FLATWORMS

FLATWORMS
Belong to the KINDGOM ANIMALIA
PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES
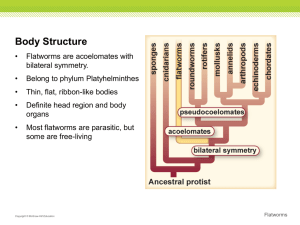
Characteristics
1.
Three germ layers (endoderm, ectoderm, mesoderm)
2.
Bilateral symmetry
3.
Cephalization (has a head)
COELOM = fluid filled body cavity
Acoelomates = without coelom
FORM AND FUNCTION
FEEDING
Free-living - carnivores or scavengers; they have a digestive cavity, mouth and pharynx
Parasites – feed on blood, tissues or pieces of cells from within a HOST
Most do not have a complete digestive system because they absorb material directly from host
Respiration, Circulation, and
Excretion
1.
Thin bodies allow for materials to diffuse
(respiration, excretion, etc)
2.
Flame Cell – specialized cells that remove excess water
Response
Ganglia – group of nerve cells that control the body (like a brain)
Eyespot – group of cells that can detect light (like an eye)
Movement
Flatworms move in 2 ways
1.Cilia helps them glide through the water
2.Muscle cells help them twist and turn
Reproduction
Sexual Reproduction – most flatworms are hermaphrodites (have both male and female sex organs)
Asexual Reproduction by fission – flatworms can split in two and regenerate
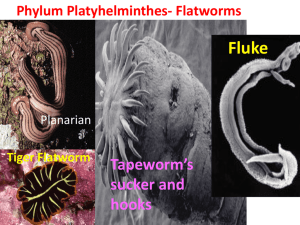
Groups of Flatworms
CLASS TURBELLARIA
- free living flatworms
- live in fresh or marine water
- ex. Planarian
Dugesia lives in freshwater, mostly a scavenger but can also feed on protists
Planarians are hermaphrodites
They can also regenerate body parts and will sometimes split in half to reproduce
(FISSION)
ANATOMY OF A PLANARIAN
Brain (ganglia) - planarian can process information about their environment
Pharynx - used for suckling food in (the mouth is at the end of the pharynx)
Eyespot - simple eye, can detect light
Flame cells - located along the lateral edges, used for excretion
Intestine - digestion (does not have an anus)
● Class Trematoda = parasitic flatworms
●a.k.a “flukes” live in mouth, skin, or gills of host
Primary host = the host in which a parasite reproduces sexually
Intermediate host = the host in which asexual reproduction occurs
Schistosoma mansoni - multiple host:
Primary host = human
Intermediate host = snail
Causes Schistosomiasis -in humans; decays lungs liver, spleen, or intestines, occurs in tropical areas with poor sanitation/sewage.
Class Cestoda =tapeworms
Long, flat, parasitic
Live in intestines
Scolex = a structure that contains suckers and/or hooks
Proglottids = body segments of the tapeworm
Each mature proglottid is a hermaphrodite
Testes produce sperm, fertilize the eggs to produce a zygote
Zygotes are passed out through the feces.
Sometimes, a dormant, protective cyst is formed in the intermediate host muscles
****This is why you should never eat incompletely cooked meat.