Bacteria Notes
advertisement

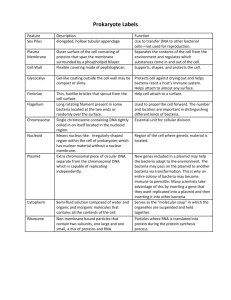
Bacteria Notes Basic Definition karyo Organisms • Bacteria: Pro Prokaryotic – Pro: Primitive or “prior to” – Karyon: Nucleus or “kernel” – Single-celled organisms without a nucleus – Has circular DNA – Often has “plasmid” DNA that helps codes for genes to increase fitness (ex. Antibiotic resistance) – Bacteria can be measured in micrometers • 0.000001m or 10-6 What are the two groups of bacteria? 1. Bacteria Cell walls with peptidoglycan Made up of types of peptide and sugar bonds 2. Archaebacteria • • Cell walls lack peptidoglycan Adapted to extreme environments: Extremely hot and cold, salty, without oxygen, etc. What are the basic shapes of bacteria? – Rod-shaped (Bacilli) Bacillus anthracis (Anthrax), Yersinia pestis (Bubonic plague) – Comma-shaped (Vibrios) Vibrio cholerae – Spherical (Cocci) Streptococcus, Staphylococcus – Spiral (Spirilla) Treponema pallidum (Syphillis) Bacterial Staining • Gram-positive: Retains the crystals of violet dye in the peptidoglycan of the cell wall. • Only has an inner layer of plasma membrane • Infection by this type can be treated by antibiotics such as penicillin, which attacks the peptidoglycan of the cell wall. Bacterial Staining • Gram-negative: Will not pick up much the violet dye because the cell wall is covered by an additional outer membrane, and instead appears pink. • Infection by this type must be treated by a broadspectrum antibiotic such as ciprofloxacin that enters bacteria and disrupts protein synthesis Outer membrane Peptidoglycan Inner membrane What is a plasmid? • Plasmids are circles of DNA that can replicate separately from the main bacterial DNA. • Plasmids may carry genes that allow bacteria to survive exposure to antibiotics. Bacterial Growth and Reproduction • Binary Fission: (video) -Asexual division -DNA replicates and cytoplasm divides -Creates two genetically identical cells from one parent cell • Conjugation: (video) -Not true sexual reproduction -Sex pilus extends between bacteria -Plasmid DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another to introduce genetic diversity • Spore Formation: -Occurs when growth conditions are unfavorable -An endospore is a “spore” with a thick internal wall of membrane that encloses and protects its DNA