The Circulatory System - McGraw Hill Higher Education

PowerPoint
® to accompany
Medical Assisting
Chapter 28
Second Edition
Ramutkowski Booth Pugh Thompson Whicker
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
1
The Circulatory System
Objectives
28-1 Spell, define, and correctly use the Key Terms in this chapter.
28-2 Describe the structure of the heart and the function of each part.
28-3 Trace the flow of blood through the heart.
29-4 List the most common heart sounds and what events produce them.
28-5 Explain how heart rate is controlled.
2
The Circulatory System
Objectives (cont.)
28-6 List the different types of blood vessels and describe the functions of each.
28-7 Define blood pressure and tell how it is controlled.
28-8 Trace the flow of blood through the pulmonary and systemic circulation.
28-9 List the major arteries and veins of the body and describe their locations.
28-10 List and describe the components of blood.
3
The Circulatory System
Objectives (cont.)
28-11 Give the functions of red blood cells, the different types of white blood cells, and platelets.
28-12 List the substances normally found in plasma.
28-13 Explain how bleeding is controlled.
28-14 Explain the differences among type A blood, type B blood, type AB blood and type O blood.
28-15 Explain the difference between Rh positive blood and Rh negative blood.
4
The Circulatory System
Objectives (cont.)
28-16 Explain the importance of blood typing and tell which blood types are compatible.
28-17 List the organs of the lymphatic system and give their locations and functions.
28-18 Define lymph and tell how it is circulated in the body.
28-19 Describe signs, symptoms, causes, and treatments of various diseases and disorders of the heart, blood vessels, blood and the lymphatic system.
5
Introduction
Circulation is the process of sending blood:
To the lungs to pick up oxygen
To the digestive system to pick up nutrients
For delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all organ systems of the body
The circulatory system consists of the heart and blood vessels.
This system also circulates waste products to certain organ systems so these wastes can be removed from the blood.
The lymphatic system is included because it also circulates fluids throughout the body. 6
Structure of the Heart
A cone-shaped organ about the size of a loose fist
Within the mediastinum and extends from the level of the second rib to about the level of the sixth rib
Slightly left of the midline of the body.
Heart is bordered:
laterally by the lungs
posteriorly by the vertebral column
anteriorly by the sternum
Inferiorly the heart rests on the diaphragm.
7
Coverings and Walls of the Heart
Heart Coverings
Pericardium - covers the heart and large blood vessels
Visceral pericardium
- innermost layer
Parietal pericardium
- lays on top of the visceral pericardium
Heart Walls:
Epicardium - the outermost layer
Myocardium - the middle layer
Endocardium - the innermost layer
8
Coverings and Walls
of the Heart
9
Heart Chambers
Heart contains four hollow chambers
Two atria – left and right
Two ventricles
– left and right
10
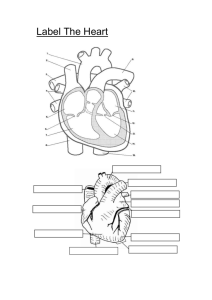
The Heart Labeled
11
The Heart – No Labels
A.
D.
E.
C.
B.
F.
G.
H.
I.
J.
K.
L.
M.
N.
O.
P.
Q.
R.
S.
Identify the Parts of the Heart
Click Next for Answers
12
The Heart – Answers
A.
Aortic arch
B.
Right pulmonary artery
C.
Superior vena cava
D.
Ascending aorta
E.
Right pulmonary veins
F.
Pulmonary semilunar valve
G.
Right Atrium
H.
Right ventricle
I.
Tricuspid valve
J.
Inferior vena cava
K.
Descending aorta
L.
Left pulmonary artery
M.
Pulmonary trunk
N.
Left pulmonary veins
O.
Left atrium
P.
Aortic semilunar valve
Q.
Mitral (bicuspid) valve
R.
Septum
S.
Left ventricle
13
Heart Valves
Tricuspid valve - prevents blood from flowing back into the right atrium when the right ventricle contracts
Bicuspid valve - prevents blood from flowing back into the left atrium when the left ventricle contracts
Pulmonary valve - prevents blood from flowing back into the right ventricle
Aortic valve - prevents blood from flowing back into the left ventricle
14
Path of Blood Through the
Heart
Oxygenated blood
Deoxygenated
Oxygenated out to body blood in blood in lungs
Deoxygenated blood in from body
Atria Contract
Deoxygenated blood out to lungs
Ventricles Contract
15
Heart Sounds
One cardiac cycle you can hear two heart sounds (lubb and dupp) when valves in the heart snap shut
Lubb – 1 st sound - when the ventricles contract and the tricuspid and bicuspid valves snap shut
Dupp – 2 nd sound - when the atria contract and the pulmonary and aortic valves snap shut.
16
Apply Your Knowledge
Your 8-year-old patient has asked you why his heart makes two noises. What would you tell him?
17
Apply Your Knowledge
-
Answer
Your 8-year-old patient has asked you why his heart makes two noises. What would you tell him?
Lubb – 1 st sound - when the ventricles contract and the tricuspid and bicuspid valves snap shut
Dupp – 2 nd sound - when the atria contract and the pulmonary and aortic valves snap shut
18
Heart Rate
Cardiac conduction system consists of a group of structures that send electrical impulses through the heart.
When cardiac muscle receives an electrical impulse, it will contract.
19
Blood Vessels
Arteries and Arterioles
strongest of the blood vessels
carry blood away from the heart easily and are under high pressure
have thick walls
Veins and Venules
no pressure in veins - does not move very easily
valves in veins prevent blood from flowing backwards
20
Blood Vessels - Capillaries
Branches of arterioles - the smallest type of blood vessel
Connect arterioles to venules - only about one cell layer thick
Oxygen and nutrients can pass out of a capillary into a body cell
Carbon dioxide and other waste products can pass out of a body cell into a capillary
21
Blood Pressure
Force blood exerts on the inner walls of blood vessels - highest in arteries and lowest in veins
Systolic pressure - ventricles contract, blood pressure is greatest in the arteries
Diastolic pressure -the ventricles relax, blood pressure in arteries is at its lowest
Reported as the systolic number over the diastolic number.
22
Control of Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is controlled to a large extent by the amount of blood pumped out of the heart
Starling's law of the heart blood enters the left ventricle, the wall of the ventricle is stretched. The more the wall is stretched, the harder it will contract, and the more blood it will pump out.
Baroreceptors also help regulate blood pressure
Low BP causes the cardiac center of the brain to increase heart rate
23
Paths of Circulation
Pulmonary Circuit
right atrium --> right ventricle --> pulmonary trunk --> pulmonary arteries --> lungs --> pulmonary veins --> heart (left atrium)
Systemic Circuit
left atrium --> left ventricle --> aorta --> arteries --> arterioles --> capillaries --> venules --> veins --> vena cava --> heart (right atrium)
24
Major Blood
Vessels
Arterial System
carry oxygen rich blood away from the heart
pulmonary arteries carry oxygen poor blood
paired - left and right artery of the same name
25
Major Blood Vessels
(cont.)
Venous System
Vessels that carry blood toward the heart
Pulmonary veins – carry oxygen rich blood
Large veins often have the same names as the arteries they run next to
Hepatic portal system
collection of veins carrying blood to the liver
26
Major Blood
Vessels
(cont.)
27
Apply Your Knowledge
Your patient wants to know what the bottom number of his blood pressure means. What would you say?
28
Apply Your Knowledge
-
Answer
Your patient wants to know what the bottom number of his blood pressure means. What would you say?
Diastolic pressure is when the ventricles of the heart relax, blood pressure in arteries is at its lowest.
29
Components of Blood
A type of connective tissue
Red blood cells
(erythrocytes)
White blood cells
(leukocytes
Platelets-contains cell fragments
Plasma - fluid part of blood (55% of blood)
Average-sized adult contains - 5 liters of blood
Hematocrit (45%) percentage of blood cells in a sample of blood
30
Red Blood Cells
Transport oxygen throughout the body
Are biconcave-shaped cells that are small enough to pass through capillaries
Hemoglobin is a pigment found on RBCs
Oxyhemoglobin carries oxygen and is bright red in color
Deoxyhemoglobin does not carry oxygen and is a darker red color
31
Red Blood Cells
(cont.)
32
White Blood Cells
Granulocytes
Neutrophils – (55%) destroying bacteria, viruses, and toxins in the blood stream
Eosinophils – (3%) getting rid of parasitic infections such as worm infections
Basophils –(1%) control inflammation and allergic reactions
Agranulocytes
Monocytes – (8%) destroying bacteria, viruses, and toxins in blood
Lymphocytes – (33%) immunity for the body
33
Blood Platelets
Fragments of cells that are found in the blood stream
Thrombocytes are important in the clotting of blood
130,000 to 360,000 platelets per cubic millimeter of blood
34
Controlling Bleeding
Hemostasis - the stoppage of bleeding
Three processes of hemostasis
Blood vessel spasm
Platelet plug formation
Blood coagulation
35
Platelet
Plug
Formation
36
Blood Plasma
Blood plasma is the liquid portion of blood.
Consists of:
Mostly water
Mixture of proteins
Albumins
Globulins
Fibrinogen
Nutrients
Amino acids
Glucose
Nucleotides
Lipids
Gases
Electrolytes
Waste products
37
Apply Your Knowledge
Does the pulmonary arteries carry high levels oxygen or low levels of oxygen in the blood?
38
Apply Your Knowledge
-
Answer
Does pulmonary arteries carry high levels oxygen or low levels of oxygen in the blood?
Pulmonary arteries carry oxygen poor blood
39
ABO Blood Group
Blood Type Antigen
Present
A A
Antibody
Present
B
Blood that can be received
A & 0
B
AB
0
B
AB
None
A
None
A & B
B & O
A, B, AB, & O
O
40
RH Blood Group
Rh positive person has red blood cells that contain the Rh antigen
Rh negative red blood cells do not contain the Rh antigen
Rh positive blood is given to Rh negative person and antibodies form
Second time this occurs antibodies will bind to the donor cells and agglutination will occur
41
Apply Your Knowledge
What type(s) of blood could a patient who has type B blood receive without complications?
42
Apply Your Knowledge
-
Answer
What type(s) of blood could a patient who has type B blood receive without complications?
Type B & O
43
The Lymphatic System
A network of connecting vessels that collect fluids between cells
Lymphatic vessels then return this fluid
(called lymph) to the blood stream
Picks up lipids from the digestive organs and transports them to the blood stream
Defend our bodies against diseasecausing agents called pathogens
44
The Lymphatic System
Lymph Nodes
digest unwanted pathogens in the lymph
start an immune response against the pathogen
Thymus
production of T lymphocytes & hormone called thymosin
Spleen
largest lymphatic organ
spleen also removes worn out red blood cells from the circulation
45
Lymph Fluid
Tissue fluid that has entered a lymphatic capillary
Pushed through the vessels by the squeezing action of skeletal muscles
Contain valves that prevent the backflow of lymph
Lymph Node
46
Diseases and Disorders of the Circulatory System
Anemia a condition in which a person does not have enough red blood cells or hemoglobin in blood to carry an adequate amount of oxygen to body cells
Aneurysm defined as a ballooning of an artery wall that results when the wall of the blood vessel becomes weak
47
Diseases and Disorders of the Circulatory System
(cont.)
Carditis - an inflammation of the heart
most commonly referred to as endocarditis, myocarditis, or pericarditis depending on the layer of the heart affected
Congestive heart failure - a slowly developing condition in which the heart weakens over time.
48
Diseases and Disorders of the Circulatory System
(cont.)
Coronary artery disease – (atherosclerosis) characterized by narrowing of coronary arteries
Heart arrhythmias – abnormal heart rhythms in which the heart beats too quickly
(tachycardia) or too slowly (bradycardia)
Heart attack (myocardial infarction) – damage to cardiac muscle that is due to a lack of blood supply
49
Diseases and Disorders of the Circulatory System
(cont.)
Hypertension (high blood pressure)
defined as consistent resting blood pressure
140/90 mm Hg or higher
Leukemia
a condition in which the bone marrow produces a large number of white blood cells that are not normal
Murmurs
simply defined as abnormal heart sounds
50
Diseases and Disorders of the Circulatory System
(cont.)
Sickle cell anemia
– a condition in which abnormal hemoglobin causes red blood cells to change to a sickle
(crescent) shape
Thrombophlebitis
– a condition in which a blood clot and inflammation develop in a vein
Varicose veins
– dilated veins and are usually seen in the legs
51
Apply Your Knowledge
The doctor has told your patient she has anemia. How would you explain this to the her?
52
Apply Your Knowledge
-
Answer
The doctor has told your patient she has anemia. How would you explain this to the her?
Anemia is a condition in which a person does not have enough red blood cells or hemoglobin in blood to carry an adequate amount of oxygen to body cells.
53
Summary
Medical Assistant
Knowledge of the circulatory system will assist you in providing care for the patient with diseases and disorders of the circulatory system.
You must have knowledge of this system especially when assisting the physician during his examination of the circulatory system.
54
End of Chapter
55