Homologous & Analogous Structures: Evolution Explained
advertisement

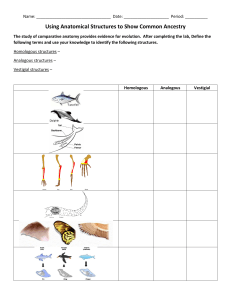
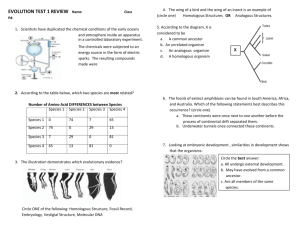
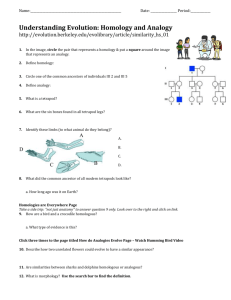
Chapter 19 Homologous and Analogous Structures Need to Know • The difference between homologous and analogous structures and how this relates to evolution. • Convergent evolution Concept 19.3: Evolution is supported by an overwhelming amount of scientific evidence • New discoveries continue to fill the gaps identified by Darwin in The Origin of Species • There are four types of data that document the pattern of evolution – – – – Direct observations Homology The fossil record Biogeography Homology • Evolution is a process of descent with modification. • Homology is similarity resulting from common ancestry. Example of homology Example of homology Video clip • Homologous structures are anatomical resemblances that represent variations on a structural theme present in a common ancestor. Example of homologous structures Humerus Radius Ulna Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Human Cat Whale Bat Example of homologous structures Pharyngeal arches Post-anal tail Chick embryo (LM) Human embryo • Vestigial structures are remnants of features that served important functions in the organism’s ancestors. • Vestigial Structure example • Vestigial Structure example Example of Convergent Evolution The wings are analogous. Example of Convergent Evolution Shark (Chondrichthyes) Dolphin (mammal) The fins and streamlined shape are analogous. Example of Convergent Evolution NORTH AMERICA Sugar glider AUSTRALIA Flying squirrel The side flaps of skin are analogous.