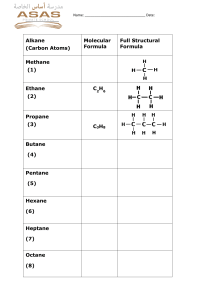
Formation of Air Pollutants A pollutant is a substance that reduces air quality and causes a risk to human health. Although carbon dioxide is leading to global warming it does not carry a direct risk to human health at low concentrations. COMPLETE COMBUSTION: hydrocarbon+oxygen --- carbon dioxide+water INCOMPLETE COMBUSTION: hydrocarbon + oxygen ----- carbon monoxide+water (other by-products include carbon (soot) and unburnt hydrocarbons) Particulates (soot), unburnt hydrocarbons (HC’s) and carbon monoxide All fossil fuels are hydrocarbons and contain the elements hydrogen and ………….. When fossil fuels are burnt …………………… in excess oxygen they only produce water and ………………………. . However, in-car engines there is not sufficient oxygen to allow the fuel to burn efficiently. Hence air pollutants such as carbon (particulates), unburnt hydrocarbons and ……………………… are released into the atmosphere. Particulates make surfaces …………… and can cause lung damage. Unburnt hydrocarbons like benzene can be ……………….. (they cause cancer). Carbon monoxide binds irreversibly to the ……………….. in red blood cells and reduces their ……………. to transport oxygen. In high concentrations carbon monoxide can cause tiredness, flu-like symptoms and even death (always check that a gas fire isn’t producing soot and have a carbon monoxide detector at home). Carbon Carbon dioxide dirty capacity completely carbon monoxide carcinogenic haemoglobin Balancing Equations Petrol , diesel (buses/lorries) and fuel oil (ships) contain the following hydrocarbons: C6H14 (hexane), C7H16 (heptane), C8H18 (octane) Balance these equations for the combustion of petrol: Complete combustion: C6H14 + O2 --------------- CO2 + H2O Incomplete combustion C7H16 + O2 --------------- CO + H2O Complete combustion C8H18 + + O2 --------------- CO2 + H2O Incomplete combustion C6H14 + O2 --------------- CO + H2O