Approach Commonly used Advantages Disadvantage
advertisement

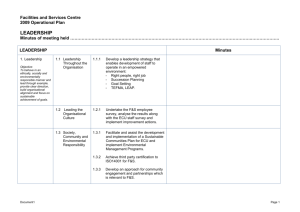
Resistance to Change How People are Affected by Change? Operational Effects The operational effects of the change caused the people impacted to alter the way in which they performed their work. Psychological Effects Any change tends to alter how each person impacted relates to and feels about what he or she is doing. When a change is first announced, everyone affected begins to wonder how the change will impact accustomed ways of working. Questions arise, because any change creates uncertainty first. Often, such uncertainty is related to each individual’s ability to cope with required operational change. Concerns about ability to cope are triggered both by individual personality characteristics, and by the nature of the change itself. Several questions may arise depending upon one’s personality and experiences. Social Effects These effects are alterations that take place in a person’s established relationship with others in his or her work group, and with the management, union officials and the organisation as a whole. The social effects of a change can have critical consequences on the way in which it is regarded, particularly when there is a possibility of alterations in personal status. This is especially the case in any organizational change, whether it is structural or personal. For a change to be introduced and implemented successfully, all three effects must be considered and dealt with systematically. 1 Part Organisational Change How People React to Change? In reactions to change, Individual and group behaviour can vary widely across a broad spectrum of possibilities. The Spectrum of possible behaviors toward Change Acceptance Indifference Passive Resistance Active Resistance Enthusiastic Cooperation Cooperation under pressure from management Acceptance Passive Resignation Indifference Apathy; loss of interest in the job Doing only what is ordered Regressive behavior Non-learning Protests Working to rule Doing as little as possible Slowing down Personal withdrawal (increase time off job and away from work) Committing “errors” Spoilage Deliberate Sabotage Sources of Individual Resistance to Change Sources of Organizational Resistance to Change 1 Part Organisational Change Overcoming Resistance to Change Research has identified six general strategies for overcoming resistance to change (Kotter & Schlesinger, 1979).. It is the manager’s job to match the demands of a change situation with the best approach to overcoming resistance with minimum disruption. Education and communication Participation and Involvement Facilitation and Support Negotiation and Agreement Manipulation and Co-optation Explicit and Implicit Coercion Cont…. 1 Part Organisational Change Methods for Dealing with Resistance to Change Approach Commonly used Advantages Disadvantage Education and Communication When there is lack of information or inaccurate information and analyses Once persuaded people will often help with the implementation of the change Can be very time consuming if lots of people are involved Participation and Involvement Where the initiators do not have all the information they need to design the change, and where other have considerable power to resist. People who participate will be committed to implementing change, and any relevant information they have will be integrated into the change plan. Can be very time consuming if participants design an inappropriate change. Facilitation and Support When people are resisting because of adjustment problems No other approach works as well with adjustment problems Can be very time consuming, expensive and still fail Negotiation and Agreement When someone or some group will clearly lose out in a change and when that group has considerable power to resist Sometimes it’s a relatively easy way to avoid major resistance Can be too expensive in many cases if it alerts other to negotiate for competence. Manipulation and Cooptation Where other tactics will not work or are too expensive It can be relatively quick and inexpensive solution to resistance problems. Can lead to future problems if people feel manipulated. Explicit and implicit coercion Where speed is essential, and the change imitator possess considerable power It is speedy and can overcome any kind of resistance. Can be risky if it leaves people mad at the initiator. 1 Part Organisational Change Change and the Person Change and Stress Change creates anxiety, uncertainty and stress, even for those managing change. Even people who are firmly committed to change may experience stress. Relationship between Performance/Self esteem and Stress Performance/ Self -esteem Cont…. Stress 1 Part Organisational Change Thresholds for Performance/Self-esteem in periods of Stress Performance/ Self -esteem Threshold? Stress Cont…. 1 Part Organisational Change Change and Rebuilding Self-Esteem There are four categories of needs that are required if the individuals involved in the change process are to rebuild their self-esteem during a program of organisational change (Figure).These include: Need for intelligible information. Need to develop new skills, even if only the skill of dealing with new people as colleagues or supervisions. Need for support to help them deal with the problems and encouragement to try out new systems. Technical support to solve problem is often needed. Access to people who can help is useful. Control over the rate of personal learning should be possible. Cont…. Need to be treated with empathy. 1 Part Organisational Change Rebuilding Self-Esteem Empathy Support Skills Intelligible information Self -esteem and Self -knowledge Action 1 Part Organisational Change Change and the Manager Organisation and their managers must recognize the change, in itself, is not necessarily a problem.The problem often lies in an ability to effectively manage change: not only can the adopted process be wrong, but also the conceptual framework may lack vision and understanding. Change is now a way of life; organisation and more importantly their managers must recognize the need to adopt strategic approaches when facing transformation situation (Burner, 1996). • • • • • • Competency and change Change and the Human Resource Effective Implementation of Change Change: Implication for Managerial Competence Required Attributes, Skills and Competencies Development of Managerial Abilities