = “cellular eating” pinocytosis = “cellular drinking” exocytosis Exocytosis • Exocytosis: molecules exit the cell in vesicles Watch & Try • http://www.classzone.com/cz/books/bio _07/get_chapter_group.htm?cin=2&rg= animated_biology&at=animated_biolog y&var=animated_biology Review Work on cell transport worksheet