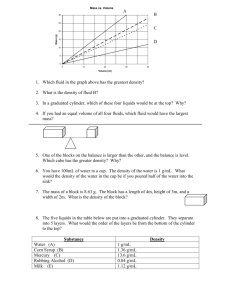
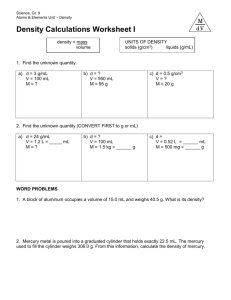
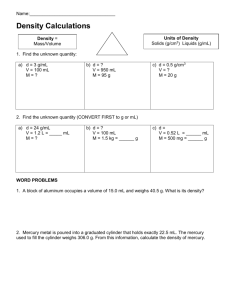
Density
advertisement

Introduction to Density Density is the measurement of the mass of an object per unit volume of that object. d=m/V Density is usually measured in g/mL or g/cm3 for solids or liquids. Volume may be measured in the lab using a graduated cylinder or calculated using: Volume = length x width x height if a box or V = pr2h if a cylinder. Remember 1 mL = 1 cm3 How to measure the density of a solid in the laboratory. • Obtain a clean graduated cylinder. • Fill the graduated cylinder with enough water to cover the object. Record the volume • Carefully place the object into the water filled graduated cylinder. • Record the new water level. • The volume of the object is the Vfinal – Vinitial. Introduction to Density Example: An object has a mass of 50.0 g and occupies a volume of 52.0 mL. What is its density? d = m / V = 50.0 g / 52.0 mL = 0.98 g/mL Example: A cylinderical piece of metal is 2.03 inches high and has a diameter 17.0 mm wide and weighs 31.599 g. Identify the metal. V=pr2h = p (1.70 cm/2)2 * (2.03 in [2.54 cm/1in]) =11.7 cm3 D = m/V = 31.599 g / 11.7 mL = 2.70 g/mL The metal is aluminum! Practice Problems #3 on density Show all of your work on the back. Use scientific notation when necessary and always given your answers with the appropriate significant figures. 15.9 mL 1. Calculate the volume, in microliters, of a • ___________ cylinder that is 32.42 mm long with a diameter of 0.0789 cm. • 1.58 g/mL 2. Calculate the density of a solution if 45.0 mL ___________ of the solution weighs 7.12 x 10-2 kg. • 3 2.59 cm ___________ 3. The Hope diamond weighs 45.52 carats and has a density of 3.51 g/cm3. What is the volume of this diamond? (1 carat = 200 mg) 3; sink 2.0 g/cm • ___________ 4. A plastic material weighing 2.2 lb is shaped into a cylinder 13.5 cm in height and 6.8 cm in diameter. Will this object sink or float in water? • 3.29 g/mL 5. A student fills a 50.0 mL graduated cylinder ___________ with 25.0 mL of water, then places a spherical object weighing 54.367 g into the graduated cylinder. The new volume is 41.5 mL. Calculate the density of the object. Group Study Problem #3 on Density Record your final answer on this sheet and show all of your work on the back. Use scientific notation when necessary and always given your answers with the appropriate significant figures. • ___________ 1. Calculate the volume, in liters, of a box that is 189 mm long by 6.75 cm wide by 7.88 in high. • ___________ 2. Calculate the density of a liquid if 13.476 mL of the liquid has a mass of 1156 cg.` • ___________ 3. What mass of mercury will occupy a volume of 10.0 cm3 if it has a density of 13.6 g/ml? • ___________ 4. What is the density (in g/ml) of a substance that weighs 2.672 lb. and occupies a volume of 7.98 qt. • ___________ 5. The mass of an irregular shaped object was measured to be 76.58 g. A student fills a 50.0 mL graduated cylinder with 20.0 mL of water, then places the object into the graduated cylinder. The new volume is 37.5 mL. Calculate the density of the object.