HERE - Streaks Science Weekly
advertisement
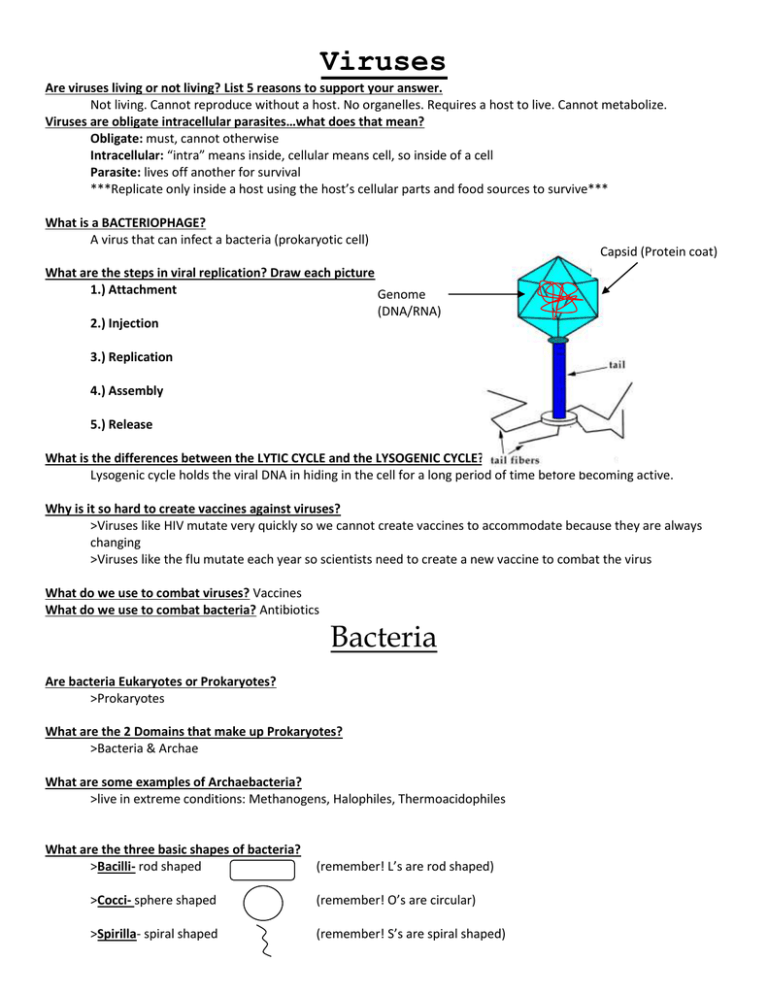
Viruses Are viruses living or not living? List 5 reasons to support your answer. Not living. Cannot reproduce without a host. No organelles. Requires a host to live. Cannot metabolize. Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites…what does that mean? Obligate: must, cannot otherwise Intracellular: “intra” means inside, cellular means cell, so inside of a cell Parasite: lives off another for survival ***Replicate only inside a host using the host’s cellular parts and food sources to survive*** What is a BACTERIOPHAGE? A virus that can infect a bacteria (prokaryotic cell) Capsid (Protein coat) What are the steps in viral replication? Draw each picture 1.) Attachment Genome (DNA/RNA) 2.) Injection 3.) Replication 4.) Assembly 5.) Release What is the differences between the LYTIC CYCLE and the LYSOGENIC CYCLE? Lysogenic cycle holds the viral DNA in hiding in the cell for a long period of time before becoming active. Why is it so hard to create vaccines against viruses? >Viruses like HIV mutate very quickly so we cannot create vaccines to accommodate because they are always changing >Viruses like the flu mutate each year so scientists need to create a new vaccine to combat the virus What do we use to combat viruses? Vaccines What do we use to combat bacteria? Antibiotics Bacteria Are bacteria Eukaryotes or Prokaryotes? >Prokaryotes What are the 2 Domains that make up Prokaryotes? >Bacteria & Archae What are some examples of Archaebacteria? >live in extreme conditions: Methanogens, Halophiles, Thermoacidophiles What are the three basic shapes of bacteria? >Bacilli- rod shaped (remember! L’s are rod shaped) >Cocci- sphere shaped (remember! O’s are circular) >Spirilla- spiral shaped (remember! S’s are spiral shaped) What are the main groups of bacteria that we talked about? >Diplo- 2 bacteria together >Tetra- 4 bacteria together >Strepto- 5 or more bacteria in a chain (remember strep-throat, and you wear chain necklaces on your throat) >Staphylo- 5 or more bacteria in a cluster Name these groups of bacteria: 1.) 4.) Streptococci Spirilla 2.) 5.) Tetrabacilli Staphylobacilli 3.) Diplococci MICROSCOPE Can you name all of the parts of the Compound Light Microscope? Practice by using the diagram below! If you can name parts A through H, you have mastered the microscope! Also, check out the microscope quiz HERE, for more practice. What do you need to do with the microscope at the end of the lab? 1.) Switch to the LOWEST objective 2.) Move the stage to the lowest position using the coarse adjustment knob 3.) Remove your slide from the microscope and properly remove the specimen and clean the slide 4.) Turn off the microscope, the camera, and the TV 5.) Put the “jacket” back on your microscope What knob do you NEVER use on medium and high power? The course adjustment knob (the big one) What does the condenser do? It changes the amount of light allowed through the specimen What magnification does the eyepiece have? 10X What is the TOTAL magnification for low, medium, and high powers? A Low: 10 x 4= 40x Medium: 10 x 10= 100x High: 10 x 40= 400x Parts of the microscope A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. B Eyepiece Objective lenses Stage Clips Stage Condenser Light source Fine focus Course focus C D H E G F How do you change mm to microns?? Multiply by 1000 HONORS: What is the field of view for each magnification? Low: 5mm Med: 2mm High: .5mm Taxonomy Description, identification, naming, and the classification of organisms are used by scientists to organize the millions of creatures that they have discovered. Aristotle created the first taxa system based on where the organism lived (air, land, water). This was rejected because it was not specific enough. Some organisms live in both land and water for example. We rely on an updated Linnaeaus Classification System using the 8 levels of classification: Domain Kingdom Phyla Class Order Family Genus Species Dear King Phillip Came Over For Grape Soda Binomial NomenclatureWhat two levels of classification make up a scientific name? Genus and Species Write the scientific name for humans correctlyHomo sapiens (hand written) What would be different if we were typing the scientific name? Text would be italicized: Homo sapiens Most General Most Specific Cells Which process has the organization of living things in the correct order from most basic to most complex? A.) Biological Molecule ->Atom -> Cell -> Organelle -> Tissue -> Organ B.) Atom -> Biological Molecule -> Cell -> Organelle -> Tissue -> Organ C.) Atom -> Biological Molecule -> Organelle -> Cell -> Tissue -> Organ D.) Organelle -> Biological Molecule -> Organ -> Atom-> Tissue -> Cell Answer: C Who discovered the first cells using a microscope? Robert Hooke, he viewed slices of cork Who viewed the first living organisms under a microscope? Anton van Leeuwenhoek (L for living) What did Schleidern, Schwann and Virchow all discovered different information about cells which led to the formation of the CELL theory! Put the correct phrase in each statement to complete the Cell Theory: A.) come only from B.) existing cells C.) one or more cells D.) basic units 1.) All living things are made of _______C________ 2.) Cells are the __________D____________ of structure and function in an organism 3.) Cells ____________A______________ the reproduction of ____________B_______________ Answer: 1.)C 2.)D 3.)A B PROKARYOTES EUKARYOTES Literally Means: “Before Nucleus” No membrane-bound organelles Bacteria- Eubacteria & Archeabacteria Literally Means: “True Nucleus” Have membrane-bound organelles Plants, Animals, Fungi, Protists Distinguish between the words… Autotrophic, Heterotrophic, Saprophytic, and Chemosynthetic Autotrophic: make own food Heterotrophic: eat others for food Saprophytic: excrete enzymes into soil in order to break down and ingest food Chemosynthetic: uses minerals and CO2 to make organic compounds for food Are Bacteria autotrophic or heterotrophic? Both CATEGORY Viral EXAMPLE DISEASES HIV, Influenza, Hepetitis Treatement/Prevention Vaccine Bacterial Staph, Strepthroat, Lyme disease, tooth decay Antibiotic Protists Girardia, sleeping sickness, Maleria, Amebic Dysentary Fungus Athletes foot, ringworm, Dutch Elm Drink clean water, wear long sleeves, mosquito nets Antifungal Label the following parts: Anterior- Head Posterior- Tail Dorsal - Back Ventral- Belly/underside Practice identifying symmetry in these aquatic animals A.) Asymmetry B.) Bilateral Symmetry C.) Radial Symmetry Which systems of the body deal with: Metabolism: Homeostasis: A B C CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE compared to SYSTEMS OF THE BODY A. Response- Which system of the body does this pertain to? Nervous system What are some examples of this system? List them from simplest to complex Nerve net, ganglia, nerve cord, brain B. ORGANIZATION AND CELLS – For each Kingdom, which organisms are prokaryotic and which are eukaryotic celled organisms? KINGDOM HETERO/AUTOTROPHIC UNICELLULAR/MULTICELLULAR EXAMPLES Archeabacteria PRO or EUKARYOTIC CELLS Prokaryotic Both Unicellular Eubacteria Prokaryotic Both Unicellular Protists Eukaryotic Both Unicellular or multicellular Fungus Eukaryotic Heterotrophic Multicellular Plants Eukaryotic Autotrophic Multicellular Animals Eukaryotic Heterotrophic Multicellular Methanogens Halophiles Streptococcus Staphylo Ameba Euglena Molds Mushrooms Trees Flowers Birds Dogs Humans C. METABOLISM - all chemical reactions in body Digestive system: What are the 2 types of digestive systems and give an example of organisms that use this. 1. gastrovacular cavity - one opening ex) sponge, jellyfish 2. digestive tract – two openings ex) earthworm, humans Respiratory System: What are the 3 types of respiratory systems and give an example of organisms that use this. 1. lungs ex)humans 2. gills ex) fish, clam 3. diffusion ex) earthworm D. HOMEOSTASIS - steady state Circulatory System – When blood always stays in the vessels it is called a CLOSED circulatory system. What type do we have as humans? CLOSED E. REPRODUCTION: List the similarities and differences between Sexual Asexual 1 Parent 2 Parents Unique offspring Produce Offspring Same Offspring