Greek Mythology Ppt
advertisement

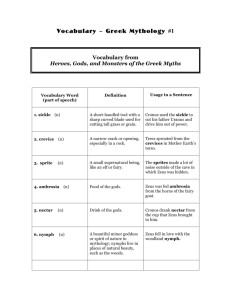
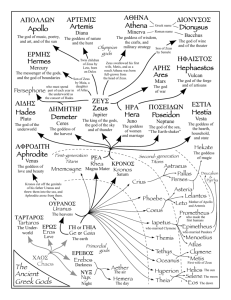
Greek Mythology An Introduction What are the characteristics of a myth? • A traditional or ancient story • Originally told by word-of-mouth • Deals with supernatural beings (Gods and Goddesses) or heroes • Explains a belief or natural happening • Seeks to answer some of life’s fundamental questions: Who are we? Why are we here? Why were myths told? Universal Themes • Myths were told to teach lessons about life. • These are called Universal Themes • Universal Themes are common across many different cultures. (EX: the danger of greed) • Identify the theme by focusing on the main character and identifying the conflicts. How did the time and place influence these stories? Athens, Greece BC •Constant warfare between city-states •Very little understanding of science or the natural world •Constant threat of earthquakes, floods, droughts, disease Greek Temple - built to certain gods - Greeks would go into temples and pray to their gods for help. These beliefs in powerful gods influenced their stories. Epic Tale: a long narrative story or poem dealing with Gods and Heroes. • A long and perilous journey in search of something valuable. • Heroes face trials, tests, and temptations. • Helped along the way by Gods, friends, or animals. • In the end, the hero is glorified. Demi-God: When a God had a child with a mortal, that child often had greater power than normal people. However, demigods could be killed. They were not immortal. Perseus/Heracles Family Tree These are the characters in the movie Clash of the Titans. Heracles is the Greek name for Hercules. He was Perseus’s great-grandson. Why were there so many of them? The Greeks were polytheists • Today, many people believe in one god (monotheism) • Many centuries ago, when the stories of mythology began, people believed in many gods (polytheism) and each god had authorities over certain powers. The Origin of the Gods •In the beginning heaven (Uranus) and earth (Gaia) had children – monsters with 50 heads and 100 arms. •The monsters were so ugly that Uranus threw the monsters into Tartaurus-the pit at the bottom of Hades. •Then Uranus and Gaia had a new group of children called Titans. They are the elder gods called Titans. •One day Uranus’s son Cronus wanted to be king, so he chopped his father into small pieces and threw HIM into the pit of Tartarus. Clash of the Titans vs. the Olympians • Cronus was now the lord of the Universe. • He feared that his children would one day kill him, so as they were born, he swallowed them whole. • His wife, Rhea grew tired of her husband eating her children, so when the youngest son Zeus was born, she fed her husband a rock and hid Zeus on an island. • When Zeus was grown, Rhea poisoned her husband Cronus who vomited up Zeus’s brothers and sisters. • Zeus led his brothers and sisters in a war against the Titans and defeated them, imprisoning them in Tartarus. The Greek God Family Tree How does this relate to Percy Jackson? The Titans The Olympians Hestia did not live on Mt. Olympus. Lived in the underworld. The 12 Olympians were the supreme gods who lived in a palace on top of Mount Olympus. These are the gods mentioned in Percy Jackson. Which god does what? Zeus • Roman name: Jupiter • King of the gods; sky; weather Interesting Information • Wrestled with and almost beaten by Heracles Hera • Wife of Zeus; queen of gods; women; marriage Interesting Information • Hated Heracles; always trying to hurt him Apollo • God of the sun; youth; music; archery; healing; prophecy • Patron of athletes • Men often visited his temples to ask questions about the future Artemis • Twin sister of Apollo • Goddess of the moon; hunting; wild animals; unmarried girls • Carried a silver bow and deadly arrows Hades • King of the underworld where the spirits of the dead belong • Also called Pluto • One of two brothers of Zeus, but not as powerful Poseidon • Ruler of the seas • The other brother of Zeus, but not as powerful as Zeus Aphrodite • Goddess of Love • One of the twelve supreme gods • Her son is Eros, also known as cupid. Athena • Goddess of wisdom; crafts; war • Wore a helmet and breastplate and carried a spear • Born from Zeus’s head Ares • God of war • His throne on Mount Olympus was covered in human skin Interesting Information • Was beaten by Hercules in a battle • Was stuffed in a jar by two giants • Not Zeus’s favorite Hephaestus • God of fire; metalworker • lame Interesting Information • Interceded in a fight between Zeus and Hera and was thrown from Mount Olympus to Earth which made him lame Hermes • Messenger god • God of secrets; tricks • Wore golden, winged sandals which carried him over sea and land • Guided dead souls to the Underworld Demeter • Goddess of agriculture; earth; corn • Sister of Zeus Persephone • Daughter of Demeter • Queen of Hades • Abducted by Hades; forced to spend six months of the year in the underworld How does this apply to us today? Do we see mythology in our lives today? Saturn - The Planet • Roman equivalent to Cronus, Zeus’s Father Jupiter • The Roman equivalent of Zeus NIKE Nike was the goddess of victory Clash of the Titans The epic tale of Perseus, Medusa, and Andromeda Read all about Percy Jackson and the Olympians in the novels by Rick Riordan. Thor • Thor was one of the Germanic gods who was the God of Thunder. The ancient Vikings believed that thunder was the result of Thor’s hammer, Mjilnor. Now that we’ve discussed Greek mythology, look for references to the Gods in movies and literature. Bring to class anything mythology-related for extra credit.