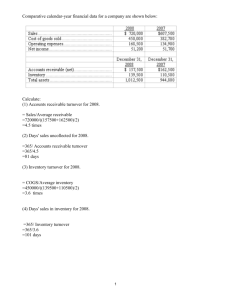
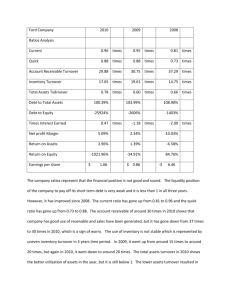
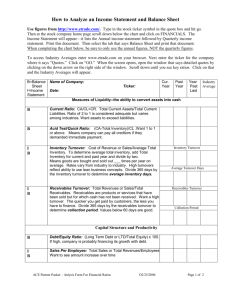
Accounting
Principles
Second Canadian Edition
Weygandt · Kieso · Kimmel · Trenholm
Prepared by:
Carole Bowman, Sheridan College
CHAPTER
19
FINANCIAL STATEMENT
ANALYSIS
BASICS OF
FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS
• Analysing financial statements involves
evaluating three characteristics of a
company:
1. its liquidity
2. its profitability
3. its solvency
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS
• Three types of
comparisons:
– Intracompany basis
– Intercompany basis
– Industry averages
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS
• Three tools:
– Horizontal analysis
– Vertical analysis
– Ratio analysis
HORIZONTAL ANALYSIS
Change
since base
period
Current year amount — Base year amount
———————————————————————
Base year amount
ANY COMPANY INC.
Assumed Net Sales
For the Year Ended December 31 (in millions)
2003
2002
2001
2000
1999
$ 6,562.8
$ 6,295.4
$ 6,190.6
$ 5,786.6
$ 5,181.4
121%
119%
112%
100%
127%
VERTICAL ANALYSIS
• Expresses each item in a financial statement as a
percent of a base amount (total assets or net
sales)
ANY COMPANY, INC.
Condensed Balance Sheets (Partial)
December 31 (in millions)
Assets
Current assets
Capital assets
Other assets
Total assets
2002
Amount
$1,496.5
2,888.8
666.2
$5,051.5
Percent
29.6
57.2
13.2
100.0%
2001
.
Amount
Percent
$1,467.7
30.1
2,733.3
56.9
636.6
13.0
$4,837.6
100.0%
RATIO ANALYSIS
Liquidity Ratios
Measure short-term ability
of the enterprise to pay its
maturing obligations and to
meet unexpected needs for
cash.
Profitability Ratios
Revenues
-
Expenses
Since 1892
=
Net
Income
Measure the income or
operating success of an
enterprise for a given period
of time.
Solvency Ratios
XYZ
Co.
Measure the ability of the
enterprise to survive over a
long period of time.
LIQUIDITY RATIOS
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Current ratio
Acid test ratio
Cash current debt coverage ratio
Receivables turnover
Collection period
Inventory turnover
Days sales in inventory
CURRENT RATIO
• Measures short-term debt-paying ability
Current ratio =
Current assets
Current liabilities
(Discussed in Chapter 4)
ACID TEST RATIO
• Measures immediate short-term debtpaying ability
Acid test ratio =
Cash + temporary investments + net receivables
Current liabilities
(Discussed in Chapter 9)
CASH CURRENT DEBT
COVERAGE RATIO
• Measures short-term debt-paying ability
(cash basis)
Cash current debt coverage ratio =
Cash provided by operating activities
Average current liabilities
(Discussed in Chapter 18)
RECEIVABLES TURNOVER
• Measures liquidity of receivables
Receivables turnover =
Net credit sales
Average net receivables
(Discussed in Chapter 9)
COLLECTION PERIOD
• Measures number of days receivables are
outstanding
Collection period =
365 days
Receivables turnover
(Discussed in Chapter 9)
INVENTORY TURNOVER
• Measures liquidity of inventory
Inventory turnover =
Cost of goods sold
Average inventory
(Discussed in Chapter 5)
DAYS SALES IN INVENTORY
• Measures number of days inventory is on
hand
Days in inventory =
365 days
Inventory turnover
(Discussed in Chapter 5)
PROFITABILITY RATIOS
•
•
•
•
•
•
Profit margin
Gross profit margin
Cash return on sales
Asset turnover
Return on assets
Return on common
shareholders’ equity
•
•
•
•
•
•
Book value per share
Cash flow per share
Earnings per share (EPS)
Price-earnings (PE) ratio
Payout ratio
Dividend yield
PROFIT MARGIN
• Measures net income generated by each
dollar of sales
Profit margin =
Net income
Net sales
(Discussed in Chapter 5)
GROSS PROFIT MARGIN
• Measures margin between selling price
and cost of goods sold generated by each
dollar of sales
Gross profit margin =
Gross profit
Net sales
(Discussed in Chapter 5)
CASH RETURN ON SALES
• Measures net cash flow generated by
each dollar of sales
Cash return on sales =
Net cash provided by operating activities
Net sales
(Discussed in Chapter 18)
ASSET TURNOVER
• Measures how efficiently assets are used
to generate sales
Asset turnover =
Net sales
Average total assets
(Discussed in Chapter 10)
RETURN ON ASSETS
• Measures overall profitability of assets
Return on assets =
Net income
Average total assets
(Discussed in Chapter 10)
RETURN ON COMMON
SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
• Measures profitability of common
shareholders’ investment
Return on common shareholders’ equity =
Net income
Average common shareholders’ equity
(Discussed in Chapter 14)
BOOK VALUE PER SHARE
• Measures the equity (net assets) per
common share
Book value per share =
Common shareholders’ equity
Number of common shares
(Discussed in Chapter 14)
CASH FLOW PER SHARE
• Measures the net cash flow per common
share
Cash flow per share =
Net cash provided by all activities
Number of common shares
(Discussed in Chapter 18)
EARNINGS PER SHARE (EPS)
• Measures net income earned on each
common share
Earnings per share =
Net income
Number of common shares
(Discussed in Chapter 15)
PRICE-EARNINGS (PE) RATIO
• Measures relationship between market
price per share and earnings per share
Price-earnings ratio =
Share price
Earnings per share
(Discussed in Chapter 15)
PAYOUT RATIO
• Measures % of earnings distributed in
the form of cash dividends
Payout ratio =
Cash dividends
Net income
(Discussed in Chapter 15)
DIVIDEND YIELD
• Measures rate of return earned from
dividends
Dividend yield =
Cash dividends per share
Share price
(Discussed in Chapter 15)
SOLVENCY RATIOS
•
•
•
•
Debt to total assets
Interest coverage
Cash interest coverage
Cash total debt coverage
DEBT TO TOTAL ASSETS
• Measures % of total assets provided by
creditors
Debt to total assets =
Total liabilities
Total assets
(Discussed in Chapter 16)
INTEREST COVERAGE
• Measures ability to meet interest
payments as they come due
Interest coverage =
Income before interest expense
and income tax expense (EBIT)
Interest expense
(Discussed in Chapter 16)
CASH INTEREST COVERAGE
• Measures cash available to meet interest
payments as they come due (cash basis)
Cash interest coverage =
Income before interest expense, income tax
expense, and amortization expense (EBITDA)
Interest expense
(Discussed in Chapter 16)
CASH TOTAL DEBT COVERAGE
• Measures long-term debt-paying ability
(cash basis)
Cash total debt coverage ratio =
Net cash provided by operating activities
Average total liabilities
(Discussed in Chapter 18)
LIMITATIONS OF FINANCIAL
ANALYSIS
• Estimates
• Historical cost
• Alternative
accounting
methods
• Atypical data
• Diversification
COPYRIGHT
Copyright © 2002 John Wiley & Sons Canada, Ltd. All rights reserved.
Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted by
CANCOPY (Canadian Reprography Collective) is unlawful. Request for
further information should be addressed to the Permissions Department,
John Wiley & Sons Canada, Ltd. The purchaser may make back-up copies
for his / her own use only and not for distribution or resale. The author and
the publisher assume no responsibility for errors, omissions, or damages,
caused by the use of these programs or from the use of the information
contained herein.