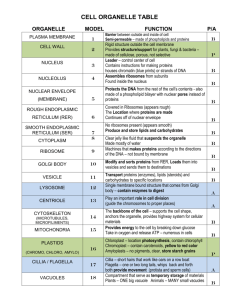
Cell Organelle Structure and Function Chart
advertisement
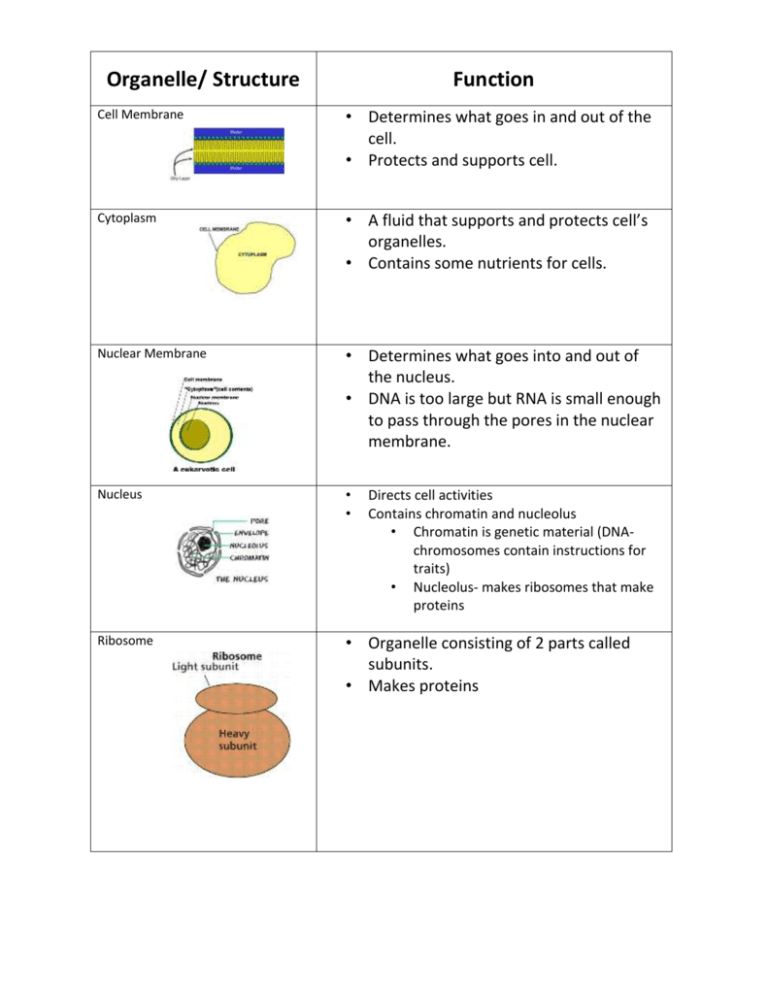
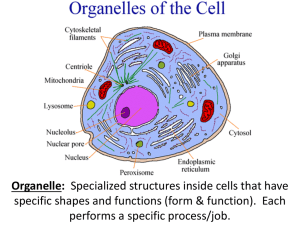
Organelle/ Structure Function Cell Membrane • Determines what goes in and out of the cell. • Protects and supports cell. Cytoplasm • A fluid that supports and protects cell’s organelles. • Contains some nutrients for cells. Nuclear Membrane • Determines what goes into and out of the nucleus. • DNA is too large but RNA is small enough to pass through the pores in the nuclear membrane. Nucleus • • Ribosome • Organelle consisting of 2 parts called subunits. • Makes proteins Directs cell activities Contains chromatin and nucleolus • Chromatin is genetic material (DNAchromosomes contain instructions for traits) • Nucleolus- makes ribosomes that make proteins Vacuole • Storage, digestion, and waste removal • In plants, vacuoles help maintain shape. Lysosome • Aids in removing excess or worn out organelles, food particles, bacteria, and viruses • Contain enzymes that break down substances • Garbage disposer Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) • Transports proteins and breaks down drugs in the cell • Does not contain ribosomes. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) • Transports proteins and breaks down drugs in the cell. • Covered in ribosomes which make proteins to be transferred. Mitochondria • Powerhouse of the cell • Produces energy from sugar through chemical reactions (cellular respiration) • Double membrane Golgi Body • Processes and packages proteins and lipids • Moves materials within and out of the cell in small sacs called vesicles • AKA golgi complex, golgi apparatus Cell Wall • Found only in plant cells and bacteria cells • Supports and protects cells Chloroplast Summary: • Found in plant cells • Contains green chlorophyll Primary function is for use during photosynthesis converting sunlight to glucose (sugar) for the plant to use for energy.