Presentation - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
advertisement

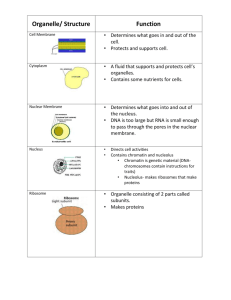
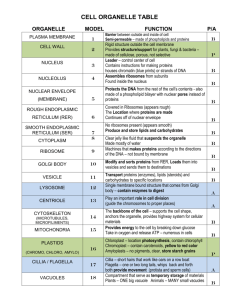
Biology 107 Cell II September 23, 2005 Cell II Student Objectives: As a result of this lecture and the assigned reading, you should understand the following: 1. Ribosomes are non-membranous organelles that are the sites of synthesis of proteins in the cell. Ribosomes consist of two subunits, the large and the small, comprised of proteins and specific RNAs, called rRNAs (ribosomal RNAs). The mRNA and the amino acids with their carriers (tRNAs or transfer RNAs) bind to ribosomes, and polypeptide chains are formed by dehydration synthesis. 2. Ribosomes may be attached to membrane or "free" (nonmembrane attached) in the cytoplasm. Cell II 3. Endoplasmic reticulum is a membranous organelle that may be subdivided into two different types with different functions. a. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is so named because it is studded with ribosomes. RER functions to make proteins for secretion by the cell or for incorporation into cellular membranes. The RER also begins the compartmentalization and processing of some proteins so they can be shipped out of the cells or distributed to specific subcompartments. b. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is a series of interconnected membrane tubules that lack ribosomes. SER and RER are continuous. One of the functions of ER lacking ribosomes is the synthesis of lipids, including phospholipids, fats and steroids. SER also contains enzymes that are involved in detoxification, and in some cells SER is involved in calcium storage and release. Cell II 4. The Golgi apparatus is a stack of flattened membrane sacs, but they are not interconnected like ER stacks. Golgi receives, modifies and segregates different proteins. a. Some of the proteins modified and sorted by the Golgi are parts of membranes (such as channel proteins or receptor molecules), some of the proteins are secreted, and some of the proteins are routed to other organelles (e.g., lysosomes). b. Within the Golgi are enzymes to add sugar molecules, sulphate groups and phosphate groups to proteins. c. Specific chemical modifications help tag and sort molecules through the Golgi into different destination streams. Cell II 5. Vesicles are relatively small membrane sacs that function to shuttle materials around the cells and between the cell surface and the membranous organelles. For those membranous organelles that do not have direct membranous continuity, vesicles provide indirect, functional continuity through pitching off, movement to a new site, fusion and transfer of materials. This shuttling system has directionality and provides points of control of passage. When vesicles fuse with a new membrane system they are adding not only contents but also membrane. 6. The lysosomes are membrane-bounded sacs (vesicles) that contain hydrolytic (digestive) enzymes necessary for the normal turnover of cell components. The membrane enclosure of the hydrolytic enzymes keeps these enzymes from destroying the cell. Ribosomes Consist of Large and Small Subunits Ribosomes May be “Free” or Bound to ER Membrane RER Contains Bound Ribosomes RER Synthesizes Integral Membrane Proteins, Lysosomal Proteins, and Proteins for Secretion from the Cell Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is involved in protein synthesis Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is involved in lipid synthesis, breakdown of certain toxins, and calcium sequestration Golgi Apparatus Golgi Apparatus Processes and Sorts Materials it Receives from the RER Lysosomes Contain Hydrolytic Enzymes Example of Pathway for Proteins Synthesized in RER and Processed/Sorted in the Golgi Synthesis and Processing of Lysosomal Proteins Cellular Trafficking Cellular Trafficking