Bio A – Cell Division Cell Division Use your book, your webquest, or
advertisement

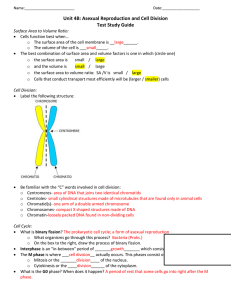
Bio A – Cell Division Cell Division Use your book, your webquest, or other sources to answer these questions. Don’t forget Bozeman Bio! 1. Think back to Cell Theory; cells come from other cells by …? 2. Why do cell need to divide? The Cell Cycle DNA changes form as it goes through the cycle. Most of the time DNA exists as long strings called chromatin, but when it needs to be sorted during mitosis, it coils up to form chromosomes, as shown at right. Even when DNA is in the form of chromatin, strings of DNA are wrapped here and there around proteins called histones (shown as the balls in the diagram.) In the beginning of mitosis, each duplicated strand of chromatin gets coiled more and more tightly around hiostones into a duplicated chromosome as in the diagram. DNA remains in chromosome form until the end of mitosis (telophase), then it unravels back into chromatin. During G1 of interphase, if you could actually see the DNA, it would look like individual strands of exceedingly long, thin spaghetti. G2, the DNA of each chromosome would like two exceedingly long, thin strands of spaghetti connected at a structure called the centromere. Part of the centromere is the kinetochore where the spindle fibers will attach so that the chromosomes can move apart. Nasty chromosome vocabulary: A chromosome can be either a single piece of chromatin all wound tightly around histones or it can be a pair of sister chromatids when replicated. When the sister chromatids separate in anaphase, each is now called a chromosome. So… a cell with 2 pairs of chromosomes would have 4 chromosomes (described as 2N=4) except when it is in anaphase and telophase, when it has 8! In fact, telophase can be considered one cell with two nuclei! But as the copies are identical and they aren’t being used for anything during mitosis, the doubled number doesn’t matter. It’s only a temporary state that will be fixed by cytokinesis. What does a chromosome look like at each phase of the cell cycle? Go back to the cell cycle diagram and draw a chromosome for each. 2 Mitosis – the part of the cell cycle in which the replicated chromosomes are sorted into the new identical, diploid daughter cells. Along with cytokinesis, it makes up the cell division phase. Use the table below and on the following page to summarize what happens when. Diagram Major Events Anaphase Metaphase Prophase Phase 3 Telophase Think about cellular structures and functions: How do chromosomes move to form the metaphase plate? How are the chromosomes separated during anaphase? At the end of Telophase, you find a cell with two nuclei. What else must happen? Cytokinesis: For each, describe how the cytoplasm gets divided. Animal Cell: Plant Cell: 4