Esters Lab 2014
advertisement

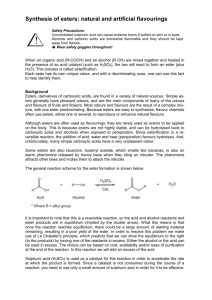
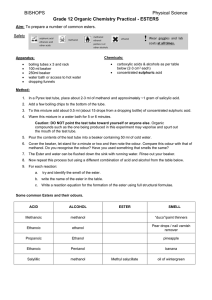
SCH 4UI – Ester Synthesis Lab - This Lab Stinks! When a carboxylic acid (R – COOH) and an alcohol (R – OH) are mixed together and heated in the presence of an acid catalyst (such as concentrated H2SO4), the two will react to form an ester (plus H2O) in a condensation reaction. This process is called esterification. Materials: Lab Equipment: Goggles & Apron Test tube rack 9 test tubes Large beaker (600 mL or larger hot plate Eye droppers Test tube holders (3) Gloves Alcohols: Methanol Ethanol 1-propanol 1-butanol 1-pentanol(isoamyl alcohol) 1-octanol Other Chemicals: 5% sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) solution Concentrated sulfuric acid (12 M H2SO4) Carboxylic acids: Methanoic Acid (formic acid) Ethanoic Acid (glacial acetic acid Butanoic acid Salicylic acid Coffee grounds Procedure: Research Section: 1) 2) 3) In the observation chart, the scent of a specific ester is given. The name of the ester is listed with scent. Draw the structure of each ester. Determine the alcohol and carboxylic acid required to synthesize each ester. When synthesizing an ester follow this procedure: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) Make sure that all group members wear goggles at all times. Get 6-9 test tubes and label them: “1”, “2”, ‘3” etc. Heat a beaker of water to temperature of 50 - 60°C on a hot plate. Select at least 3 of the given esters plus 2 or 3 other researched esters to synthesize. Add 10 drops of alcohol into a numbered test-tube. Add 10 drops of carboxylic acid to the test tube. Carefully add 10 drops of concentrated sulfuric acid (12 mol/L H2SO4) to the mixture in the test tube. Mix the contents of each test tube using the knocking method. Place the test tube in a beaker of hot water for at least three minutes. The heat will increase the rate of reaction between the alcohol and carboxylic acid. 10) Detect odours with caution. Breathing some of these vapours can cause dizziness, headache and drowsiness. Waft the odours. Do not breathe deeply! 11) You may wish to add a few drops of 5% sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) solution to a mixture if the smell is not obvious. This will react with an unreacted acid and allow the scent of the ester to be more obvious. (Caution – this reaction will be accompanied by fizzing and popping). This works particularly well with butanoic acid. 12) Empty out your test tubes into the waste container and place the test tubes inside the soaking bin. Safety Precautions: concentrated sulfuric acid is a strong oxidizing agent. It will start a fire if mixed incorrectly with any of the alcohol or other acids used in this experiment. Use exactly as directed. Concentrated sulfuric acid is also strongly corrosive (always wear goggles). All of the liquid acids are corrosive – gloves are recommended. Detect odours with caution. Breathing some of these vapours can cause dizziness, headache and drowsiness. Waft the odours. Do not breathe deeply! All alcohols and organic acids used in this experiment are flammable. Keep these materials away from flames and other heat sources. (Formic Acid is particularly flammable – use with the utmost caution) Research: 1) 2) 3) Research up to 4 other esters that you could synthesize given the chemicals in the materials list. Place the information into your chart (expected odour, name, structure, alcohol required & carboxylic acid required) and have it ready to be checked by the teacher. Synthesize these esters and state the actual odour you created. Analysis and Discussion: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) Why do you think that that you were instructed to use an electric hot plate instead of a Bunsen burner? Why do you think that you were instructed to waft the odours instead of sniffing them directly? Complete the observation chart to indicate the IUPAC name of each ester formed and the odour associated with it. Use structural diagrams to write each of the esterification reactions. What role does the H2SO4 play? How does it affect the esterification reaction? What evidence is there that the esters synthesized in this investigation are soluble or insoluble in aqueous solution? Explain this in terms of the molecular structure of esters. Evaluate the effectiveness of each reaction – were the odours recognizable? Was the use of sodium bicarbonate effective? Aspirin is acetylsalicylic acid (A.S.A.) – a type of ester. Since acetyl is known as ethyl in IUPAC nomenclature, suggest how this ester is formed by writing a reaction using structural diagrams. (A picture of salicylic acid is drawn below) Name: ______________________________ Partners: ______________________________________________________ Date: ______________________ Observation Chart Odour *wintergreen pears (Pear Drops) or bananas name methyl salicylate draw the structure alcohol methanol carboxylic acid salicylic acid pentyl ethanoate nail polish remover ethyl ethanoate apples methyl butanoate pineapple ethyl butanoate Aspirin (ASA) (don’t synthesize – just list reactants and structure) Acetylsalicylic acid (ethyl salicylate) * use 15 drops of methanol and 1 g of salicylic acid for this test. ** see the esters chart for other possible esters. actual odour