Phylum : PLATYHELMINTHES Platy : Flat Helminth : Worm
advertisement

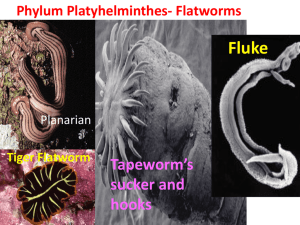
Phylum PLATYHELMINTHES Platy = Flat Helminth = Worm CHARACTERISTICS • All show BILATERAL symmetry • Posses three tissue (germ) layers: 1. Ectoderm 2. Mesoderm 3. Endoderm • Most exhibit CEPHALIZATION. • Majority Do NOT exhibit segmentation TYPICAL FLATWORMS GETTING FOOD • Some flatworms are free-living aquatic worms. They obtain their food from cruising around and feeding off of tiny living animals or scavenging off of recently dead animals. • Others are PARASITIC, they feed off of the blood, tissue fluids or tissue cells of their living host. THREE CLASSES OF FLATWORMS – Free Living Flatworms. Most common example : Planaria • TURBELLARIA •TREMATODA – Parasitic Flatworms known as flukes, most are less than one centimeter. •CESTODA – Long Parasitic worms with hooks to attach to intestinal wall of host. TURBELLARIA - Planarians TREMATODA - Flukes Section of Moose Liver Infected with Liver Flukes LIFE CYCLE OF BLOOD FLUKE CESTODA - Tapeworms TAPEWORM REMOVAL DEWORMING •Do You Have Pets? •Do You Have Worms? - Ever think you have rice in your stool/feces; but you haven’t had rice for a long, long time?