FINANCIAL AWARENESS
Checking & Savings Accounts
Lesson 3: Managing a Checking Account – Part 2
Instructor PowerPoint
Copyright © 2009, Thinking Media, a division of SAI Interactive, Inc. All rights reserved. The Career Ready 101 logo is a registered trademark and Career Ready 101 is
a trademark of SAI Interactive, Inc.
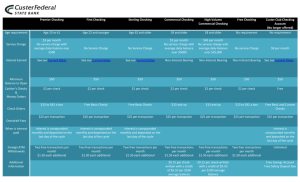
Sample Checking Account
Statement
Distribute Handout #1: Sample Checking
Account Statement
2
Checking Account Statement
Each month, you should receive a Checking
Account Statement or Bank Statement from
your bank detailing all of the transactions
for the specified time period.
It is extremely important to
review your bank statement
upon receipt to check for
discrepancies and errors.
3
Checking Account Statement
At most banks, if you do not report an error
or discrepancy within 60 days of receipt of
your statement you will be held responsible
for those transactions.
You should compare your
Transaction Register to the
monthly Checking Account
Statement and balance your
account.
4
Reading a Bank Statement
Most monthly statements include the same information.
Bank and Customer Information
At the top of the statement you will see the bank name
and branch location and your personal information to
include name, address and account number.
You will also see the type
of account (i.e., checking,
savings, money market, etc.)
and the period of time for the
transactions.
5
Reading a Bank Statement
Summary Section
The summary section of the statement will
show the total amount for the specified time
period for the following:
• Beginning Balance (this should match the
Ending Balance on
your previous
statement)
6
Reading a Bank Statement
Summary Section Cont.
• Deposits & Credits (+) (includes all direct
and manual deposits and if applicable,
reversed charges)
• Net Interest Earned (+) (if checking account
earns interest)
• Automatic Transfers (+) (if you have funds
automatically transferred to your checking
account from another account)
7
Reading a Bank Statement
Summary Section Cont.
• Withdrawals (-) (includes all ATM and Debit
Card transactions and automatic payments)
• Fees (-) (if applicable, bank service charges)
8
Reading a Bank Statement
Summary Section Cont.
• Checks Converted (-) (These are checks that
were electronically converted by the
merchant.
• This process is similar to a debit card in that
the money is immediately deducted from
your account.)
• Checks (-) (checks that were written and
cleared during the specified time period)
9
Reading a Bank Statement
Summary Section Cont.
• Ending Balance (this is the balance in your
account as of the end of the specified time
period.
• Note: This Ending Balance does not usually
match the Balance in your Transaction
Register.
• You have to reconcile your account to
ensure it is balanced.
10
Reading a Bank Statement
Summary Section Cont.
• Minimum Balance (this is the lowest balance in
your account during the specified time period)
• Average Balance (this the average balance on your
account during the specified time period)
• Annual Percentage Yield Earned (if you have an
interest bearing checking account, this is the
annual percentage amount you earn on the
account.)
11
Reading a Bank Statement
Summary Section Cont.
• Interest This Period (if applicable, the amount of
interest earned during the specified time period.)
• YTD Interest (if applicable, the amount of interest
earned Year to Date (YTD) on the account. YTD is a
calendar year Jan. to Dec. and is used for tax
purposes.)
12
Exercise #2: Managing a
Checking Account
Distribute Exercise #2: Managing a Checking
Account.
You will use this handout throughout
Managing a Checking Account –
Part 2 to mark your
responses to questions.
13
Exercise #2: Managing a Checking Account
Question 1
Directions:
Circle the best answer to the question.
Question 1
Where on a Checking Account Statement would
you find the total amount of deposits?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Interest This Period section
Deposits & Credits section
Withdrawals section
Ending Balance section
14
Reading a Bank Statement
Deposits & Credits Section
This section of the statement will show a detailed
listing of all the deposit and credit transactions
during the specified time period.
It will include the transaction date, a description of
the transaction and the amount of the transaction
with the total deposits and credits.
15
Reading a Bank Statement
Interest Section
If applicable, this section will show a detailed
listing of the interest earned on the account
for the specified time period. It will include
the date the interest was posted to the
account and the amount.
16
Reading a Bank Statement
Automatic Transfers Section
If applicable, this section will show a detailed
listing of the automatic transfers to include
the date the transfer was posted to the
account, a description of the transfer and the
amount.
17
Reading a Bank Statement
Withdrawals Section
This section will show a detailed listing of all the ATM,
debit card and automatic payment transactions
during the specified time period.
It will include the transaction date, a description of
the transaction and/or business name and the
amount of the
transaction with
the total withdrawals.
18
Reading a Bank Statement
Fees Section
If applicable, this section will
detail all fees deducted from
the account.
It will include the date the fee was
deducted, a description of the fee
and the amount of the fee with the
total fees deducted from the account during
the specified time period.
19
Reading a Bank Statement
Checks Converted Section
This section will show a detailed list of the checks
that were converted by the merchant to an electronic
withdrawal.
It will include the date the check was converted, the
check number, a description of the transaction and/or
business name and the amount of the transaction
with a total of checks converted.
20
Reading a Bank Statement
Checks Converted Section Cont.
Note: Checks that are converted by a merchant to an
electronic withdrawal are not normally returned to the
bank.
Therefore, if you receive check
enclosures or check images with
your monthly statement, these checks
will not be included.
21
Reading a Bank Statement
Checks Section
This section will show a detailed list of all the checks
that were posted to your account during the specified
time period.
It will include the date, the check number and
amount.
The checks are listed in number order.
22
Reading a Bank Statement
Checks Section Cont.
If you see a (*) next to a check number, it means there
is a break in the check number sequence.
Missing check numbers may appear in
the Checks Converted section of the
statement or they have not cleared
your account yet.
Note: The totals shown at the bottom
of each section should match the totals
shown in the Summary Section of the
statement.
23
Reading a Bank Statement
Daily Balance Summary Section
This section will show your daily account balance for
every business day during the specified time period.
You can look for trends in highs and lows and try to
adjust your budget to better manage your money.
Check Enclosures or Check Images
If applicable, your processed checks or
check images will be included with the
statement.
You can use this information to balance
your account or keep them as proof of
payment.
24
Reading a Bank Statement
Account Balance Worksheet
Most bank statements include an Account
Balance Worksheet that you can use to
reconcile your account to make sure you
balance.
25
Exercise #2: Managing a Checking Account
Question 2
Question 2
What is an automatic transfer?
A. When a payment is automatically withdrawn from
your account
B. When funds are automatically transferred to your
account from another account
C. When a payment is electronically withdrawn from
your account
D. When a written check is converted to an electronic
withdrawal
26
Exercise #2: Managing a Checking Account
Question 2 – Answer
Question 2
What is an automatic transfer?
A. When a payment is automatically withdrawn from your account
B. When funds are automatically transferred to your account
from another account
C. When a payment is electronically withdrawn from your account
D. When a written check is converted to an electronic withdrawal
Answer
B. An automatic transfer is when funds are automatically
transferred to your account from another account.
27
Exercise #2: Managing a Checking Account
Question 3
Directions:
Study the attached Bank Statement, then answer the
question.
Question 3
What is the Ending Balance on this bank statement?
A. $1,203.43
B. $928.00
C. $1,175.10
D. $542.32
28
Exercise #2: Managing a Checking Account
Question 3 – Answer
Directions:
Study the attached Bank Statement, then answer the
question.
Question 3
What is the Ending Balance on this bank statement?
A. $1,203.43
B. $928.00
C. $1,175.10
D. $542.32
Answer
C. The Ending Balance on this
bank statement is $1,175.10.
29
Sample Account Balance
Worksheet
Distribute Handout #2: Sample Account
Balance Worksheet
30
Balancing a Bank Statement
Upon receipt, take the time to balance your
Transaction Register to your monthly
Checking Account Statement.
Remember the quicker you respond to an
error or discrepancy, the more likely you will
be able to resolve the issue.
31
Balancing a Bank Statement
First, compare and check-off all
of the transactions that are on
the Checking Account Statement
in your Transaction Register.
Remember there is a Checkmark
column in your Transaction
Register for this purpose.
32
Balancing a Bank Statement
If there is an item on your statement that is
not listed in your Transaction Register,
determine if it is correct.
If the item is correct, write it in your
Transaction Register and subtract
it from your balance.
If the item is incorrect, call your
bank immediately to have it
investigated.
33
Balancing a Bank Statement
Remember to also write and deduct any
service charges and fees in your Transaction
Register.
If your checking account earns interest, list
the interest in the Deposit or Credit (+)
section and add it to your
account balance.
34
Balancing a Bank Statement
The following are the steps to follow to balance
your Checking Account Statement:
Step 1
Using the Account Balance
Worksheet included on your
Checking Account Statement,
write the amount shown on your
statement for the Ending Balance
where indicated.
35
Balancing a Bank Statement
Step 2
Add up all deposits which are not included on
the statement and write this amount where
indicated on the Account Balance Worksheet.
Step 3
Add up the Ending Balance and additional
deposits. Write this amount where indicated on
the worksheet.
36
Balancing a Bank Statement
Step 4
Using your Transaction Register, list all of the checks,
ATM and debit card withdrawals that are not included
on the statement where indicated on
the Account Balance Worksheet.
Add these outstanding transactions
together and write the total where
indicated on the worksheet.
37
Balancing a Bank Statement
Step 5
Subtract the total outstanding
transactions from the Ending
Balance and additional deposits
total.
This amount should equal your
Transaction Register balance.
38
Troubleshooting Account Balance
If your account does not balance, compare each
transaction on the statement to your register again
checking closely for the following:
• Look for a transaction in your register that
matches or is close to the amount you are off.
• Look for transposed numbers (i.e., wrote $12
instead of $21).
• If the receipt was difficult to read, you could be
off by a couple of dollars or cents.
39
Troubleshooting Account Balance
• Did you lose a receipt and guess at the
amount?
• Did you write down the amount
before taxes?
After double checking your
account and addition, if you
still cannot locate the discrepancy
contact your local bank branch for
their assistance.
40
Exercise #3: Balancing a
Checking Account
Distribute Exercise #3: Balancing a Checking
Account
Directions: Look at the Checking Account Statement,
Account Balance Worksheet and Transaction Register,
then answer this question.
Question
Why doesn’t the Account Balance
Worksheet and Transaction
Register balance?
41
Exercise #3: Balancing a Checking
Account – Instructor Guide
Troubleshooting Error in Account
When your Transaction Register balance does not
match the balance on the Account Balance
Worksheet, you need to subtract to determine how
much you are off.
First look for a transaction in
your register that matches or
is close to the amount you are off.
42
Troubleshooting Error in Account Cont.
If you still cannot locate the error, next compare
each transaction on the statement to your register
again checking closely for transposed numbers or
incorrect amounts.
In the example, the Debit Card purchase on 10/9 at
Dale’s Bowling Alley was written as $50.30 instead
of $55.30, thus making the account off by $5.
43
Troubleshooting Error in Account Cont.
You can see how easy it is to make a simple
mistake. You need to update your Transaction
Register regularly and double-check that your
entries and math are correct.
44
Lesson 3: Managing a Checking
Account – Part 2
END OF LESSON
NEXT SECTION
LESSON 3: MANAGING A CHECKING
ACCOUNT– PART 3