Introduction to plants
advertisement

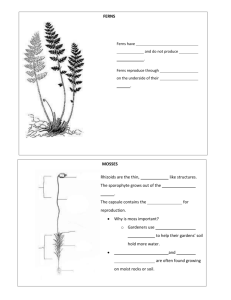
Introduction to plants Chapter 12 Warm up • How many types of plants do you know? Can you name them. Objectives • • • • • Identify four characteristics that all plants share. Distinguish between sporophyte and gametophyte. Define nonvascular plants. Define vascular plants. Recognize mosses an an example of nonvascular plants. • Describe the life cycle of a moss. • Recognize ferns as seedless vascular plants. • Describe the lifecycle of a fern. Introduction • How can you differentiate a plant from an animal? Characteristics of plants • Plants come in different sizes and different shapes. So, what do cactuses, water lilies ferns and all other plants have in common? 1- 2- Cuticle • Most plants live on dry land and need sunlight to live. But why don’t plants dry out? • A cuticle is a waxy layer that coats most of the surfaces of plants that are exposed to air and keeps plants from drying out. 3- cell wall • How do plants stay upright? • Carbohydrates and proteins in the cell wall form a hard material. • Cell wall support and protect the plant cell. 4- Reproduction • Plants have two stages in their lifecycle: 1- the sporophyte stage 2- the gametophyte stage Sporophyte and gametophyte stages Sporophyte stage • In this stage the plant make spores. In a suitable conditions such as damp soil the spore of some plants grow. These new plants are now called gametophyte. Gametophyte stage • During this stage, female gametophytes produce eggs and male gametophyte produce sperms. • Egg and sperm are sex cells. Once they join the fertilized egg grows into a sporophyte that makes spores and the cycle starts again. Plant classification • Although all plants share basic characteristics, they can be classified into four groups. • At first plants can be: 1- vascular plants 2- nonvascular plants Vascular and nonvascular plants Nonvascular plants • Examples: Moses, liverworts and hornworts. • They don’t have specialized tissues to move water and nutrients through the plant. • Depend on diffusion to move materials from one part to another. • They are small in size. Vascular plants They have vascular tissue: specialized tissue for the transport of water and nutrients. • They can be of different sizes and shapes. • Live almost everywhere • Have true roots, stems and leaves. • Are divided into three groups: seedless plants, flowering plants with seeds and nonflowering plants with seeds Seedless plants Seedless plants Vascular Plants Nonvascular Plants Ferns Mosses, liverworts and hornworts Types of Mosses Characteristics of Mosses • No true roots, No vascular tissues (no transport) • Simple stems & leaves • Have rhizoids for anchorage. • Live in Damp terrestrial land Life cycle of mosses Seedless vascular plants: Ferns • roots, feathery leaves & underground stems • have vascular tissues (transport & support) • Spore-producing organ on the underside of leaves (reproduction) • Damp & shady places • Example: ferns, horsetail and club mosse Wrap up • What are the four characteristics between plants? • Describe the lifecycle of a plant. • Classify the different groups of plants. • Differentiate between mosses and ferns. • What is the difference between gametophyte of a moss and that of a fern. Assignments • The skill worksheets • Section review