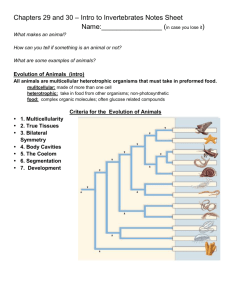
Bioligy - Flatworms VS Cnidarians
advertisement
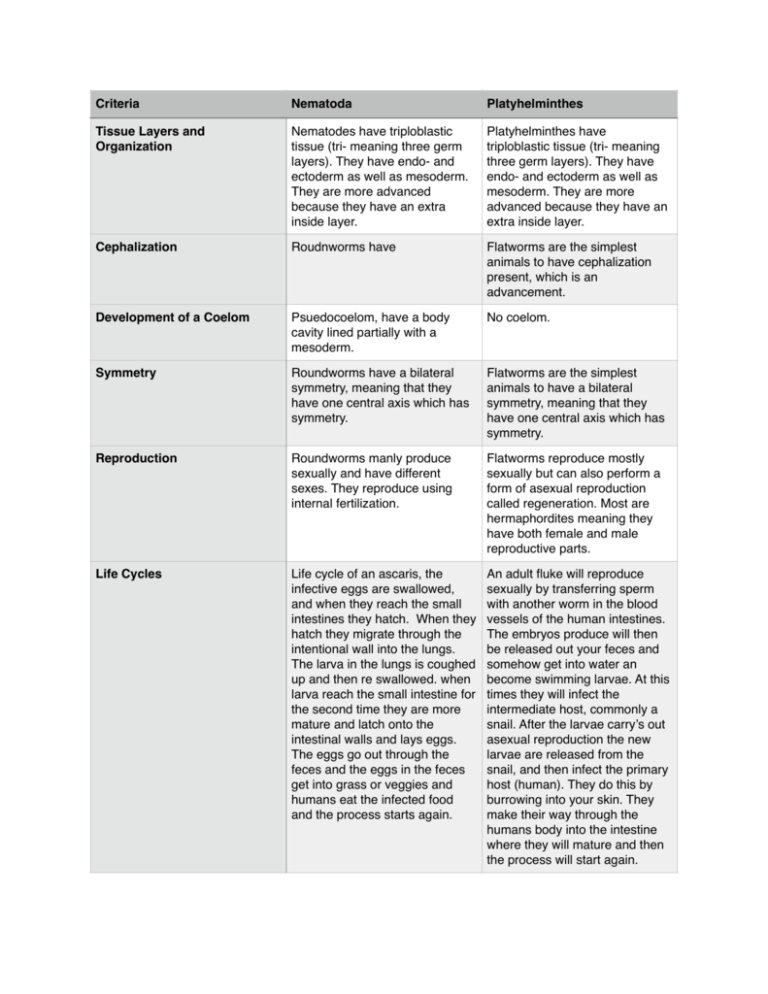
Criteria Nematoda Platyhelminthes Tissue Layers and Organization Nematodes have triploblastic tissue (tri- meaning three germ layers). They have endo- and ectoderm as well as mesoderm. They are more advanced because they have an extra inside layer. Platyhelminthes have triploblastic tissue (tri- meaning three germ layers). They have endo- and ectoderm as well as mesoderm. They are more advanced because they have an extra inside layer. Cephalization Roudnworms have Flatworms are the simplest animals to have cephalization present, which is an advancement. Development of a Coelom Psuedocoelom, have a body cavity lined partially with a mesoderm. No coelom. Symmetry Roundworms have a bilateral symmetry, meaning that they have one central axis which has symmetry. Flatworms are the simplest animals to have a bilateral symmetry, meaning that they have one central axis which has symmetry. Reproduction Roundworms manly produce sexually and have different sexes. They reproduce using internal fertilization. Flatworms reproduce mostly sexually but can also perform a form of asexual reproduction called regeneration. Most are hermaphordites meaning they have both female and male reproductive parts. Life Cycles Life cycle of an ascaris, the infective eggs are swallowed, and when they reach the small intestines they hatch. When they hatch they migrate through the intentional wall into the lungs. The larva in the lungs is coughed up and then re swallowed. when larva reach the small intestine for the second time they are more mature and latch onto the intestinal walls and lays eggs. The eggs go out through the feces and the eggs in the feces get into grass or veggies and humans eat the infected food and the process starts again. An adult fluke will reproduce sexually by transferring sperm with another worm in the blood vessels of the human intestines. The embryos produce will then be released out your feces and somehow get into water an become swimming larvae. At this times they will infect the intermediate host, commonly a snail. After the larvae carry’s out asexual reproduction the new larvae are released from the snail, and then infect the primary host (human). They do this by burrowing into your skin. They make their way through the humans body into the intestine where they will mature and then the process will start again. Criteria Nematoda Platyhelminthes Feeding, Excretion, and Circulation They exchange gases through their body walls and they also use their body walls to excrete metabolic waste. They use diffusion to carry nutrients through their bodies. They feed on many different organisms, fungi, bacteria, by using their mouths. They are the first phylum with an excretory system made up of “flame cells”. Along with cnidarians they get their nutrients and oxygen by diffusion. Flatworms feed on recently deceased waste or tiny aquatic animals. They have a singular opening into a digestive cavity by which food enters and excretes. Response and Motility They expand and contract the length of their body to move using specialized muscle. Also they have a simple nervous system consisting of several ganglia. Free-Living flatworms typically move by gliding and twisting and turning. This allows them to react rapidly to environmental stimuli. Also they have a more advanced nervous system including a head made up of ganglia that controls the nervous system. They also have and eyespot which can detect light in the environment.