Flatworms: Characteristics, Anatomy & Reproduction
advertisement

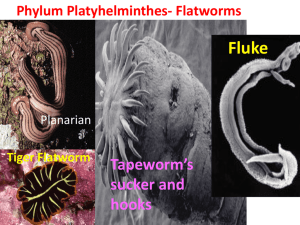
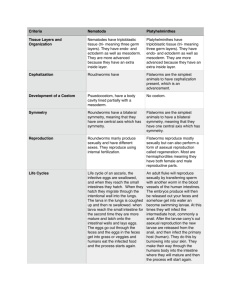
FLATWORMS Belong to the KINDGOM ANIMALIA PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES “Platyhelminthes” comes from the Greek meaning “flat worm” Examples: blood flukes, tapeworms, planarians http://shapeoflife.org/video/animation/flatworm-animation-body-plan http://shapeoflife.org/video/behavior/flatworms-invasive-flatworm-hunts-earthworms VOCABULARY Brain (ganglia) - planarian can process information about their environment Pharynx - a tube that the flatworm pushes out of its body in order to feed. Used for suckling food in (the mouth is at the end of the pharynx) Eyespot - simple eye, can detect light Flame cells - located along the lateral edges, used for excretion Intestine - digestion (does not have an anus) Parasite: organism living in or on another species getting its food from the tissues or fluids of its host. Cilia: a hair-like growth from a cell that, when present in large numbers, can produce currents to move water. Stereo senses: paired senses (like ears and eyes) that are on both sides of the head allowing an object to be accurately located in space. Hermaphrodite: an organism that produces both female and male sex cells. Bilateral symmetry: a body form with a central longitudinal plane that divides the body into two halves that mirror each other. Fission: asexual reproduction in flatworms. Characteristics 1.Three germ layers (endoderm, ectoderm, mesoderm) 2.Bilateral symmetry 3.Cephalization (has a head) COELOM = fluid filled body cavity Acoelomates = without coelom FORM AND FUNCTION FEEDING Free-living - carnivores or scavengers; they have a digestive cavity, mouth and pharynx Parasites – feed on blood, tissues or pieces of cells from within a HOST Most do not have a complete digestive system because they absorb material directly from host Question Time! •Flatworms are a. Acoelomates b. Pseudocoelomates c. Coelomates Question Time! •Flatworms have •A. Radial Symmetry •B. Bilateral Symmetry •C. No Symmetry Question Time! •True or False Flatworms can be parasites, carnivores, and/or herbivores. Respiration, Circulation, and Excretion 1.Thin bodies allow for materials to diffuse (respiration, excretion, etc) 2.Flame Cell – specialized cells that remove excess water Response Ganglia – group of nerve cells that control the body (like a brain) Eyespot – group of cells that can detect light (like an eye) Movement Flatworms move in 2 ways 1.Cilia helps them glide through the water 2.Muscle cells help them twist and turn Question Time! •What is the name of the specialized cells that function in excretion to remove excess water? Question Time! •What is the name of the specialized nerve cells that control the body, like the brain? Question Time! •What are the 2 ways by which flatworms move? ANATOMY OF A PLANARIAN Reproduction Sexual Reproduction – most flatworms are hermaphrodites (have both male and female sex organs) Asexual Reproduction by fission – flatworms can split in two and regenerate Planarians are hermaphrodites They can also regenerate body parts and will sometimes split in half to reproduce (FISSION) Question Time! •How do flatworms reproduce asexually? (What is the vocabulary word?) Question Time! •How do flatworms reproduce sexually? (What is the vocabulary word?) Groups of Flatworms CLASS TURBELLARIA - free living flatworms - live in fresh or marine water - ex. Planarian Dugesia lives in freshwater, mostly a scavenger but can also feed on protists ●Class Trematoda = parasitic flatworms ●a.k.a “flukes” live in mouth, skin, or gills of host Primary host = the host in which a parasite reproduces sexually Intermediate host = the host in which asexual reproduction occurs Larvae use intermediate host to develop, then enter final host mature and are released again. Schistosoma mansoni - multiple host: Primary host = human Intermediate host = snail Causes Schistosomiasis -in humans; decays lungs liver, spleen, or intestines, occurs in tropical areas with poor sanitation/sewage. Class Cestoda =tapeworms Long, flat, parasitic Live in intestines Scolex = a structure that contains suckers and/or hooks Proglottids = body segments of the tapeworm Each mature proglottid is a hermaphrodite Testes produce sperm, fertilize the eggs to produce a zygote Zygotes are passed out through the feces. Sometimes, a dormant, protective cyst is formed in the intermediate host muscles ****This is why you should never eat incompletely cooked meat.