Metamorphic Rocks
advertisement

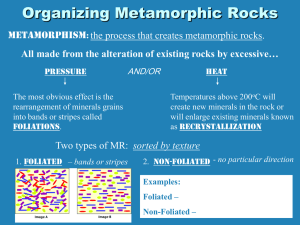
Metamorphic Rocks Metamorphic Rocks "Changed form" rocks Produced from ___________ • Igneous rocks • Sedimentary rocks • Other metamorphic rocks Metamorphism • Takes place where preexisting rock is subjected to ____________ and _________ unlike those in which it formed • Degrees of metamorphism • Exhibited by rock texture and mineralogy • Low-grade (e.g., shale becomes slate) • High-grade (obliteration of original features) Force and Stress Force is push or pull, expressed as amount of acceleration experienced by a mass What happens if same amount of force is applied to two wooden pillars? Stress = force per area 08.01.a How Rocks Respond to Force and Stress Small amount of stress: block remains unchanged 08.01.b Strain Displacement Rotation Consider the structural behavior of rocks at shallow versus deep conditions At shallow depths, most rocks _____ 08.01.c Temperature and pressure increase with depth Rocks ____ in deep conditions Consider how minerals respond at shallow versus deep conditions Shallow: minerals may be _________ Deep: minerals may __________ 08.01.c Different Kinds of Stress ________ pressure ________ stress Fluid pressure counteracts stress 08.02.a Strength of Rock Small stress Increase stress Too much stress = failure Strength of continental crust 08.02.b Observe three kinds of stress and resulting structures ___________ _______ _____ Shallow levels: rocks ________ Deeper levels: rocks ____ 08.02.c Metamorphic agents • _____ • __________ (stress) • From burial (confining pressure) • From differential stress during mountain building • Chemically active ______ • Mainly _____ and other volatiles • Promote recrystallization by enhancing ion migration Processes that Cause Metamorphism Burial Subduction Hot fluids Change in stress Heating Shearing 08.09.a Causes of Metamorphism Pressure Tectonic stress 08.08.a Temperature Response of Rock Fluids Deform Grow larger minerals Cut by Veins Grow new minerals Physical Processes During Metamorphism Deformation of objects Rotation 08.08.b Folding Shearing Fracturing Chemical Processes During Metamorphism Pressure solution Recrystallization Remobilization 08.08.c Types of Metamorphism • _______, or thermal, metamorphism • Occurs near a body of magma • Changes are driven by a rise in temperature • ________ metamorphism • Directed pressures and high temperatures during mountain building • Produces the ________ volume of metamorphic rock Observe how metamorphic conditions vary with depth Heating by magma (contact metamorphism) Regional metamorphism Subduction-zone metamorphism 08.09.b1 Metamorphic Textures • ________ texture • Minerals are in a parallel alignment • Minerals are perpendicular to the compressional force • ___________ texture • Contain equidimensional crystals • Resembles a coarse-grained igneous rock Foliation of Metamorphic Rock Foliation Processes Foliated Rocks • Slate • Fine-grained • Splits easily • Schist • Strongly foliated • "Platy" • Types based on composition (e.g., mica schist) Foliated Texture • Gneiss • Strong segregation of silicate minerals • "Banded" texture Non-Foliated • Marble • Parent rock is limestone • Large, interlocking calcite crystals • Used as a building stone • Variety of colors • Quartzite • Parent rock – quartz sandstone • Quartz grains are fused Why should I care about rocks? Metallic mineral resources • Gold, silver, copper, mercury, lead, etc. • Concentrations of desirable materials are produced by • Igneous processes • Metamorphic processes Why should I care about rocks? • Most important ore deposits are generated from hydrothermal (hot-water) solutions • • • • Hot Contain metal-rich fluids Associated with cooling magma bodies Types of deposits include • _____ deposits in fractures or bedding planes, and • ___________ deposits which are distributed throughout the rock Why should I care about rocks? Nonmetallic mineral resources • Make use of the material’s • Nonmetallic elements • Physical or chemical properties • Two broad groups • Building materials (e.g., limestone, gypsum) • Industrial minerals (e.g., fluorite, corundum, sylvite) You use rocks and minerals from To Birth Death