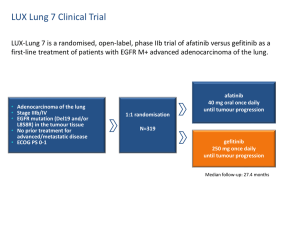
Afatinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment…
advertisement

Afatinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer harboring activating EGFR mutations: LUX-Lung 7 Keunchil Park, Eng-Huat Tan, Li Zhang, Vera Hirsh, Kenneth O’Byrne, Michael Boyer, James Chih-Hsin Yang, Tony Mok, Miyoung Kim, Dan Massey, Victoria Zazulina, Luis Paz-Ares ESMO Asia 2015 Disclosures • Employment: Samsung Medical Center • Advisory Boards: Boehringer Ingelheim (uncompensated) Background • Afatinib and other EGFR-targeting agents, erlotinib and gefitinib, are approved first-line treatments for EGFR M+ NSCLC1 • Afatinib (second-generation TKI) irreversibly inhibits signaling of EGFR, HER2-HER4, whereas gefitinib and erlotinib (first-generation TKIs) reversibly inhibit EGFR2–4 • LUX-Lung 7 is the first prospective global randomized trial evaluating two EGFR-directed therapies in patients with EGFR M+ NSCLC 1. Sebastian M, et al. Eur Respir Rev 2014;23:92–105. 2. Costanzo R, et al. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2013;13(10):1207–18. 3. Li D, et al. Oncogene 2008;27:4702–11. 4. Solca F, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2012;343:342–50. EGFR = epidermal growth factor receptor; M+ = mutation-positive; HER = human epidermal growth factor receptor; NSCLC = nonsmall cell lung cancer; TKI = tyrosine kinase inhibitor Study Design • Stage IIIB/IV adenocarcinoma of the lung • EGFR mutation (Del19 and/or L858R) in the tumour tissue* • No prior treatment for advanced/ metastatic disease Primary endpoints: • PFS (independent) • TTF • OS Afatinib 40 mg once daily† Stratified by 1:1 • Mutation type (Del19/L858R) • Brain metastases (present/absent) Gefitinib 250 mg once daily • ECOG PS 0/1 Secondary endpoints: • • • • • • • ORR Time to response Duration of response Duration of disease control Tumour shrinkage HRQoL Safety • Treatment beyond progression allowed if deemed beneficial by investigator • RECIST assessment performed at Weeks 4 and 8, and every 8 weeks thereafter until Week 64, and every 12 weeks thereafter * Central or local test. † Dose modification to 50 mg, 30 mg, and 20 mg permitted in line with prescribing information. Del19 = exon 19 deletions; ECOG PS = Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; EGFR = epidermal growth factor receptor; HRQoL = health-related quality of life; L858R = exon 21 L858R point mutation; ORR = objective response rate; OS = overall survival; PFS = progression-free survival; RECIST = Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors; TTF = time to treatment failure Statistical Design • Main study objective: to estimate the HR for PFS, TTF, and OS* on afatinib, relative to gefitinib • Sample size was based on controlling the width of the 95% CI for the PFS HR, allowing for a width of ±0.25 on the log scale after observing 250 events • All statistical testing was at two-sided 5% alpha level with no adjustment for multiplicity • Time-to-event endpoints were analyzed via stratified Coxregression analysis and log-rank test * At the time of PFS analysis, OS endpoint is still immature. CI = confidence interval; HR = hazard ratio; OS = overall survival; PFS = progression-free survival; TTF = time to treatment failure Study Conduct: 64 Sites / 13 Countries Canada France, Germany, Ireland, Norway, Spain, Sweden, United Kingdom Australia China Republic of Korea Singapore Taiwan • Recruitment: December 2011–August 2013 • Median follow-up for PFS: 27.3 months PFS = progression-free survival Patient Disposition Screened, n = 571 Randomized, n = 319 Treated with afatinib n = 160 Stopped treatment n = 140 (87.5%) Treated with gefitinib n = 159 TTF event Stopped treatment n = 149 (93.7%) On treatment n = 20 (12.5%) On treatment n = 10 (6.3%) PFS event By investigator: 131 (81.9%) By independent: 124 ( 77.5%) PFS event By investigator: 135 (84.9%) By independent: 122 (76.7%) As of August 21, 2015 PFS = progression-free survival; TTF = time to treatment failure Baseline Characteristics Afatinib (n = 160) Gefitinib (n = 159) 63 (30–86) 63 (32–89) 57 / 43 67 / 33 59 41 55 45 16 16 Smoking status, % Never smoked Light ex-smoker Current / other ex-smoker 66 13 21 67 12 21 Baseline ECOG PS, % 0 1 32 68 30 70 NSCLC stage, % IIIB IV 5 95 2 98 EGFR mutation, % Del19 L858R 58 42 58 42 Median age, years (range) Gender, % Female / Male Race, % Asian Non-Asian Brain metastases*, % PFS in overall population * Stable brain metastases: Incidentally found asymptomatic brain metastases not requiring any local brain radiation and steroid therapy. Asymptomatic brain metastases previously radiated and >1 week off corticosteroids and/or anti-convulsants treatment before study randomization. Concomitant brain radiation not allowed. Del19 = exon 19 deletions; ECOG PS = Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; EGFR = epidermal growth factor receptor; L858R = exon 21 L858R point mutation; NSCLC = non-small cell lung cancer PFS by Independent Review 0.8 Afatinib (n = 160) Gefitinib (n = 159) 11.0 10.9 Median PFS (months) PFS in overall population Estimated PFS probability 1.0 HR (95% CI) 0.6 p-value 0.4 p = 0.0176 27% p = 0.0184 0.73 (0.57–0.95) 0.0165 18% 0.2 15% 8% 0 No. of patients Afatinib Gefitinib 0 3 6 9 12 15 160 159 142 132 112 106 94 83 67 52 47 22 18 21 24 27 Time (months) 34 14 27 9 21 7 13 5 30 33 36 39 42 6 3 3 3 1 1 0 1 0 0 CI = confidence interval; HR = hazard ratio; PFS = progression-free survival PFS in Prospectively Defined Subgroups Factors N HR (95% CI) 319 0.73 (0.57–0.95) L858R 133 0.71 (0.48–1.06) Del19 186 0.76 (0.55–1.06) Brain metastases Absent 268 0.74 (0.56–0.98) Present 51 0.76 (0.41–1.44) Baseline ECOG PS 0 98 0.89 (0.54–1.47) 1 221 0.71 (0.52–0.95) Male 122 0.88 (0.59–1.31) Female 197 0.65 (0.47–0.91) EGFR mutation Gender Age Race Smoking history <65 years PFS in overall population Total PFS 177 0.68 (0.48–0.97) ≥65 years 142 0.85 (0.59–1.22) Non-Asian 137 0.72 (0.49–1.06) Asian 182 0.76 (0.54–1.06) Never smoked 212 0.80 (0.58–1.10) Light ex-smoker 40 1.09 (0.56–2.14) Current or other ex-smokers 67 0.48 (0.27–0.85) 1/4 Favours afatinib 1 4 Favours gefitinib CI = confidence interval; Del19 = exon 19 deletions; ECOG PS = Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; EGFR = epidermal growth factor receptor; HR = hazard ratio; L858R = exon 21 L858R point mutation; PFS = progression-free survival Time to Treatment Failure 0.8 Afatinib (n = 160) Gefitinib (n = 159) 13.7 11.5 Median TTF (months) PFS in overall population Probability of being on treatment 1.0 HR (95% CI) 0.73 (0.58–0.92) p-value 0.6 0.0073 0.4 0.2 0 No. of patients Afatinib Gefitinib 0 3 6 9 12 15 160 159 148 144 133 120 113 103 91 74 68 59 18 21 24 27 Time (months) 56 43 48 30 40 21 25 11 30 33 36 39 42 18 6 9 6 5 2 0 2 0 0 CI = confidence interval; HR = hazard ratio; TTF = time to treatment failure Objective Response and Duration of Response (Independent Review) 80% 80 p = 0.0083 ORR ORR (%) 70% Median DoR (months) 56% Gefitinib (n = 89) 10.1 8.4 (7.8–11.1) (7.4–10.9) PFS in overall population 60 60% Afatinib (n = 112) 95% CI 40 40% 20% 20 0%0 Afatinib AfatinibGefitinib n = 89/159 n = 112/160 CI = confidence interval; DoR = duration of response; ORR = objective response rate Efficacy in Patients With Del19 Mutation Median PFS (months) 12.7 HR (95% CI) 0.76 (0.55–1.06) 11.0 PFS in overall population 0.8 p-value 0.6 0.1071 0.4 0.2 0 –20 –40 –60 –80 ≥20% increase (n = 0) ≥0–<20% increase (n = 3) >0–<30% decrease (n = 15) ≥30–<50% decrease (n = 29) ≥50% decrease (n = 41) 70 (80%) with ≥30% reduction 40 0 0 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 33 36 39 42 Time (months) No. of patients Afatinib 93 83 67 58 43 31 22 18 14 9 Gefitinib 93 76 64 53 32 17 11 7 6 4 Afatinib (n = 93) Gefitinib (n = 93) PFS in overall population ORR Afatinib 20 –100 73% 66% 4 3 2 3 1 1 0 1 0 0 Maximum decrease from baseline (%) Estimated PFS probability 40 Gefitinib Maximum decrease from baseline (%) Afatinib 1.0 Gefitinib 20 0 –20 –40 –60 –80 –100 ≥20% increase (n = 0) ≥0–<20% increase (n = 2) >0–<30% decrease (n = 18) ≥30–<50% decrease (n = 27) ≥50% decrease (n = 41) 68 (77%) with ≥30% reduction CI = confidence interval; Del19 = exon 19 deletions; HR = hazard ratio; ORR = objective response rate; PFS = progression-free survival Efficacy in Patients With L858R Mutation Gefitinib Median PFS (months) 10.9 10.8 HR (95% CI) 0.71 (0.47–1.06) PFS in overall population 0.8 p-value 0.6 0.0856 0.4 0.2 0 –20 –40 –60 –80 ≥20% increase (n = 1) ≥0–<20% increase (n = 3) >0–<30% decrease (n = 12) ≥30–<50% decrease (n = 21) ≥50% decrease (n = 24) 45 (74%) with ≥30% reduction 40 0 0 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 33 36 39 42 Time (months) No. of patients Afatinib 67 59 45 36 24 16 12 9 Gefitinib 66 56 42 30 20 5 3 2 Afatinib (n = 67) Gefitinib (n = 66) PFS in overall population ORR Afatinib 20 –100 66% 42% 7 1 4 1 2 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Maximum decrease from baseline (%) Estimated PFS probability 40 Maximum decrease from baseline (%) Afatinib 1.0 Gefitinib 20 0 –20 –40 –60 –80 –100 ≥20% increase (n = 4) ≥0–<20% increase (n = 4) >0–<30% decrease (n = 23) ≥30–<50% decrease (n = 19) ≥50% decrease (n = 13) 32 (51%) with ≥30% reduction CI = confidence interval; HR = hazard ratio; L858R = exon 21 L858R point mutation; ORR = objective response rate; PFS = progression-free survival Overall Summary of AEs Afatinib (n = 160) Gefitinib (n = 159) Any AE 98.8 100.0 Drug-related AEs 97.5 96.2 AEs leading to dose reduction* 41.9 1.9* Events, % PFS in overall population Drug-related AEs leading to discontinuation Serious AEs Drug-related serious AEs Drug-related fatal AE * No dose reductions foreseen for gefitinib according to prescribing information. † Including four patients with drug-related ILD (no drug-related ILD on afatinib). ‡ One patient died of hepatic failure. 6.3 6.3 44.4 37.1 10.6 4.4† - 0.6‡ AE = adverse event; ILD = interstitial lung disease Drug-Related AEs (>10%) Afatinib (n = 160) All Grade 3 All Grade 3 Diarrhea 90.0 11.9† 61.0 1.3 Rash/acne* 88.8 9.4 81.1 3.1 Stomatitis* 64.4 4.4 23.9 - Paronychia* 55.6 1.9 17.0 0.6 Dry skin 32.5 - 37.1 - Pruritus 23.1 - 22.6 - Fatigue* 20.6 5.6 14.5 - Decreased appetite 16.3 0.6 11.9 - Nausea 16.3 1.3 13.8 - Alopecia 10.6 - 15.1 - Vomiting 10.6 - 3.8 0.6 ALT increased 9.4 - 23.9 7.5‡ AST increased 6.3 - 20.8 2.5 * Grouped terms of AEs. † Plus one case of grade 4 diarrhea. ‡ Plus one case of grade 4 increased ALT. PFS in overall population AE category, % Gefitinib (n = 159) AE = adverse event; ALT = alanine aminotransferase; AST = aspartate aminotransferase Drug-Related AEs Leading to Discontinuation in >1 Patient 5.0% 5.0 4.5% Afatinib 4.0% 4.0 Gefitinib Patients (%) 3.5% 5 (3.1%) 5 (3.1%) 3.0% 3.0 4 (2.5%) 2.5% 3 (1.9%) 2.0% 2.0 2 (1.3%) 1.5% 2 (1.3%) 1.0% 1.0 0.5% 0.0% 0.0 0% A G 0% Diarrhoea Diarrhea * Grouped terms of AEs. A G Fatigue+ Fatigue* A 0% 0% G A 0% G A 0% G Toxic skin ALT increase AST AST ALT Toxic skin eruption increase increase increase eruption A ILD ILD G AE = adverse event; ALT = alanine aminotransferase; AST = aspartate aminotransferase; ILD = interstitial lung disease Summary and Conclusion • Afatinib significantly improved PFS of patients with EGFR M+ NSCLC relative to gefitinib. Results are consistent across subgroups • Afatinib treatment was associated with a significant improvement in response rate and TTF • Improvement in efficacy was observed in both Del19 and L858R populations • OS data were immature (current HR: 0.87, 95% CI: 0.66–1.15) • AEs in both groups were consistent with previous experience and were manageable, leading to equally low rates of treatment discontinuation • LUX-Lung 7 confirms the benefit of irreversible ErbB blockade with afatinib over reversible EGFR inhibition with gefitinib in treatment of EGFR M+ NSCLC AE = adverse event; CI = confidence interval; Del19 = exon 19 deletions; EGFR = epidermal growth factor receptor; ErbB = erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene; HR = hazard ratio; L858R = exon 21 L858R point mutation; M+ = mutation-positive; NSCLC = non-small cell lung cancer; OS = overall survival; PFS = progression-free survival; TTF = time to treatment failure Acknowledgments Thank you to all of the patients and their families, and the LUX-Lung 7 study investigators and their teams for participating in this study Back-Up Maximum decrease from baseline (%) Maximum decrease from baseline (%) Tumour Shrinkage (Independent Review) 40 Afatinib 20 0 –20 –40 –60 –80 –100 115 (77%) with ≥30% reduction ≥20% increase, n = 1 (<1%) ≥0–<20% increase, n = 6 (4%) >0–<30% decrease, n = 27 (18%) ≥30–<50% decrease, n = 50 (34%) ≥50% decrease, n = 65 (44%) 40 Gefitinib 20 0 –20 –40 –60 –80 –100 ≥20% increase, n = 4 (3%) ≥0–<20% increase, n = 6 (4%) >0–<30% decrease, n = 41 (27%) ≥30–<50% decrease, n = 46 (30%) ≥50% decrease, n = 54 (36%) 100 (66%) with ≥30% reduction PFS With TKI in Common Mutation: LUX-Lung 3/6 and LUX-Lung 7 0.8 Median PFS (months) HR (95% CI) 0.6 LL3 Afatinib (n = 204) LL6 Afatinib (n = 216) 13.6 11.0 LL7 Afatinib Gefitinib (n = 160) (n = 159) 11.0 10.9 PFS in overall population Estimated PFS probability 1.0 p-value N/A N/A 0.73 (0.57–0.95) N/A N/A 0.0165 Afatinib (n = 204) Aftatinib (n = 216) Afatinib (n = 160) Gefitinib (n = 159) 0.4 0.2 0 0 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 Time (months) 27 30 33 36 CI = confidence interval; HR = hazard ratio; N/A = not applicable; PFS = progression-free survival