Biology 272b: Comparative Animal Physiology
advertisement

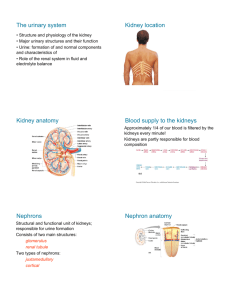
Biology 2672a: Comparative Animal Physiology Kidneys and tubules Kidneys Regulation of salts and water in body Excretion of nitrogenous wastes Production of Urine More concentrated: conserving water/ excreting more salts More dilute: excreting more water Glomerular filtration Bowman’s capsule Pressure maintained by vasoconstriction of efferent vessels Primary Urine: Dilute, no proteins etc. Porous walls + high pressure Water and solutes <10kDa out Water, sugars, salts, amino acids, Urea (sometimes assisted by active transport) Large things (e.g. proteins) remain behind Fig. 27.1b An Amphibian nephron Reabsorption of salts Water reabsorption modulated here Concentrated Urine (permeable distal tubule) -antidiuresis Dilute Urine (impermeable distal tubule) -diuresis Mammalian kidneys, the big picture Cortex Medulla Renal Pelvis Ureter Urine Flow Blood Tubules Tubules Collecting tubes Reabsorption, Cunning osmotic Filtration trickery concentrates waste products Fig. 27.6a The nephron – not quite a oneway journey… Fig. 27.6 Thick ascending loop of Henle Salt Re-absorption Collecting Duct Urine out, concentration of definitive Urine Loop of Henle Thin ascending loop of Henle Bowman’s capsule Ultrafiltration, Production of primary urine Thick segment of descending loop of Henle Re-absorption of sugars, amino acids, water Thin segment of descending loop of Henle Fig. 27.6 Solute reabsorption In thick segment of descending limb of loop of Henle Glucose Amino Acids Water Also some in the thick ascending limb Concentration gradient in kidney Fig. 27.13 The concentration gradient Established by active transport of salts in loop of Henle Leads to a gradient of urea as well e.g. Fig. 27.12 Concentration of urine Occurs in collecting ducts Driven by osmotic gradient across kidney Both urea and salts Can be manipulated by altering permeability of collecting duct to water Fig. 27.14a Changing concentration of definitive urine Fig. 27.14 Concentrating Urine Essential for water conservation on land Allows the selective removal of salts Expected to be particularly highly developed in desert mammals… Reducing excretory water loss Efficient kidneys Get rid of a lot of salt and wastes per unit water Mammals, birds, insects Efficient from gut re-absorption of water Dry Faeces Predictions about desert mammal kidneys Longer loop of Henle = greater concentration gradient Expect desert mammals to have longer loops of Henle and to produce more concentrated urine Cortex Medulla Medulla Renal Pelvis Medullary thickness is a measure of the length of the loops of Henle Medullar + Pelvis = good measure of concentrating power Fig. 27.6a Medullary thickness is positively correlated to maximum urine concentration Fig. 27.8 Medullary thickness is related to body size and habitat Fig. 27.9 Microvasculature of kidneys Lab Rat Sand Rat Fig. 27.10a,c Interspecific variation in urine concentration correlates with habitat in large mammals, too Mesic Xeric Table 28.2 Insects Highly efficient (most successful terrestrial animals) Open circulatory system No high pressure filtering Malpighian tubules Marcello Malpighi (1628-1694) Malpighian tubules Foregut & Midgut Hindgut Malpighian tubules Anywhere from 2 to 200, depending on species A blind-ended tube with walls exactly 1 cell thick Float in haemolymph Open into hindgut Malpighian tubules No high pressure filtration Active transport-driven formation of dilute urine Cells Haemolymph Lumen Fig 27.21 Haemolymph Principal cell Mitochondria packed into evaginations Stellate cell Lumen Haemolymph K+ Channel Proton pump generates electrochemical gradient V-ATPase (H+ pump) Lumen Requires ATP K+ follows via electrogenic transporter Haemolymph Cl- Channel Cl- follows K+ gradient Water follows osmotic gradient into tubule lumen Aquaporin V-ATPase (H+ pump) Lumen Malpighian tubules summary Active transport sets up ion gradients Proton pump; K+, Cl- Na+,K+-ATPase also involved (breaking news!) Water follows Passive transport of nitrogenous wastes, amino acids etc. Active transport of large molecules Alkaloids, proteins etc. Water and solute reabsorption Urine from tubules is dilute and contains lots of things the insect doesn’t want to lose Reabsorption of water and solutes in hindgut/rectum Determines final concentration of the urine Reading for Thursday Thursday: Guest lecture (Dr. Scott MacDougall-Shackleton; birdsong) Reading on OWL Tuesday: Navigation Pp 454-465