SCH3U Combustion Reactions
advertisement
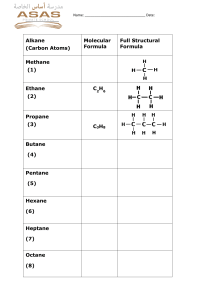
Types of Chemical Reactions (3.2) Combustion Reactions The Fire Triangle • for a combustion reaction to occur, 3 things must be present: 1. Fuel 2. Oxygen 3. Heat • a hydrocarbon is a compound that is composed only of the elements carbon and hydrogen • ex: methane gas CH4(g) • combustion of a hydrocarbon always produces the compounds, carbon dioxide and water. • ex: CH4(g) + 2 O2(g) CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g) Hydrocarbons • A general formula for a hydrocarbon is CxHy • Hydrocarbons are often used as fuels • Examples Name Formula methane CH4(g) propane C3H8(g) butane C4H10(g) acetylene C2H2(g) Combustion Reactions • Combustion of hydrocarbons can be complete or incomplete. • the products depend on the amount of O2 present Complete Combustion • occurs when a sufficient amount of O2 is present • all the C atoms and H atoms react to form CO2 and H2O • In general: hydrocarbon + oxygen carbon dioxide + water CxHy + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(g) Incomplete Combustion • occurs if there is not a sufficient amount of O2 – ie. fuel is not completely converted into carbon dioxide and water • products include H2O as well as any combination of the following: – CO –C – CO2 • examples: 2 CH4(g) + 3 O2(g) 2 CO(g) + 4 H2O(g) 2C3H8(g)+ 7O2(g) 2C(s) + 2CO(g) + 2CO2(g) + 8H2O(g)