Evolutionary Evidence - Northwest ISD Moodle
advertisement

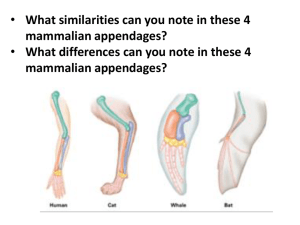
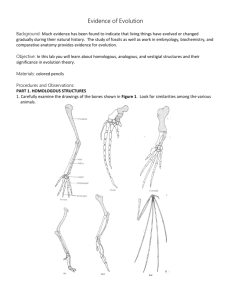
Evolutionary Evidence Part 3: Anatomical Homology Bellringer • In your science journal, write and respond to the following question: –Describe how the forelimbs of vertebrates, illustrate homologous structures. Provide examples. Objectives: • I can define and compare vestigial, homologous, and analogous structures. • I can examine and describe homologous and analogous structures. • I can analyze vestigial structures between species and determine the likelihood of common ancestry. • I can analyze homologous structures between species and determine the likelihood of common ancestry. • I can analyze analogous structures between species and determine the likelihood of common ancestry. What are the different types of evidence used to support the evolutionary theory? There are several places we can see indirect evidence of evolution/evolutionary relationships: fossils, biogeography similarities in anatomy, biochemistry/DNA, and embryology. One form of evidence in the unity of life….. Anatomical evidence What are homologous structures? What evidence do they provide? Science sees structural similarities as evidence that organisms evolved from a common ancestor. Crocodile forelimb Bird wing Whale forelimb Homologous parts are similar in structure, but may be very different in specific function. Structural features with a common evolutionary origin are called homologous structures. What are analogous structures? What evidence do they provide? The body parts of organisms that do not have a common evolutionary origin but are similar in function are called analogous structures. Analogous parts are very different in structure, but perform similar functions. Limbs of vertebrates are examples of homologous structures. See the picture below. The wings of a bird and a fly are examples of analogous structures. What are vestigial structures? • Vestigial structure—a body structure in a present-day organism that no longer serves its original purpose, but was probably useful to an ancestor. What are vestigial structures? • In some cases, a functioning structure in one species is smaller or doesn’t function in a closely related species. • Vestigial structures are features that are reduced forms of functional structures in other organisms. • Evolutionary theory predicts that features of ancestors that no longer have function for that species will become smaller over time until they are lost (disappear). – Ex. Appendix, snake pelvis, human tails What is convergent evolution? • Convergent evolution occurs when unrelated species evolve similar traits. • Example: bird wings and fly wings